Chapter 4: Fundamentals of Population - Course
advertisement

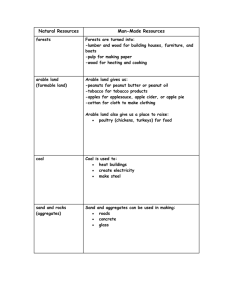
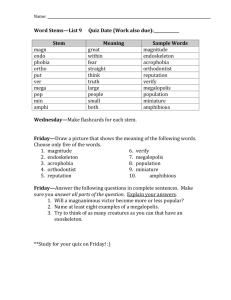
Chapter 4: Fundamentals of Population, Location, Distribution & Density Demography – Study of population. Key issues in population geography are population growth & migration. World population is growing in poorer countries by 80 million per year. Distribution of population describes location where people live, Population Density is the measure of number of people per unit area. Arithmetic population density is an average and is not a true measure. Physiological population density is the total population to area of cultivable land. There is strong correlation between high population density & areas with expanses of arable (farmable) land. Population data is unreliable!! Why – because of high costs involved and disorganized information. Population density is not a measure of global economic position or technology advances. The three largest populations are in EURASIA. The smallest of them is the most urbanized and well developed. Is there a connection of population & development? Population explosion – 20th century Population growth linear till industrial revolution Immigration is the movement of people across borders Refugees are people who are dislocated from their homeland. Humanity is unevenly distributed over land. No country has equally distributed population. Countries with advanced technology have more clustered cities Major population concentrations are in East Asia (mainly farmers), South Asia – both of which have fertile rivers and Europe which is rich in coal fields. All three areas are coastal regions. These 3 areas account for 4 billion out of 6 billion world population. There are no high density zones in North America. Megalopolis refers to urban agglomerations