The Civil Rights Movement Chapter 25
advertisement

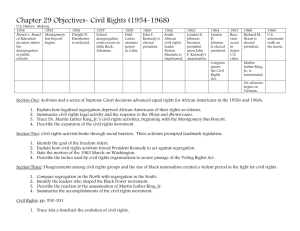
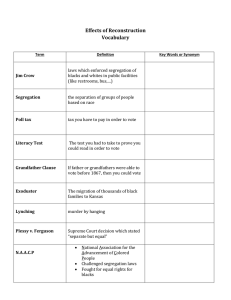
The Civil Rights Movement Chapter 25 What court case upheld the principle of ‘separate but equal’? Brown v Board of Education 2. Dred Scott v Sanford 3. Plessy v Ferguson 4. McCulloch v Maryland 1. Origins of the Civil Rights Movement 1865- the Civil War ended 13th Amendment (1865)- officially ended slavery 14th Amendment (1868)- identified who was a US citizen & specified that all US citizens have “equal protection of the laws”. 15th Amendment (1870)- states may not interfere with any man’s right to vote= gave black men the vote. Origins of Civil Rights Movement 1896-Plessy v Ferguson – established “separate but equal” segregation (segregation by law)mostly in the South. * “Jim Crow Laws” De facto segregation – segregation by custom (no law)- popular in the north Poll taxes, literacy tests, lynching Niagara Falls Movement NAACP (1909)worked to end segregation. The Beginnings NAACP- (1939-1961) led by attorney Thurgood Marshall; fought segregation, lynching. Thurgood Marshall- later 1st black justice on Supreme Court CORE- Congress of Racial Equality (1942)- used “sit-ins” to fight against segregation. *Brown v Board of Education (1954) ◦ Called for desegregating public schools ◦ Overturned Plessy v Ferguson’s ‘separate but equal’ Southern Manifesto 1956 101 Southern members of Congress Denounced the ruling in Brown, as a clear abuse of judicial power & pledged to reverse it Encouraged white Southerners to defy the Supreme Court Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. Became National leader of the civil rights movement At age 26 Led Montgomery Bus Boycott ◦ In response to Rosa Parks ◦ Huge success with desegregation immediately Influenced by Gandhi – non-violent protest Civil Disobedience – essay written by Henry David Thoreau. ◦ Can disobey a law if it is unjust **The Montgomery Bus Boycott 1955 1955- Rosa Parks- arrested for sitting in the “white section” of the Montgomery public transit. Martin Luther King Jr. –chosen to lead a boycott of the public bus system in Montgomery, Alabama. **King’s methods – passive non-violent resistance; “Civil Disobedience” Boycott lasted 1 year; Supreme Court ruled in Park’s favor. Montgomery bus transit system desegregated. *Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) ◦ Established by King (1st president) ◦ Group of black ministers with goal of ending segregation & encouraging blacks to vote Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. 1957- Governor Faubus ordered troops to Little Rock High to prevent 9 African Americans from entering *Little Rock 9 Importance: Governor had used the National Guard to oppose the federal government Result: Eisenhower sent federal troops to Little Rock to enforce federal law Little Rock 9 The Civil Rights Act of 1957 1st civil rights law since Reconstruction Created a Civil Rights division within the Department of Justice (federal government can seek court injunctions against anyone interfering with an ind. Right to vote). Created US Commission on Civil Rights- investigate voting rights violations * SCLC- began a push to register 2 million new African-American voters. The Sit-In Movement 1960- The Greensboro Lunch Counter Sit-IN- 4 African-American students from NC A&T sat at the white lunch counter of Woolworth’s. Next day- 29 more students appeared at the lunch counter End of the week- 300 students End of the Month- the movement spread to 54 cities (9 states). Student Non-Violent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) formed April 1960; attracted young people. Marion Barry-John Lewis 1st leaders 1960-1965- played a role in desegregation of public facilities Sent young volunteers into the Deep South to register African-Americans to Vote. *The Voter Education Project SNCC- sponsored to register African-Americans in the South to vote. 1964- local officials in Mississippi murdered 3 SNCC workers “African Americans have had 350 years of cooling off and if they cooled off anymore they would be in a deep freeze” CORE- sponsored *Freedom Riders ◦ Integrated bus ride from NC to Mississippi ◦ 1962-Kennedy ended bus segregation federally *George Wallace ◦ 1963-Governor of Alabama ◦ Blocked African Americans from entering the University of Alabama ◦ Federal officials forced him to move James Meredith ◦ Wanted to attend the University of Mississippi ◦ 1962-JFK sent 500 federal marshals to escort him Birmingham Protests (1963) Martin Luther King Jr. wanted to push for a Civil Rights Law to be passed Chose Birmingham- violent place Bull Conner- former head of Police running for Mayor King arrested Letter from a Birmingham Jail King wrote to white leaders Explained why his use of non-violent protests After MLK’s release- Bull Conner & Police used dogs, fire hoses, & clubs on protestors while Americans watched on TV. ** Kennedy ordered a new Civil Rights bill be written up Southern Senators threatened to filibuster. August 28, 1963 Purpose- urge Congress to pass a Civil Rights law 200,000 demonstrators march on Washington Dr. King’s “I have a dream” speech March on Washington **Civil Rights Act of 1964 Filibustered for 87 days in the Senate & finally passed ◦ Prevention of racial discrimination ◦ Segregation is illegal ◦ Required businesses to end discrimination in the workplace *24th Amendment ◦ Outlawed poll taxes in federal elections 1965-Demonstrations to register to vote 2,000 arrested March from Selma to Montgomery (50 miles) Bloody Sunday ◦ Marchers beaten by state troopers as they crossed the bridge out of Selma "I was hit in the head by a state trooper with a nightstick... I thought I saw death." —John Lewis, SNCC The Voting Rights Act (1965) Federal examiners sent to register African-Americans & oversee elections Suspended literacy tests Result- more than 250,000 AfricanAmericans registered to vote. Martin Luther King Jr. won the Nobel Peace Prize (1965) Racism & poverty still persistent Los Angeles- 1965 Due to police brutality 34 killed, 900 injured $30 million property damage Race riots erupted all over the country Urban blacks saw the changes for Southern blacks – they wanted the same *Kerner Commission ◦ Detailed study of urban riots ◦ Blamed white society & racism for problems in inner cities Dr. King & wife moved into apartment in Chicago. Draw attention to need for improvement of slum neighborhoods in big cities Not very successful Chicago Movement Black Power Founder-Stokely Carmichael Attracted young AfricanAmericans African Americans should control the social, political & economic aspects of their culture Emphasized black power & self-discipline rather than assimilation Symbol of the Black Power movement Nation of Islam ◦ Aka Black Muslims ◦ Malcolm X was a spokesperson ◦ Separation from whites & govern themselves Killed by member of the Nation of Islam The Black Panthers Founded in 1966 by Huey Newton, Bobby Seale, Eldridge Cleaver in Oakland, California Emphasized economic self-sufficiency, black nationalism, self-defense Believed violent Revolution was necessary to get political & economic equality. The Assassination of Martin Luther King Memphis, TN April 4, 1968 – King was assassinated on his hotel balcony by a sniper Assassin – James Earl Ray Significance- Civil Rights lost its most eloquent leader.