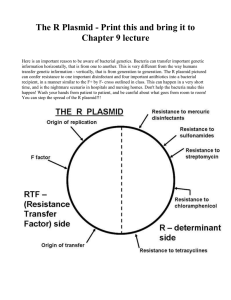
The three ways in which genetic recombination occur in bacteria are:
advertisement

The three ways in which genetic recombination occur in bacteria are: Tranformation - bacteria are able to take up foreign DNA through their cell membranes. This foreign DNA most often remains as an extrachromosomal structure called the plasmid. Sometimes the foreign DNA can integrate into the bacterial genome. Transduction - The transfer of small segments of bacterial DNA by viruses. When viruses invade the bacterial cell, they make use of the bacterial protein machinery to produce virions. During a process called packaging where genetic material is packed into the newly formed virus, bits of bacterial DNA are also included. These new virions then carry the bacterial DNA into the next cell that they infect. Conjugation - Also termed sexual reproduction between bacteria containing an F plasmid (F+) and one that lacks the plasmid (F-). A temporary structure called the conjugation tube is formed between the two interacting bacteria and the exchange of genetic material takes place.