THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
advertisement

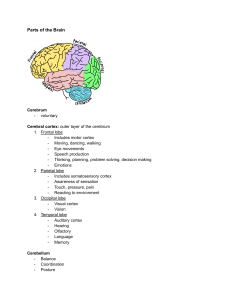
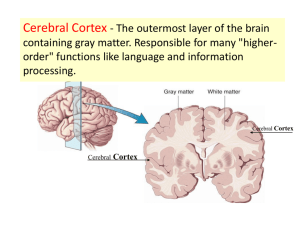
THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR THE HINDBRAIN Medulla attaches to spinal cord; circulation, breathing, reflexes, muscle tone Pons, “bridge”, connects brainstem to cerebellum; sleep, arousal Cerebellum, “little brain”, coordination, equilibrium, organizes sensory info. MIDBRAIN Segment that lies btwn the hindbrain and the forebrain Helps w/voluntary movement Reticular formation: runs through hindbrain and midbrain---muscle reflexes, breathing, pain perception, sleep, arousal FOREBRAIN Largest and most complex region of the brain, with a variety of structures Thalamus, hypothalamus, and limbic system are the core of the forebrain Near top of brainstem THALAMUS All sensory information, except smell, must pass through to get to cerebral cortex May play active role in integrating info. from various senses HYPOTHALAMUS Regulates basic biological needs 4 F’s: fighting, fleeing, feeding, and sexual behavior Links brain and endocrine system LIMBIC SYSTEM Loosely connected network of structures located along the border btwn the cerebral cortex and deeper subcortical areas “Pleasure center” Includes parts of the thalamus and hypothalamus, the hippocampus, amygdala, and septum HIPPOCAMPUS AND AMYGDALA Plays a role in memory Some believe it deals with spatial memory Others say it groups memories for factual info Amygdala may control emotional responses CEREBRUM Seat of complex thought Learning, remembering, thinking, consciousness Cerebral cortex is the convoluted outer layer of the cerebrum CEREBRUM Divided into 2 halves---the cerebral hemispheres: right and left halves 2 halves connected by the corpus callosum Each hemisphere divided into 4 parts, called lobes OCCIPITAL LOBE Back of the head Includes the cortical area Most visual signals are sent and processing begins Called the primary visual cortex PARIETAL LOBE Called the primary somatosensory cortex Registers sense of touch Involved in integrating visual input and monitoring body’s position in space TEMPORAL LOBE Near the temples Contains the primary auditory cortex devoted to auditory processing Speech and language FRONTAL LOBE Largest lobe Contains the primary motor cortex---muscle movement Prefrontal cortex: higher functions---working memory, relational reasoning, memory of temporal sequences