File
advertisement

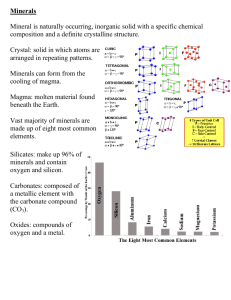
Guiding Question What is a mineral and how do we identify minerals? What Do NOW: do we call the items on your tray? What similarities do these items share? What differences do you observe? Where do we find these items? Can you name or identify any of these items? Can you think of any ways that we use these items in the real world? MINERALS Use the guided note sheet to take notes today. The building blocks of rocks….. Did any of you use minerals before coming to school this morning??? All of these items used to build a house are made of minerals! How Minerals Affect Your Life The Average American will use - 30,415 pounds of salt 1.7 million pounds of stone, sand and gravel 83,890 gallons of petroleum 42,581 pounds of iron ore 1,078 pounds of lead **Total – 3.75 million pounds of minerals, metals and fuels in your lifetime!! MINERALS = a naturally occurring, inorganic solid with a definite chemical composition and a particular crystalline structure (orderly arrangement of atoms) 1) Naturally occurring Formed in processes on or in the earth with no human input 2) Inorganic Not made by living process *It has never been alive! Amber and sugar are not minerals because they formed from living things. 3) Definite chemical composition All minerals are elements or compounds with definite chemical composition ex) mineral halite (NaCl) has a distinctive salty taste -Copper (Cu) - Beryl (Be3Al2Si6A18) 4) Crystal Structure The atoms of the mineral are arranged in patterns that repeat over and over again. ex) Graphite versus Diamond Uses of Minerals…. Ores - used for metals, extracted by mining (ex. iron) Gems – rare and beautiful, often used for jewelry Now let’s master minerals!! What are some physical properties we know? Here are physical properties we will use to identify minerals: Color Many different minerals have the same color and appearance… example pyrite and gold Color is measured by looking at the sample. Luster The way the mineral reflects light. Either metallic or non-metallic. Nonmetallic can be: Dull, Pearly, Silky, and Glassy Measured by visually viewing the mineral Streak The color of the mineral in the powdered form. Example: Gold has a yellowish streak. Pyrite has a greenishblack streak. Measured by scratching the mineral on a “streak” plate and viewing the color of the powder left on the plate. Hardness Hardness is the ability of a mineral to resist being scratched. Measured by using Mohs Hardness Scale Diamond is the hardest mineral. On a scale from 1-10, diamond is a 10! Practice You find a mineral and conduct a scratch test on it. It cannot be scratched with a fingernail, but it can be scratched by an iron nail. Using Mohs hardness scale, what is the hardness?