Cardiovascular Disorder Chart
advertisement
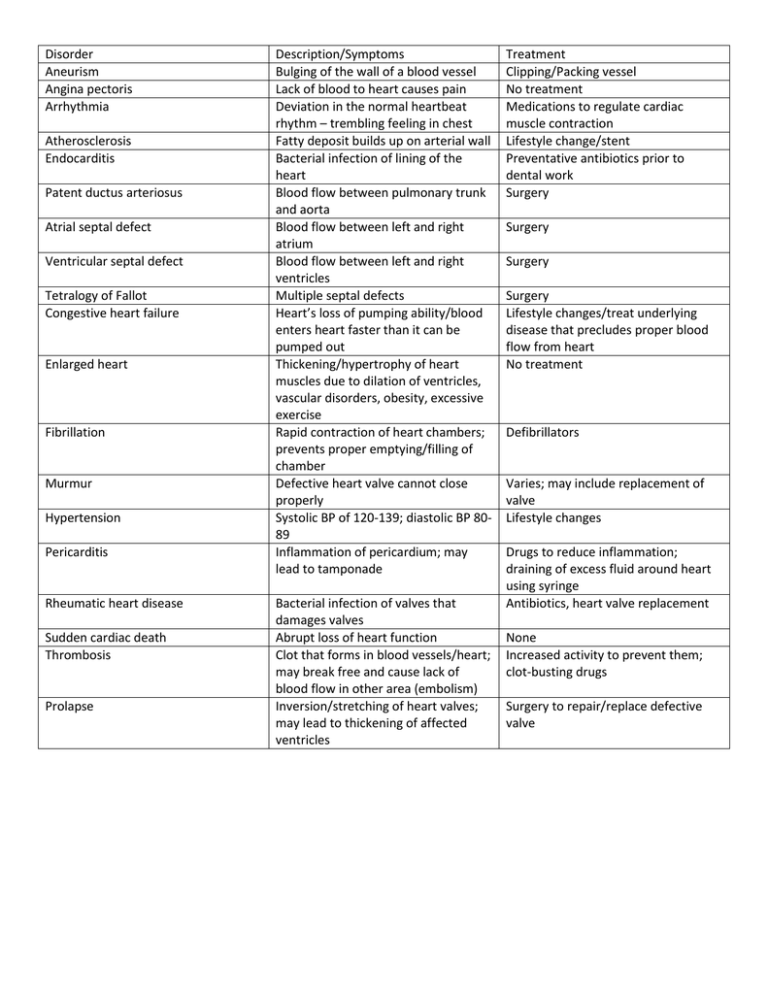
Disorder Aneurism Angina pectoris Arrhythmia Atherosclerosis Endocarditis Patent ductus arteriosus Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Tetralogy of Fallot Congestive heart failure Enlarged heart Fibrillation Murmur Hypertension Pericarditis Rheumatic heart disease Sudden cardiac death Thrombosis Prolapse Description/Symptoms Bulging of the wall of a blood vessel Lack of blood to heart causes pain Deviation in the normal heartbeat rhythm – trembling feeling in chest Fatty deposit builds up on arterial wall Bacterial infection of lining of the heart Blood flow between pulmonary trunk and aorta Blood flow between left and right atrium Blood flow between left and right ventricles Multiple septal defects Heart’s loss of pumping ability/blood enters heart faster than it can be pumped out Thickening/hypertrophy of heart muscles due to dilation of ventricles, vascular disorders, obesity, excessive exercise Rapid contraction of heart chambers; prevents proper emptying/filling of chamber Defective heart valve cannot close properly Systolic BP of 120-139; diastolic BP 8089 Inflammation of pericardium; may lead to tamponade Bacterial infection of valves that damages valves Abrupt loss of heart function Clot that forms in blood vessels/heart; may break free and cause lack of blood flow in other area (embolism) Inversion/stretching of heart valves; may lead to thickening of affected ventricles Treatment Clipping/Packing vessel No treatment Medications to regulate cardiac muscle contraction Lifestyle change/stent Preventative antibiotics prior to dental work Surgery Surgery Surgery Surgery Lifestyle changes/treat underlying disease that precludes proper blood flow from heart No treatment Defibrillators Varies; may include replacement of valve Lifestyle changes Drugs to reduce inflammation; draining of excess fluid around heart using syringe Antibiotics, heart valve replacement None Increased activity to prevent them; clot-busting drugs Surgery to repair/replace defective valve