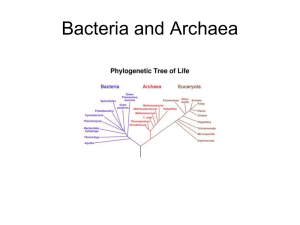
Reproduction in Bacteria
advertisement

Reproduction in Bacteria The majority of time, prokaryotes reproduce _________ by a process known as ______________. Sexual reproduction is not very common in prokaryotes, but does occur in some, such as Escherichia coli, by a process known as ___________. Asexual Reproduction (Binary Fission) Asexual reproduction is the formation of a new individual from a ____ organism. It results in a genetically ___________ offspring. In favourable conditions, a bacterium can grow and divide through binary fission in as little as ___ minutes. Binary fission is prokaryotes can be broken down into stages: 1. DNA replicate (____________ ________), resulting in identical copies of genetic material 2. The two strands of DNA will then ___________ 3. A new ____________ and _____ ______ will develop through the midsection of the prokaryote 4. The cells will eventually become two _________________, which may separate or remain attached Sexual Reproduction (Conjugation) Sexual reproduction is a process involving ___ organisms and results in offspring that are genetically ____________ from both parents. Conjugation in prokaryotes can be broken down into stages: 1. Two bacteria join together by forming a specialized structure called a _______. 2. Genetic information (_____________) is ________ through the pilus, resulting in an altered set of characteristics. 3. Following the transfer, the two bacteria separate and can then undergo binary fission. The result of the uptake of a new piece of DNA by conjugation can have many effects including: 1) 2) In both cases, if the piece of DNA is inserted into the chromosome, then the process is called ______________________. This produces a permanent change in the DNA of the cell, which is ___________ to the ________________ of that cell. During unfavourable conditions, some prokaryotes survive by forming dormant or resting cells, called _________, which can withstand harsh environments such as ______ and ______. When suitable conditions return, the prokaryote will re-emerge and begin _______________. Bacterial Growth Bacterial growth curves take on a particular pattern, which shows the rate at which bacteria will reproduce when conditions are optimal. A typical growth curve consists of 4 different phases: Lag phase – Exponential growth phase – Stationary phase – Death phase – Bacterial Growth Curve The maximum number of organisms a particular environment can support is termed the _____________________ Growth rate is the time it takes for a population of bacteria to __________ in number Like all organisms, bacteria thrive under __________ conditions The primary reason that our planet isn’t buried under a thick layer of bacteria can be attributed to the fact that conditions are rarely ______ for the bacteria to grow. Scientists who study bacteria try to create the optimal environment in the lab: culture medium with the necessary ___________, _________, ___, and ________________, in which bacteria grow predictably Generation times for some common bacteria under optimal conditions of growth Bacterium Medium Escherichia coli Glucose-salts Bacillus megaterium Sucrose-salts Streptococcus lactis Milk Streptococcus lactis Lactose broth Staphylococcus aureus Lactobacillus acidophilus Rhizobium japonicum Mycobacterium tuberculosis Treponema pallidum Heat infusion broth Milk Mannitol-salts-yeast extract Synthetic Rabbit testes Growth Rate (minutes)