cerebellum, medulla oblongata and pons
advertisement

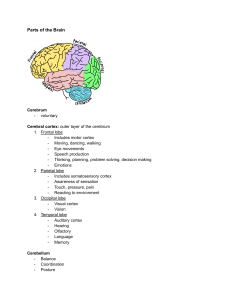
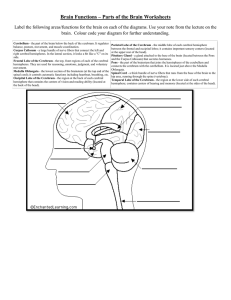
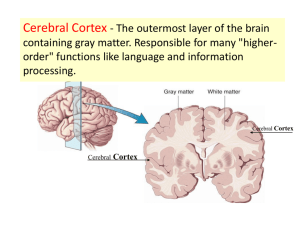
I. Brains 3 major regions A. Hindbrain – cerebellum, medulla oblongata and pons 1. Cerebellum – the old brain, found in all lower living organisms a. Literally- “little” brain” b. Coordinates movement & equilibrium c. Organizes sensory information about muscular movements sent from cerebrum d. Damage disrupts fine motor skills 2. Medulla oblongata – lowest region on brain stem a. Responsible for unconscious vital functions b. Control breathing, circulation, muscle tone and reflexes like sneezing, coughing and salivation 3. Pons – connects cerebellum to brain stem through complex bridge of nerve fibers a. Controls sleep and arousal B. Midbrain – brainstem between hindbrain and cerebellum - Center for dopamine production in substantia niagra, failure of dopamine synthesis causes Parkinson’s Disease symptoms 1. Reticular formation- runs from hindbrain through midbrain and contributes to muscle reflexes, breathing and pain perception 2. Best known for regulating sleep and arousal C. Fore brain – largest and most complex region containing thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system and cerebrum 1. Thalamus – all sensory information must pass through tis to get to cerebral cortex (except smell) a. Made of somas or clusters of cell bodies which relay sensory information to the cortex b. Creates a general awareness of the region from where an impulse has originated 2. Hypothalamus – plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis by regulating a variety of visceral activities. Also acts as a link between nervous system and endocrine system. (Linked with pituitary gland) a. Controls autonomic nervous system, heart rate, and blood pressure, temp. b. Plays major role in. regulating basic biological drives; fight or flight, feeding, mating and reproduction c. Lateral surface of hypothalamus is important in control of hunger d. Regulates water and electrolyte balance 3. Limbic system – involved with emotional experience and expression, located along border between cerebral cortex and deeper subcortical areas a. Not a well-defined system with clear boundaries b. By causing pleasant or unpleasant feelings about experiences, it increase chances for survival D. Cerebrum – largest most complex part of the human brain. Responsible for all higher order thinking 1. Cerebral cortex – convoluted outer layer of the cerebrum. 1.5 sq. ft. 2. Left and right hemispheres 3. Corpus callosum – bridge that connects both hemispheres 4. Lobes – 4 major regions a. Parietal lobe – sense of touch in primary somatosensory cortex b. Temporal lobe - primary auditory cortex speech and language c. Frontal lobe- largest area; contains primary motor functions d. Occipital lobe - primary visual cortex in cortical area