ANSWER KEY: Chapter 12 Review# 1-10, 12, 17, 18, 20, 22 & 24
advertisement

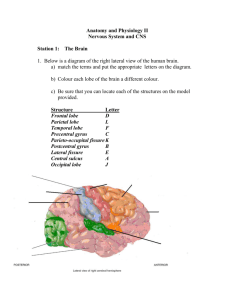
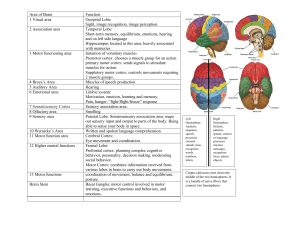
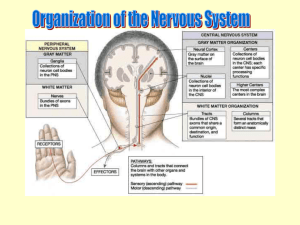
ANSWER KEY: Chapter 12 Review# 1-10, 12, 17, 18, 20, 22 & 24 Multiple Choice: 1. A 2. D 3. C 4. A 5. (1) d, (2) f, (3) e, (4) g, (5) b, (6) f, (7) I, (8) a 6. B 7. C 8. A 9. (1) a, (2) b, (3) a, (4) a, (5) b, (6) a, (7) b, (8) b, (9) a 10. D Short Answer: 12. A) Having a highly convoluted (folded) cerebrum is advantageous because the convolutions increase the cortical surface area, allowing a greater number of neurons to occupy the limited space B) The grooves in the cerebrum are called sulci (shallower) and fissures (deeper) and the outward folds are called gyri C) The median longitudinal fissure divides the cerebrum into left and right hemispheres D) The central sulcus divides the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe and the lateral sulcus divides the parietal lobe from the temporal lobe. 17. A) Functional areas of the left cerebral hemisphere: B) Drawing is associated with the right hemisphere, which is involved with creative imagination, intuition, global view, capacity of synthesis and ease of memorization. The left brain is considered the rational brain and it operates based on logical, linear, sequential reasoning, separate from emotions, intuition, creativity, or capacity to dare trying different solutions. C) Functional Area Primary motor cortex Premotor cortex Somatosensory association area Primary somatosensory cortex Visual area Auditory area Prefrontal cortex Wernicke’s area Broca’s area Description Gives rise to all voluntary somatic motor responses Controls learned motor skills of a repetitious or patterned nature Integrates & analyzes different somatosensory inputs (temp, touch, pressure or pain) Receives somatosensory info from receptors in skin and proprioceptors in muscles; IDs region of body being stimulated Receives info from retinas of the eyes Receives info from the hearing receptors of the inner ear Most involved with elaboration of thought, intelligence, motivation and personality. Associates experiences necessary for production of abstract ideas, judgment, planning and conscience and important in planning out motor activity. Speech area involved in comprehension of language; especially when words need to be sounded out or related “motor speech area” involved in word articulation, producing the movements necessary for speech. 18. a) The limbic system is located in the medial aspect of each cerebral hemisphere b) The structures that make up the limbic system are the: cingulate gyrus, parrahippocampal gyrus, hippocampus, regions of the hypothalamus, mammillary bodies, septal nuclei, amygdaloid nucleus, anterior thalamic nuclei, and fornix. (**NOTE: You will not need to list or ID all these structures, just know general location and overall role) c) The limbic system acts as our emotional or feeling brain. 20. The CNS is protected by the cranial bones, the meninges, the cerebrospinal fluid and the blood-brain barrier. 22. The blood-brain barrier is formed mainly by capillaries with endothelial cells joined by tight junctions. This makes them highly selective, ensuring that only certain substances gain access to neural tissue. 24. a) a concussion occurs when brain injury is slight and the symptoms are mild and transient. Contusions occur when significant tissue damage occurs. b) Brain stem contusions result in unconsciousness(irreversible coma) because the reticular activating system is damaged.