Contemporary US and Canada
advertisement

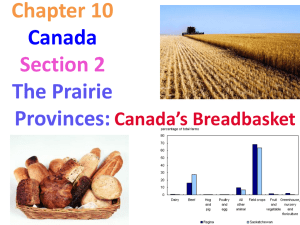
US and Canada Contemporary Issues One Superpower • Since the fall of the USSR, the US has been the only superpower in the world – Used diplomatic and military power to keep peace and further US interests US Government • Representative Democracy (Republic) – People rule through elected representatives • Three Branches – Executive • The President – Approves or vetoes laws – Legislative • Make the laws • Congress – House of Representatives: Based on population – Senate: 2 per state – Judicial • Supreme Court • 9 Justices: one Chief Justice and 8 Associate Justices • Review laws to make sure they are okeydokey Supreme Court Justices Chief Justice Name, Assoc. Justice Antonin Scalia 1986– N.J. Reagan Anthony M. Kennedy 1988– Calif. Reagan Clarence Thomas 1991– Ga. Bush Ruth Bader Ginsburg 1993– N.Y. Clinton Stephen G. Breyer 1994– Calif. Clinton N.Y. Bush 2005– John G. Roberts Place Appointed by Samuel A. Alito, Jr, 2006– N.J. Bush Sonia Sotomayor 2009– N.Y. Obama Elena Kagan 2010– N.Y. Obama Canada’s Government • Independence from GB in 1931 – Symbolic head is the Queen of England • Parliamentary Government Stephen Harper’s Awkward Family photo – Legislative and executive combined in a Parliament – Majority leader: Prime Minister (currently Stephen Harper) US Economy • World’s Largest national economy (it is 2nd if the EU is counted as one economy) – The U.S. is one of the world's wealthiest nations, with abundant natural resources, a well-developed infrastructure, and high productivity. – It has the world's sixth-highest per capita GDP – The U.S. is the world's thirdlargest producer of oil – It is the second-largest trading nation in the world behind China • Its five largest trading partners are : European Union, Canada, China, Mexico and Japan. Composition of the Economy • • most of the U.S. economy is composed of services the United States is the world's largest manufacturer, 18% of world’s manufacturing – output is greater than of Germany, France, India, and Brazil combined – Main industries: • • • petroleum, steel, automobiles, construction machinery, aerospace, agricultural machinery, telecommunications, chemicals, electronics, food processing, consumer goods, lumber, and mining. The US leads the world in airplane manufacturing Agriculture: – less than 2% of economy BUT almost ½ of world’s grain produced • Of the world's 500 largest companies, 132 are headquartered in the United States. This is twice the total of any other country Canadian Economy • 11th largest economy • 75% in service industry – Service industry tends to dominate post-industrial economies • Logging and oil very important • NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement) – Jan. 1, 1994 – Eliminated trade barriers and tariffs between Mexico, US and Canada by 2008 – NAFTA created the world's largest free trade area, which now links 450 million people producing $17 trillion worth of goods and services – One goal to boost Mexico’s economy creating better markets for the US and reduce immigration from Mexico REGIONS OF NORTH AMERICA Northeast • 5% of land; 20% of population • New England: ME, VT, MA, NH, CT, RI • Mid Atlantic: PA, NY, NJ • Characteristics: – – – – – – First area settled by Europeans “gateway” of immigration Fishing Heavily industrial and urbanized Megalopolis: “BosWash” “Rust Belt "declining traditional industries – Atlantic seaboard cities (Boston, NYC, Philly) are international trade centers Megalopolis • BosWash or the Northeast Megalopolis • especially Washington, D.C., Baltimore, Philadelphia, New York City, and Boston—are, tied to each other through the intermeshing of their suburban zone • Currently about 50 million people Midwest • 12 States: ND, SD, NE, KS, MN, IA, MO,IL, IN, OH, MI, WI • “heartland”, ⅕ of land, ¼ of population • Economy split between agriculture and industry • “Breadbasket” more food produced than any other comparable area in world – Corn, wheat, soybeans, dairy • Excellent waterways: great lakes, Ohio and Mississippi The South You are here! • • • 16 States: TX, LO, OK, KS, MS, AL, GA, SC, NC, VA, TN, KY, WV, MO, AR, FL ¼ of land of the US Mix of cultures: – Early European settlement – Descendants of enslaved persons – Cajuns (French Canadian) and Creoles (Fr, Sp, and Af.) • • • • “Sunbelt” because of climate “Bible Belt” because of conservative views lower percentages of high school graduates, lower housing values, lower household incomes, and lower cost of living than the rest of the United States (summed up as: boo, yay!, boo, yay!) Humid subtropical climate was a hindrance to industrialization until AC invented The West • • • • 13 states California most populous state West is most rapidly growing region western U.S. is the largest region, more than half the land of the US • Most geographically diverse: – – – – – Pacific Coast temperate rainforests the Rocky Mountains the Great Plains and prairie all of the desert areas located in the United States (the Mojave, Sonoran, Great Basin, and Chihuahua deserts) • “Old West” major part of American folklore REGIONS OF CANADA General Canada Stats – 75% of Canada's population resides within 100 miles of the U.S. border. – 90% of all Canadians live within 200 miles of the boundary. Atlantic Provinces • Prince Edward Island, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Newfoundland • 8% of population (2.3 million) • Rugged terrain, severe weather • Logging, fishing, mining Core provinces • Population: • • Canada's core region lies entirely within the provinces of Quebec and Ontario. The core is the historical hearth and has the overwhelming share of the country's population & economic activity. • Advantages of the Core Region – Canada’s heartland, 62% of population (18.6 million) – Accessibility resources to link it to major U.S. markets, where 88% of Canada's exports are destined – Open to U.S. immigration and investment – Close to power resources (hydroelectric and fossil fuels) • • Most settlement along Great Lakes and St. Lawrence Economic Activity: Farming (1/3 of Canada's total), manufacturing, and hydroelectricity Core Provinces • Ontario – Ottawa: National capital – Toronto: Provincial Capital – Population mostly of English descent • Quebec (French Canada) – French official language – 1960s some terrorist and propaganda movement against English institutions – 1977 Parti Québécois held power in Quebec • They had run an unsuccessful campaign to become independent in the early 70s • 1995, with the Parti Québécois back a second referendum on sovereignty took place – rejected by a slim majority (50.6 percent NO to 49.4 percent YES) – A poll in Jan of 2012 said that 43% of Quebeckers supported separation Prairie and Pacific Provinces • Prairie Provinces – – – – Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta 5 million Economy: farming, mining, oil Part of the Great Plains, 50% of agriculture in Canada – Diverse population: Eastern and Western Europeans, FrenchCanadians, Asians, Indian, etc… • Pacific Province – British Columbia (only one province in this region) – 4 million – Part of Rocky Mountains – Population centered around southwest: Vancouver (Canada’s largest port) and Victoria The Territories • Yukon, Northwest, and Nunavut • 41% of land of Canada • Not enough population to be provinces; 100,000 • Nunavut added in 1999 because of large percentage of Inuit – Nunavut means “our land” in Inuit Tundra in Nunavut Dailies: People to Know • • • • • Who is the new pope? Who is John Kerry? Who is John Roberts? Who is Stephen Harper? Who is Chuck Hagel? Dailies: • What is a Megalopolis? • What Cities make up the Northeast megalopolis? • What are two nicknames of the Midwest? • What are two nicknames of the south? • What was the goal of NAFTA in Mexico?