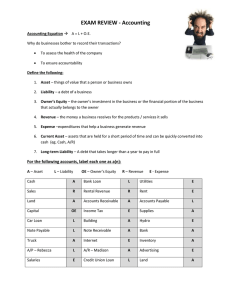
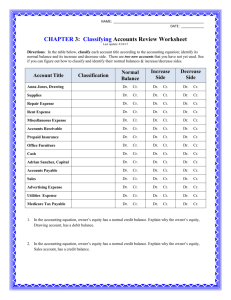
Financial Statements
IAS 1
Wiecek and Young
IFRS Primer
Chapter 2
Related Standards
2
FAS 130 Reporting Comprehensive Income
Related Standards
3
IFRS 5 Non-current Assets Held for Sale and
Discontinued Operations
IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures
IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in
Accounting Estimates and Errors
Purpose and Components of
Financial Statements
4
Comparable statements more useful
IAS 1 looks to enhance comparability
Applies to general purpose financial
statements
–
Meets the needs of most users
–
“Financial statements are a structured
representation of the financial position and
financial performance of the entity.”
IAS 1 - Overview
5
Statement of financial position
Statement of comprehensive income (this may be
augmented by a separate income statement)
Statement of changes in equity
Statement of cash flows
Notes including significant accounting policies and
explanatory information
Statement of financial position at the beginning of
the earliest comparative period when an entity
applies an accounting policy retrospectively or
makes a retrospective restatement
Fair Presentation and Compliance
with IFRSs
Should present fairly - faithful representation
Entity must:
–
–
–
6
select and apply appropriate accounting policies keeping in
mind the GAAP hierarchy,
present the information such that it provides, relevant,
comparable and understandable information, and
provide additional disclosures where necessary.
Note disclosures are not a substitute for proper
accounting
May depart from GAAP
Going Concern and Accrual Based
Accounting
7
Accrual basis
Going concern assumed
If not – new basis of accounting
Materiality
8
Omissions or misstatements of items are
material if they could, individually or
collectively, influence the economic decisions
of users taken on the basis of the financial
statements. Materiality depends on the size
and nature of the omission or misstatement
judged in the surrounding circumstances.
The size or nature of the item, or a
combination of both, could be the
determining factor.
Presentation
Identify what is included
Must display the following
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
9
the name of the entity
whether the financial statements are
consolidated or not
the date of the balance sheet or period covered
the reporting currency and
the level of rounding (e.g. $000s)
Frequency of reporting,
comparability and consistency
10
At a minimum – annual statements
Comparative required unless IFRS permits or
requires otherwise
At least two statements and a third if
retrospective application or restatement
Presentation and classification should
generally stay the same
Statement of Financial Position
Information to be Presented in the
Statement of Financial Position
–
Sufficiently different
–
–
–
11
Based on size, function, nature and liquidity, nature,
timing
Different measurement bases
Specific items to be presented separately
May present relevant subcategories
Details re share capital
Current Assets and Liabilities
12
Segregate current versus non
Order of liquidity
Combined
Amounts beyond 12 months
Current Assets
An entity classifies assets as current assets
when:
(a) it expects to realize the asset, or intends to sell or consume it, in its
normal operating cycle;
(b) it holds the asset primarily for the purpose of trading;
(c) it expects to realize the asset within twelve months after the reporting
period; or
(d) the asset is cash or a cash equivalent (as defined in IAS 7) unless
the asset is restricted from being exchanged or used to settle a
liability for at least twelve months after the reporting period.
13
Current Liabilities
14
An entity classifies liabilities as current
liabilities when:
Statement of Comprehensive Income
15
(a) revenue;
(b) finance costs;
(c) share of the profit or loss of associates and joint ventures accounted for using
the equity method;
(d) tax expense;
(e) a single amount comprising the total of:
(i) the post-tax profit or loss of discontinued operations and
(ii) the post-tax gain or loss recognized on the measurement to fair value less
costs to sell or on the disposal of the assets or disposal group(s)
constituting the discontinued operation;
(f) profit or loss;
(g) each component of other comprehensive income classified by nature (excluding
amounts in (h));
(h) share of other comprehensive income of associates and joint ventures
accounted for using the equity method; and
(i) total comprehensive income.
Total comprehensive income
16
…the change in equity during a period
resulting from transactions and other events,
other than those changes resulting from
transactions with owners in their capacity as
owners.
includes all components of profit or loss and
of other comprehensive income as noted
above
Other Comprehensive Income
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
17
changes in the revaluation surplus for property,
plant and equipment and intangible assets,
certain actuarial gains/losses on defined benefit
plans,
gains/losses arising on translation of financial
statements of foreign operations,
gains/losses arising from remeasuring available for
sale securities and
gains/losses on cash flow hedges.
(IASCF, IAS 1.7)
Presentation of Income Statements
Nature of Expense presentation
Revenue X
Other income
X
Changes in inventories of finished goods and work in progress
Raw materials and consumables used X
Employee benefits expense X
Depreciation and amortization expense X
Other expenses
X
Total expenses
(X)
Profit before tax
X
18
X
Presentation of Income Statements
19
Function of Expense presentation:
.
Presentation
of Income Statements
Which one?
–
–
20
Either may be issued
Survey - 55% presented the statement by function
of expense and 45% by nature of expense
Statement of Changes in Equity
1.
2.
3.
21
This statement presents the following:
total comprehensive income
for each component of equity, the effects of
retrospective application/restatement
reconciliation between the carrying amount
of each component of equity at the
beginning and end of the period.
Statement of Changes in Equity
Notes:
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
22
augment the basic statements
include information about the way they have been
prepared
provide additional descriptive and supportive
information
should be cross-referenced
accounting policies
key sources of estimation uncertainty
nature and structure of an entity’s capital and how
it is managed
Samples of and Excerpts from
Selected Statements
23
Samples of and Excerpts from
Selected Statements
24
Statement of Comprehensive Income
25
Statement of Changes in Equity
26
Looking Ahead
27
Part of MoU
Phase A complete
Phase B – in progress
Discussion paper issued in 2009
Phase B
28
consistent principles for aggregating information in
each financial statement
the totals and subtotals that should be reported in
each financial statement
whether the direct or the indirect method of
presenting operating cash flows provides more
useful information
whether components of other comprehensive
income should be reclassified to profit or loss and, if
so, the characteristics of the transactions and events
that should be reclassified and when reclassification
should be made
Phase B
(taken from Summary of tentative preliminary views (IASB and FASB))
29
Copyright © 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted
by Access Copyright is unlawful. Requests for further
information should be addressed to the Permissions
Department, John Wiley & Sons Inc., 111 River Street, Hoboken,
NJ 07030-5774, (201) 748-6011, fax (201) 748-6008, website
http://www.wiley.com/go/permissions. The purchaser may make
back-up copies for his or her own use only and not for
distribution or resale. The author and the publisher assume no
responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages caused by the
use of these programs or from the use of the information
contained herein.