Plessy vs. Ferguson - Centennial School District
advertisement

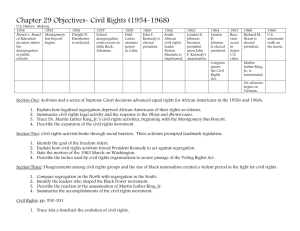
Civil Rights • The political, social, and economic rights of a citizen. WWII and Civil Rights • Better access to good jobs helped set the stage for the civil rights movement Little Rock Nine • Integrated Central High School • Elizabeth Eckford- girl that went on her own • Marked the 1st time a sitting president sent federal troops into the south to enforce the Constitution since Reconstruction. Plessy vs. Ferguson • The Supreme Court ruling allowing “separate but equal” facilities Brown v. Board of Education • 80% of southern whites opposed the decision. • Many Southern politicians disobeyed the ruling. NAACP • National Association for the Advancement of Colored People. • focused on working through the court system. • Initiated a series of court cases that chipped away at the “separate but equal” doctrine. Thurgood Marshall • Lawyer for NAACP • 1st black Supreme Court Justice Orval Faubus • Governor of Arkansas during Little Rock Nine integration Rosa Parks arrest led to a call for a boycott of the Montgomery bus system successful in keeping most blacks off the buses Bus Boycott • Resulted in the emergence of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. as the leader of the Montgomery Improvement Association. Rolling Churches • Station wagons used to give protesters rides during the Montgomery Bus Boycott. • First leader of the Montgomery Improvement Association • Ordained Baptist minister • adopted many of his philosophies & teachings for the civil rights movement from Gandhi MLK, Jr. Civil Rights demonstrators in the 1950’s utilized • boycotts • non-violent sit-ins • passive resistance Boycott • Not buying or using a product or dealing with a certain company in order to exert economic pressure for change. Sit-ins • Nonviolent protests against restaurants and lunch counters who refused to serve black customers. • Chose Lyndon B. John F. Kennedy Johnson as his running mate because Johnson was a Southern Senator capable of holding the white vote from the south. • Along with RFK, helped Martin Luther King after he was arrested for violating his probation. Freedom Riders • The purpose in 1961 was to test the Supreme Court decision that ruled that all bus stations and terminals serving interstate travelers should be integrated. James Meredith • Integrated the Univ. of Mississippi with the help of federal troops Eugene “Bull” Connor • Police Chief who used fire hoses, dogs, and cattle prods to disperse a crowd marching in Birmingham, Alabama • After watching television coverage of the brutal tactics used against protestors by the Birmingham police, even opponents of the civil rights movement were appalled by the police violence. Voting Rights Act of 1965 • Provided for the end of literacy tests and other barriers to voting. 1963 March on Washington • Participants hoped to convince Congress to pass civil rights legislation. • Location of Dr. Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream” speech. “black power” • Impatient with the slow progress of the civil rights movement. • African American movement that worked for the economic, political, and social goals of blacks, without the help of whites. Malcolm X • Outspoken member of the Nation of Islam who advocated black separatism Stokely Carmichael • He became the militant leader of the SNCC The Watts Riots • Took place in Los Angeles, California The Black Panthers • Black Power • Black nationalism • Community development Emmet Till • From the Chicago visiting South • Killed by two white men • Not Guilty verdict by an all-white jury The Civil Rights Act of 1964 • Forbid segregated theaters. • Forbid segregated restaurants. • Forbid segregated hotels & motels • Banned discrimination in the selling or renting of a home. George Wallace • Governor who stood in the doorway at the University of Alabama De jure segregation • Segregation that is imposed by law. de facto segregation • By custom, not by law. • Example- concentration of urban African Americans in slum areas