Types of Government
advertisement

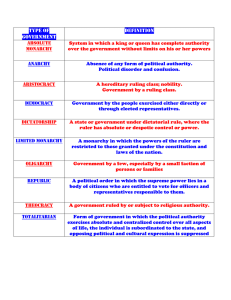
Types of Government Objective Students will demonstrate an understanding of the main forms of government by obtaining proficiency on a quiz Agenda Bellringer Review Questions Types of Government notes Independent work: Organizer p. 12 Feudalism DECENTRALIZED political system based on a RIGID SOCIAL HIERARCHY due to a need for PROTECTION. This form of government is associated with MANORIALISM which is the ECONOMIC SYSTEM based on SELF SUFFICIENCY Absolute Monarchy Form of government in which there is only ONE ruler (King, later on could be Queen) and this ruler does not seek approval from any one or any legislative body to do whatever they want. Rule by DIVINE RIGHT. Examples: England (Charles I, James I), Russia (Ivan IV), Spain (Ferdinand) Limited Monarchy Form of government in which there is ONE ruler (King, later on could be Queen) who MUST seek permission to raise taxes, wage war, etc… from the people they govern through a legislative body (ie: parliament) Examples: England (William and Mary) Totalitarianism Form of government that controls all aspects of citizens’ lives under the authority of one single charismatic leader. Characterized by extreme censorship and no political discourse (speech/parties). Economic, social, political, and cultural control. Examples: Joseph Stalin (Russia), Benito Mussolini (Italy), Adolf Hitler (Germany), Mao Zedong (China) Communism Originally an economic system, communism has become a form of government that advocates class warfare which leads to a society in which all property is publicly owned and each person works and is paid according to their abilities and needs. Examples: China, Cuba, Soviet Union Democracy (true) Form of government in which the entire population of a country decides on all actions the country takes (majority rule) as determined through voting Examples: Ancient Greece (Pericles) Republic Form of government in which the whole population of a country elects representatives (majority rule/voting) that make decisions for the whole country. Examples: USA, France, Ancient Rome