Chemical Reactions - Brookwood High School
advertisement

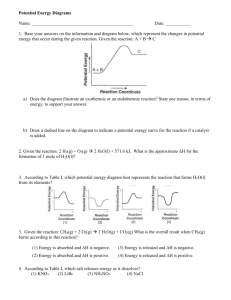
Vocabulary Week 17!! • • • • • reactants products synthesis decomposition combustion • • • • • shibboleth propitiate chortle unremitting inure Remember… • Nuclear reactions • Chemical reactions involve changes involve changes with with atom’s atoms’ electrons nucleus • Reactants –Starting substances in a reaction –Arrow points away from reactants + • Products –Substances formed during a reaction –Arrow points to products Chemical Reactions Types 1. Synthesis 2. Decomposition 3. Single displacement 4. Double displacement 5. Combustion Synthesis • Two or more substances react to produce one product A + B AB 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl Decomposition • Single reactant breaks down into two or more products AB A + B 2 NaN3 → 2 Na + 3 N2 Sodium azide decomposes into nitrogen gas and is used in air bags. Single Displacement • Atoms of one element replace the atoms of another element in a compound A + BX AX + B Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2 Tums is used to neutralize stomach acid Double Displacement • Exchange of positive ions between substances AX + BY BX + AY CaCO3 + H2SO3 H2CO3 + CaSO4 Double Replacement • Marble can become eroded by acid rain. Calcium sulfate, a product, leaves a white coating on the statue. Combustion • Oxygen combines with a substance and releases energy (and usually products include carbon dioxide and water) A + O2 CO2 + H2O + bi-products C8H18 + O2 CO2 + H2O + energy Type of Reaction Example Synthesis A + B AB Decomposition AB A + B Single Replacement A + BX AX + B Double Replacement AX + BY AY + BX Combustion A + O2 CO2 + H2O + products Changes in Matter • Evidence of chemical reaction: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Gas is produced Color Change Change in smell Formation of solid—precipitate Light is produced Temperature change -exothermic -endothermic • Some reactions occur in water • When a solid substance is dissolved in water it is an aqueous solution (aq) Reactivity Series • Helps determine if a reaction will occur • If the single element is higher on the list yes a reaction will occur • If the single element is lower on the list NO REACTION A + BX AX + B Al + PbNO3 Most Active Lithium Rubidium Potassium Calcium Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Manganese Zinc Iron Nickel Tin Lead Copper Silver Platinum Gold 1. Al (s) + PbNO3 (aq) 2. Cu (s) + MgSO4 3. Al (s) + SnPO4(aq) 4. Zn (s) + K3PO4(aq) 5. Fe (aq) + KCl (aq) 6. Mg (s) + NaNO3 (aq) 7. Zn (s) + CuCl2 (aq) 8. Na (s) + Au(OH)2 (l) 9. Zn (s) + Cu(NO3)2 (aq) 10. Fe (s) + Ni(ClO3)2 (aq) 11. Au (s) + CaSO4 (aq) 12. Mg (s) + LiBr (aq) 13. Ni (s) + CaSO4 (aq) 14. Al (s) + KClO2 (aq) 15. Mn (s) + Na3PO4 (l) 16. Al (s) + Sn(NO3)2 (aq) 17. Ag (s) + PbCl4 (aq) 18. Zn (aq) + FeI3 (aq) 19. K (s) + Cu(ClO3)2(aq) 20. Pb (s) + Au3(PO4)2 (aq) Law of Conservation of Mass • Mass/matter can not be created nor destroyed • Atoms you start with (reactants) must still be there when you end (products) • This is called balancing the equation • Mass Reactants = Mass Products Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2 • Big numbers = Coefficients –can change • Small numbers = Subscripts –DO NOT CHANGE, if you change you no longer have the same substance Steps to balancing equations 1. Write formulas for all compounds (sometimes it is given) 2. Separate Reactants and products by a line 3. Count how many atoms of each element are present on the reactant and the product side (element inventory) 4. Change coefficients so that element inventory is balanced 5. Simplify coefficients 6. Check work Al + C3H8 + O2 O2 Al2O3 CO2 + H2O KNO3 O2 + CS2 KNO2 + CO2 O2 + SO2 Cu + Cu + H2O Cl2 CuO + CuCl2 H2 Al(NO3)3+ NaOH Al(OH)3 + NaNO Fe + H2SO4 Fe2(SO4)3 + H2 KOH + Al + HBr KBr + Al2S3 S8 H2O Al(OH)3 + H2CO3 Al2(CO3)3 + H2O Al(OH)3 + HBr AlBr3 + H2O Vocab Week 18! Last one this semester! • • • • • single displacement double displacement reactivity series precipitate aqueous • • • • • obsequious moribund winnow flaccid rife Na + NaNO3 Li AlCl3 + Na2O + LiCl + Al N2 NH3 FeS2 + + HCl O2 NH4Cl Fe2O3 + SO2 sodium hydroxide sodium oxide + water sodium reacts with water to produce sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas carbon tetrahydride reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water chlorine + sodium iodide chloride + iodine sodium hydrogen chlorite water chlorine (III) oxide + ammonium phosphate + barium hydroxide ammonium hydroxide + barium phosphate Type of Reaction Example Synthesis A + B AB Decomposition AB A + B Single Replacement A + BX AX + B Double Replacement AX + BY AY + BX Combustion A + O2 CO2 + H2O + products 1. Ba (s) + O2(g) BaO2 (s) 2. HNO3 (aq) + LiOH(aq) LiNO3(aq) + H2O(l) 3. 2Sb(s) + 3 I2 (g) 2SbI3 (g) 4. C3H8 + O2(g) CO2 (g) + H2O(g) 5. H3PO4(aq)+ LiOH (aq) Li3PO4(aq) + H2O(l) 6. Fe(s) + CuSO4 (aq) FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s) 7. CS2 (g) + O2(g) CO2 (g) + S2(s)