Early New England Colonies
advertisement

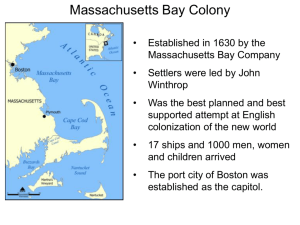
Calvinism inspired by Puritan Reformation ◦ Foundation for Puritanism, Scottish Presbyterians, French Huguenots and Dutch Reformed ◦ All groups were significant players in colonization of America Henry VIII separated from Catholic Church but kept many Catholic ways Wanted to “purify” Church of England ◦ Get rid of “Catholic” traditions ◦ Emphasize literacy and Bible study ◦ Appealed to poor Separatists ◦ Puritans who wanted to split from Church of England ◦ Only wanted the “visible saints” allowed into the church King James I ◦ Tried to force all English to follow his religion ◦ Afraid challenge in religion would lead to challenge politics Separatists fled to Holland Left Sept 16 1620, 102 passengers Separatists did not want to be influenced by Dutch culture arrived December 21st Landed at Cape Cod wrong location so did not have legal right to make a government Was outside of the charter given to the Virginia Company Pilgrims would use Bible as their laws Made a government for settlers ◦ William Bradford – Governor Feared non-Separatists would corrupt the colony ◦ Captain Miles Standish – head the militia • Pledged loyalty to King and follow laws • Agreed to follow the will of majority • Precedent of self-government in American colonies Wampanoag Indian Most of his people had been killed Had been kidnapped by English sea captain then escaped Learned English When Pilgrims arrived, they found Squanto Squanto’s help • Facilitated peace treaty between Massasoit and the Pilgrims • Worked as interpreter • Showed how to plant corn, fertilize soil, trap beaver • Showed where to fish First Thanksgiving celebrated first successful harvest in 1621 1629 Charles I allowed Archbishop William Laud to persecute Puritans ◦ Led to non-Separatist Puritans wanting to leave England Charter was vague ◦ Allowed Puritans to create headquarters in Massachusetts ◦ Allowed Puritans to make their own laws and officers effect: settlers govern themselves Great Migration 1630-1642 ◦ 70,000 Puritans left England 20,000 to New England Congregational Church ◦ Puritan church in America ◦ Needed membership to vote Town government open to all property owners ◦ Increased public participation in government Was NOT democracy ◦ Feared “common” people interfering with establishment of society built on Puritan ideals John Winthrop was first governor Settlers ◦ Were wealthy, educated ◦ Communities were built around a church (congregation) No Religious toleration ◦ Must be a Puritan “City Upon a Hill” John Winthrop Colony would be an example for the rest of the world Believed that God would insure the success of colony ◦ Gave Puritans strength to survive bad times and dangers Dissenter ◦ Argued for complete split from Church of England ◦ Said state could not legislate religious behavior Massachusetts government was based on religion ◦ Massachusetts Bay charter illegal because settlers took land from Indians Expelled from Massachusetts in 1635 Challenged Puritan teachings ◦ Antinomianism Since life is predestined, people are under no obligation to follow edicts of either church or government Was convicted of heresy and banished from Massachusetts in 1638 moved to Rhode Island Eventually went to New York and was killed by Indians Epidemic in 1621 killed most Indians around Plymouth Pequot War 1637 English and Narragansett fought against Pequot English annihilate Pequot's •Metacom (King Philip) 1675 created Indian alliance to resist spread of English –Attacked 52 Puritan towns –War ended, Metacom defeated –Indian survivors forced to move onto reservations –Ended Indian threat to New England Netherlands became major commercial power following independence from Spain ◦ 1609 Hudson sails for Dutch in Hudson Valley and Canada ◦ 1626 purchase Manhattan ◦ 1628 Dutch take Caribbean Islands from Spain and Brazil and Indian Ocean ports from Portugal ◦ Dutch East and West India Companies led most trade and had own armies ◦ Becomes banking capital of Europe • New Amsterdam (New York City) – Bought Manhattan for $24 – Was run solely for Dutch West India Company’s interests – Very autocratic – Dutch would trade with anyone – Wanted to make money New Netherlands were vulnerable because surrounded by British colonies King Charles of England gave land including New Netherland to Duke of York in 1664 Duke of York sent fleet to make Dutch surrender ◦ Dutch surrender without a fight ◦ Stuyvesant did not have ammunition to fight Growth was limited due to aristocratic tendencies and corrupt governors that allowed for power to be concentrated in hands of a few families Quakers – Society of Friends ◦ Wouldn’t pay taxes to Anglican Church ◦ Treated everyone as equals ◦ Rejected authority of priests, ministers ◦ Followed “inner light” ◦ Believed in equality, pacifism ◦ Spoke out against slavery William Penn ◦ King Charles II grants land to Penn as repayment for loan in 1681 ◦ Pennsylvania created for haven for persecuted people and to experiment with a more liberal government ◦ Advertised broadly for settlers Encouraged artisans to settle Paid Indians for the land for Philadelphia ◦ Resulted in positive relations New York, New Jersey, Delaware, Pennsylvania Soil was fertile and broad, allowed for growth of grain “Bread Basket Colonies” Rivers and deep harbors encouraged trade Delaware, Hudson, Susquehanna Forests led to timber, furniture and shipbuilding Economy balanced between trade and farming Ethnically mixed Largest amounts of religious tolerance and democracy Good land was available The Settlements of the Lower South This map shows the towns and fortifications of North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, as well as the overlapping claims by the Spanish and the English to the territory south and west of Fort King George. The many Georgia forts reflect that colony's role as a buffer state between rice-rich South Carolina and the Spanish troops stationed in Florida. Founded by James Oglethorpe in 1733 ◦ Savannah was principle port Created as place to send criminals, drunk and idle poor Served as barrier to Spanish and French settlements Allowed religious toleration for Christians except Catholics King Charles granted land to supporters in 1670 Made wealth from trading food with sugar plantations of Caribbean ◦ Also traded Indian slaves to West Indies and New England Rice becomes major export ◦ Slaves from West Africa had the expertise to allow growth of rice Charleston becomes busiest seaport in South ◦ North was mostly discontented Virginians, seen as independent and rebellious ◦ South was aristocratic, wealth, plantation driven ◦ 1712, Carolinas split ◦ Charleston, S. C. and major harbor Planters saw themselves as English country gentlemen, not Americans