Mendelian Genetics Bellwork & Refresher

Mendelian Genetics Refresher Bellwork/activity
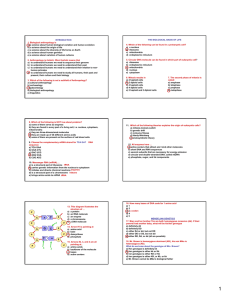
Rabbit ear length is an inherited trait controlled by simple dominance, with long ears (L) being dominant over short (l). Using a Punnett square, predict the possibility of a long eared rabbit with the heterozygous genotype and a short eared rabbit producing the recessive phenotype. l l
L
Ll
Ll
50% l ll ll
Types of Inheritance
Simple Dominance – In the heterozygous genotype, the dominant allele hides the recessive allele
Incomplete Dominance – In the heterozygous genotype, the “dominant” allele
blends with the “recessive” allele. The phenotype is somewhere in between.
RR Rr rr
Codominance – In the heterozygous genotype, BOTH alleles are equal.
Alleles:
I A I B i
(note: in blood type, O is recessive to A and B) ii
I A I B
I
Genotypes….draw the phenotype:
A I A I A i
I B I B I B i
Incomplete Dominant
R
Incomplete Recessive r
Type A
I A
Type B
I B
Type O i
Instructor Directions: 20 Minutes total
1.
Post the bellwork question. Give time to answer the question. Have pairs check and discuss with each other. Ask students to provide the answer and the justification (one square of a Punnett square is a 25% chance of that genotype in the offspring with each pregnancy; the short ears are the ll genotype.)
2.
Go over bolded vocabulary as needed.
3.
The second sheet can be a handout or can be placed on an elmo for students to copy.
4.
Provide each group of students with a set of allele discs. Allele discs should be copied as follows: a.
Incomplete Dominant (Red): Print in color on transparency paper OR use sharpie to color transparency OR use colored cellophane. 2 per
group b.
Incomplete recessive: Print on white paper 2 per group c.
Type A: Print on white paper 2 per group d.
Type B: Print on white paper 2 per group e.
Type O print on colored paper 2 per group
5.
Provide colored pencils or crayons (Red, white and pink) for each group
6.
Have students use the allele disks to model each genotype, recording what they see as they go.