Prokaryotes:
advertisement

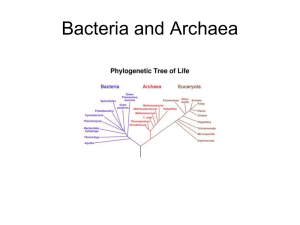
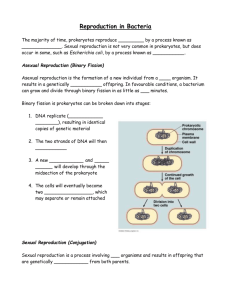
Prokaryotes: Archaea & Bacteria The Tree of Life • All living things classified in three domains: –Bacteria –Archaea –Eukarya Amazing Living Things • Microbes indispensable to life: • Produce much of Earth’s: • Oxygen • Decomposition • Over half of Earth’s biomass • More bacterial cells than human cells in your body! Prokaryotes • Prokaryotes have: – Circular DNA, RNA, ribosomes, cytoplasm, plasma membrane – Most prokaryotes have a cell wall, a capsule (around the cell wall) and a flagellum • Prokaryotes don’t have: – Organelles such as nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria. Generalized Prokaryote Nucleoid DNA Plasmid DNA Cytosol Flagellum Capsule Plasma Membrane Cell Wall Prokaryotic DNA • The area that contains the genetic material is referred to as the nucleoid. • The genes are usually in one continuous circular loop of DNA. • There may be other small circles of DNA outside the nulceoid called plasmids. Bacteria/Archaea • Habitats (name a place, and they live there!) – They are specialists • human skin, mouth, respiratory tract, large intestine, urogenital tract, etc. • salty Dead Sea • extreme pH • archea in deep sea vents: 90-106o C – Aerobes and anaerobes Some Prokaryotes Thrive in Extreme Conditions Cyanobacteria in Yellowstone Hot Springs Archaea • Unique lipid membranes, cell walls, and rRNA • Methanogens – Convert CO2 to methane – Swamps, hot springs, vent communities, cow stomachs • Halophiles - survive concentrated salt environment • Thermoacidophiles - thrive in hot, acidic environment • Generally in EXTREME environments Bacteria • Evolve Rapidly • Most of the time are asexual • Classified by shape, locomotion, pigments, nutrients, colonies Bacteria • Shape: – Cocci - round – Bacilli - rod – Spirilla - spirals Three Common Bacterial Shapes (b) (a) (c) bacillus cocci spirillus The Prokaryote Flagellum Flagella Bacterium Bacteria • Reproduction • Reproduction is asexual, by simple splitting (binary fission) • Daughter cells are genetic clones of the parent cell Binary Fission DNA Bacteria - Reproduction • Binary fission: – Very fast, up to once every 20 minutes – One bacterium-> 1021 in 24 hours. • Conjugation: (sexual reproduction) – Used only occasionally. Bacteria – Sexual Reproduction • Conjugation: – Genetic variation through pili (structures similar to flagella) and plasmid DNA – DNA is exchanged between bacterial cells – Occurs through a special large, hollow pilus – One bacterium acts as a donor, transferring DNA to the recipient. Conjugation Donor Recipient Sex Pilus Benefits of Bacteria • Symbiosis (mutualism) – Ruminants’ digestive tracts – Nitrogen fixing in soil, nodules on certain legumes – Bacteria on/in the human body: intestines and vitamin K and B12 • Biodegradation - oil • Food production - cheese, yogurt, sauerkraut • Decomposers Our Relationship With Bacteria Bacterial Pathogens • Some cause disease = pathogenic • In humans: – Strep throat – Toxins - tetanus, botulism – Pneumonia – "Flesh-eating" bacteria – Plague – Tuberculosis – Cholera – Lyme disease ANTIBIOTICS= anti bacterial!!! The Causes of Tooth Decay Transmission of Bacterial Pathogens • • • • Airborne Water Food Direct (skin contact, blood, and other body fluids) • Insect vectors and other hosts such as deer tick (Lyme) or mosquito. Germ Theory of Disease • Theory that microorganisms are the cause of disease. • 1859 – Louis Pasteur – Credited with the idea that human diseases were caused by bacteria and viruses (germ theory) – Very important discovery in the field of medicine Infectious Diseases • Average age of death, in first world countries, jumped 30+ years in last century due to antibiotics, and enhanced hygiene and nutrition. • Antibiotic-resistant infections on the rise in hospitals in the U.S. – This is due to bacterial evolution in response to widespread use of antibiotics!