CHEMISTRY CH 21 ASSESSMENT REVIEW 21.1.1 Analyze
advertisement

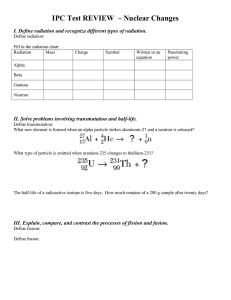
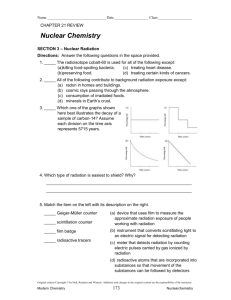
CHEMISTRY CH 21 ASSESSMENT REVIEW 21.1.1 Analyze common sources of background radiation Define isotope, and give an example of a pair of isotopes. What do the numerical superscript and the subscript show for an isotope? What information can you get from this isotope symbol: 126𝐶 21.1.2 Compare and contrast alpha, beta and gamma radiation (include positron emission). Compare the energy levels of alpha, beta and gamma radiation. Give an example of a material that can stop each type of radiation. What happens to mass number and atomic number during an alpha, beta, positron emission and gamma decay? What particle (or type of radiation) is given off during alpha (α), beta (β), positron emission and gamma decay? What is the source of a beta particle? A positron? 21.1.3 Apply the concept of half-life of a radioactive element Define half-life. What is the half-life of C-14? A sample was analyzed using C-14. If it has only 6.25% of C-14 of a similar sample today, how old is it? A rock was analyzed using Rb-87 (half-life = 48 billion years). If it has only 12.5% of Rb-87of a similar sample today, how old is it? 21.2.1 Compare and contrast nuclear fission and nuclear fusion List a least 3 differences between fission and fusion. Identify pros and cons for each. Describe fission and give an example of a fission reaction. Describe fusion and give an example of a fusion reaction. Deuterium and tritium are isotopes of hydrogen. Write their nuclear notation, and: A) Identify the mass number for deuterium? How many neutrons, protons and electrons does it have? B) Identify the mass number for tritium? How many neutrons, protons and electrons does it have? 21.2.2 Demonstrate equations that represent the changes that occur during radioactive decay Write a nuclear equation for the alpha decay of: C-14. Write a nuclear equation for the beta and gamma decay of: C-14. Complete the following reaction: 234 4 90 𝑇ℎ → 2𝐻𝑒 + ? Complete the following reaction: 0 234 90 𝑇ℎ → −1𝑒 + ? 21.2.3 Trace the operation and structure of a fission reactor Define fuel rods, control rods, moderator, turbine and explain the function of each 21.3.1 Distinguish the biological effects of radiation and the units used to measure levels of exposure Define gray, sievert and identify most common sources of exposure 21.3.2 Illustrate medical and nonmedical used for radioactivity List 2 medical and 2 nonmedical uses for radiation. Describe three lifestyle or environmental factors that will greatly increase your exposure to radiation. See the next page for some sample questions from 21.2 and 21.3 Section 21.2 and 21.3 Questions to consider, and understand: 1) What are the advantages and disadvantages for nuclear fission? 2) What are the advantages and disadvantages for nuclear fusion? 3) Why/how are foods irradiated? Does this make food radioactive? 4) Describe sources of background radiation 5) Why is ionizing radiation potentially hazardous to your health? 6) What are some lifestyle and or environmental factors that increase our exposure to radiation? 7) How do we measure radiation exposure? What are the ranges of physiological effects? 8) How are nuclear waste materials disposed?