The Human Brain
advertisement

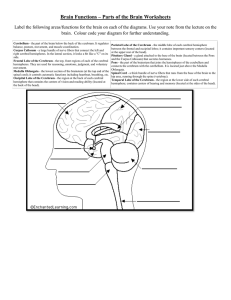
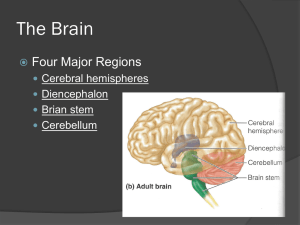
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure • Composed of 100 billion cells • Makes up 2% of bodies weight • Contains 15% of bodies blood supply • Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection • Surrounded by the cranium • Surrounded by protective membranes called meninges • Fluid within the spaces of the meninges called, cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) Major Parts of The Brain Medulla Oblongata • Attached to the spinal cord at the base of the brain • Contains reflex centers for vomiting, hiccupping, coughing, and swallowing. • 1. 2. 3. 4. Contains control centers for: Heart rate Force of heart contractions Blood pressure Breathing rate Cerebellum • The cerebellum processes input from other areas of the brain, spinal cord and sensory receptors to provide precise timing for coordinated, smooth movements of the skeletal muscular system. Thalamus • The sensory relay center of the brain. • Receives sensory information from parts of the body and directs these messages to the appropriate parts of the brain Hypothalamus • Main control center for the autonomic nervous system. • Also controls feelings of hunger, body temperature, aggression, sex drive, thirst, circadian rhythms, fear, control of sex hormones • Secretes hormones that control the pituitary gland Midbrain • Important visual and auditory functions • Controls eye movements • Important functions dealing with movement. Pons • 1. 2. 3. 4. Functions include: Arousal Sleep Level of consciousness Assist in control of autonomic functions. Limbic System • The limbic system encompasses structures that are critical for forming memories and experiencing pleasure, as well as for various motivational and emotional activities. The Cerebrum • Largest part of the Human Brain • This part of the Brain has many convolutions that give it a very large surface area. Functions of the Cerebrum: • All information from our senses are sorted and interpreted in this part of the brain • Voluntary muscles that control movement and speech are contained in the cerebrum • Memories are stored in the cerebrum • The cerebrum is the decision making part of the brain. • The cerebrum is thought to be the center of human consciousness Regions of the Cerebrum Cerebral Cortex – The outer lining of the cerebrum • The cerebral cortex has several important functions 1. Experience of sensation 2. Voluntary movement 3. All thought processes associated with consciousness Cerebral Hemispheres • The cerbral cortex is organized into two halves called hemispheres, the right and the left. • A structure called the corpus callosum bridges the right and left hemispheres (250 million nerve fibers) Corpus Callosum Right vs. Left Hemisphere • Voluntary muscles on one side of the body are controlled by nerves in the opposite hemisphere of the brain. • The same generally holds true for sensory information. For example things seen in the left eye are processed on the right side of the brain. Hemispheric Dominance • Close to 90% of the population is right handed. • Most of us also show dominance with respect to our legs, eyes, and ears. • Each hemisphere of the brain is also dominant for other behaviors : Left Hemisphere • Language • Math • Logic Right Hemipshere • Spatial abilities • Face Recognition • Visual imagery • Music • These are merely generalizations as both sides of the brain work together to perform most functions Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex • The cortex of the Cerebrum is divided into Four Lobes: 1. Frontal Lobe 2. Parietal Lobe 3. Temporal Lobe 4. Occipital Lobe Frontal Lobe • Control of voluntary muscles • Reasoning • Critically thinking Parietal Lobe • Receives sensory information from from skin and skeletal muscles • Associated with sense of taste Temporal Lobe • Perception and recognition of auditory stimuli • Memory Occipital Lobe • Concerned with many aspects of vision.