File - CBA Executive Banking School - Year 1
advertisement

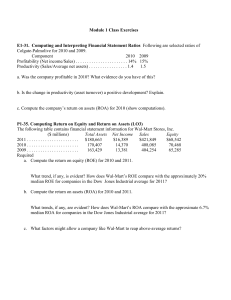
MarketSim Reports Dr. Tom Smythe Introduction We will be looking at six reports that you will use throughout the next 10 days with MarketSim All are accessed under the Results tab and are arranged by year You will use more detailed versions of some but these are the “biggies” The first three: Balance Sheet, Income Statement, and ROE Decomp, represent the bank and its performance at the bank level The second group: Customer, Distribution by Channel, and Product Financial, help you identify and measure performance of marketing strategy 2 Balance Sheet (B/S) Representation of what a bank traditionally does – Asset Transformation Raise funding (deposits, CD’s, borrowing, equity) and deploy that money in higher earning assets (securities, loans, credit cards) Some funding has no interest cost (basic checking), while others do (CD’s) The transaction services are a cost to the bank The B/S represents how we raised funds and deployed them as of a point in time In reality, the B/S changes everyday because the business keeps going 3 Balance Sheet (B/S) The B/S shows traditional business choices banks make Do we raise deposits (slower, more stable) or do we borrow (most costly, risk of not being able to refund) Do we deploy in mortgages, car loans, credit cards, or some mix Non-traditional bank business (trust, investment advisory) don’t show up on the B/S but flow directly to the Income Statement Risk is reflected in B/S choices Changes in the B/S from period to period reflect shifts in business strategy and competition Bigger changes have bigger implications for changing the risk profile AND potential changes to profits 4 Income Statement (I/S) The I/S is a report on profit or loss Internally, deposit creation and lending are profitable, allowing business areas to focus energy from a marketing strategy perspective Is the bank succeeding in its strategy from an accounting perspective Net Interest Income from Assets is the profit (loss) of lending relative to the internal cost of funds Net Interest Income from Liabilities is the profit (loss) from raising deposits at price lower than the internal margin The sum of NII(A) and NII(L)is Total Net Interest Income (TNII) Not all assets will “perform” so the bank estimates the losses as Loan Loss Provisions and they are deducted from TNII Treasury Balancing Cost (TBC) represents the cost to the bank of borrowing to meet excess loan demand or to deploy excess deposits 5 Income Statement (I/S) Bank also generates revenue from non asset transformation things like account fees, overdraft, ATM fees, trust services, etc. These are Non Interest Revenue (NIR) The Net of TNII, LLP, TBC, and NIR is Total Revenue Bank also has expenses that are related to running the business Internally we can separate these into variable, fixed, delivery, etc. External viewers of an I/S will not have this detailed information – it is proprietary and will be key to managing your business The sum of all costs and taxes are deducted from Total Revenue to get bottom line (from an accounting perspective), Net Income after taxes 6 Customer Report Representation of the market segmentation you have for your bank At Risk Customers are those that your bank has but could lose due to competitive pressures or by your strategic choices As you make decisions about marketing strategy, this will reflect those choices, as well as the responses of competitors While you may want to target Blue Collar, your ability to attract that group will also be dependent on your distribution and product choices and the choices by competitors There may be times where you choose to pare a certain customer group If you don’t intent to, this identifies those you may need to focus on because it’s more costly to acquire a new customer than keep one usually Contribution Per Customer measure the ability to generate profit from each customer All else equal we want this to be higher Achieved based on distribution and product mix, i.e. cross-selling 7 Distribution Report by Channel This report gives detailed expense information for your bank’s distribution channels for the current and previous year This allows you to determine if costs are rising are falling in total but also by distribution channel Different channels have different costs, especially fixed and variable This information is highly dependent on which customer segments you wish to target If you target retirees, you are likely to need a more robust branch network, which will, by definition have higher fixed costs All else equal, we want to lower costs but some distribution channels are more heavily populated by certain groups 8 Distribution Report by Channel As with the Customer report, this is internal to the bank, i.e. not available to outsiders Number of transactions will drive Fixed and Variable Expense per Transaction Fixed per should decline with more transactions and variable rise, although often in discreet steps The goal is to optimize (minimize) the Total Expense per Transaction As before with Customer, your actual volume of business, and therefore expenses, is dependent on customer target, products, and competition 9 Product Financial Report All of the products can be categorized into three groups: Deposits, Interest Bearing Revenues, and Non-Interest Revenues 10 Deposits Interest Bear Rev Checking (7 Types) Credit Cards CD’s Loans Savings Lines of Credit MMDA Home Equity Mortgage Each product essentially is an I/S for the category. In the case of the Deposits and Interest Bearing Revenues, it gives number of accounts and balances. These will also have Spread Revenue and MAY have Non-Interest Revenue (fees). Variable and fixed costs represent the people and space costs of doing business (operating expenses) - - Product Financial Report 11 - In the case of the Non-Interest Revenues, the same information is available; however, the will not have Spread Revenue but WILL have Non-Interest Revenue (fees). As before, variable and fixed costs represent the people and space costs of doing business (operating expenses) Non-Interest Rev Annuities Mutual Funds Insurance Investments - For each product, you see its profitability before taxes. Like the Customer and Distribution Report by Channel, the products will reflect you marketing strategy AND competition. E.G. if you choose Millennials (customer), they are likely to be most heavily concentrated in online and mobile (distribution) with an inclination to simple checking, savings, car loan, and credit cards (products) - - 11 ROE Decomp/Key Ratios Business choices (B/S) lead to dollar performance (I/S and others) By themselves, dollar measures aren’t good metrics, especially when comparing to benchmarks/other banks. Scale/size matters Ratios take scale out of the mix Most ratios scale (have a denominator) of assets or equity ROE = Net Income/Equity ROA = Net Income/Assets ROA measures a bank’s ability to generate profits from its asset base ROE measures a bank’s return to shareholders in accounting terms Leverage (Assets/Equity) measures the amount a bank has “borrowed” to fund its business ROE is a composite of profitability and leverage More leverage means more financial risk ROE = Leverage x ROA 12 ROE Decomp/Key Ratios The Loan to Deposit Ratio is a gauge of bank liquidity The higher the value, the more borrowed money used The choice of a higher or lower value is a balancing act for management Efficiency Ratio [Total Costs/(Net Int Inc + Non-Int Rev) measures the bank’s cost structure In relative terms, a lower number is better, but profits must be sustained Under investing could lead to a low ratio now but may lead to lower future profits Loan Loss Provision/Assets partially measures credit risk In MarketSim, it is determined by the simulation (bank level) In practice, managers have some discretion Lower numbers mean higher profitability, but possible at a future cost Products per customer is self-explanatory It is a measure of market penetration It is less costly to cross-sell than get new customers generally 13 14 EVALUATIONS Click here to fill out your evaluation for this class: https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/ZH93C8V We value your feedback!