Mkt 340 Class6-Media - Cal State LA
advertisement

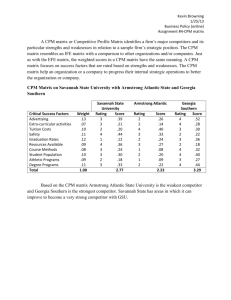
Advertising Budgeting, Media, and Media Planning Mkt 340 Prof. Bill White The Advertising Budget Setting the Budget Percentage of Sales Payout Plan Competitive Budgeting The Task or Objective Method What’s the objective? What type and how much media needed? Can we afford it? Arbitrary Administering and Protecting the Budget Media Defined The vehicles that carry the ads to the target market. Which is most important? Picking the correct media or having great creative? What are the types of media? Examples of Nontraditional Media ABC Inflight ActMedia Aislevision Aladdin’s Castle Beyond the Wall Channel One CineSpot CNN Airport Network Cover Concepts Book Covers Go Cards Instant Coupon Machine Military MediaBoards Miller Airship Resort Sports Network Roadmark Fleet Advertising Screenvision U Airplanes Supermarkets Supermarkets Malls College posters High schools Cinemas Airports High schools Health clubs, restaurants Supermarkets Military bases Blimps Resorts Trucks Cinemas College newspapers Sample of a Syndicated Media List MAGAZINES RADIO NETWORK TV CABLE NETWORKS Allure Adult Contemporary American Gladiators Arts & Entertainment American Baby All News America’s Funniest.. American Movie Classics American Health All Sports America’s Most… Black Entertainment TV American Hunter AOR/Progressive Rock Baywatch The Box American Legion Black Beverly Hills 90210 Bravo * * * * * * * * Working Woman Religious/Gospel Washington Week… TV Food Network WWF Magazine Soft Contemporary Wild America USA Network Yachting Spanish Wings VH-1 Yankee Urban Contemporary WKRP in Cincinnati The Weather Channel YM Variety The X-Files WGN-TV Source: Mediamark Research, Inc., Spring 1995. Organization of the Media Function Media planner Media buyer Media researcher Important Trends in Media Convergence Interactivity Creativity Optimization Key Media Terms Media plan: document that establishes how media will be used to disseminate an advertiser’s message, including objectives and strategy. Media objective: statement in media plan that explains the goals of the plan; usually states how many of the target will be exposed to advertising messages in a given time period, and how often. Media strategy: statement in media plan that outlines how objectives will be accomplished; shows where and when advertising messages will appear, and at what cost. Media Planning Media Planning = Selection + Scheduling Factors Influencing Media Planning Decisions Target Market Profile Looking at Brand/Product Dynamics The Creative Execution Budget Considerations and Media Deals The Competitive Situation Availability and Timing Considerations Cost Efficiency (CPM = Cost per thousand (CPM): cost of reaching 1,000 members of target audience with media vehicle(s) or plan.) CPM Formula and Example CPM = Cost X 1,000 Audience Which is more cost efficient on a CPM basis? A-- :30 TV Commercial in “Friends” $250,000 X 1,000 = $12.50 CPM = 20,000,000 B-- :30 TV Commercial in “Monday Night Football” $300,000 CPM = X 1,000 = $10.00 30,000,000 Media Selection Media are evaluated based on selectivity. There are two types of selectivity: Class Selectivity is the ability of a medium to reach the target market without waste. Geographic Selectivity is the ability of a medium to cover a particular geographic area without spillover. How would you rate the different major media in terms of class and geographic selectivity? Media Scheduling Reach (% of target audience with opportunity for exposure to media vehicle(s) or media plan in a given time frame) + Frequency (average number of times target is likely to be exposed to the ad in a given time frame) 100% The Difference between Reach and Frequency Media Scheduling (continued) Reach + Frequency + Continuity (how long the campaign runs— continuous vs. flighting vs. pulsation) 100% Reach, Frequency, and Continuity Relationships with a Fixed Budget Media Scheduling (continued) Reach + Frequency + Continuity + Dominance/Impact (the attention-getting ability of the media vehicle(s) selected to run the ad) 100% Evaluating the Media: Key Terms Rating point: the % of a given population group that uses a specified media vehicle. Share: Households/persons using television (HUT, PUT): % of homes or people watching TV at a given time. Gross rating point (GRP): total number of ratings for different media vehicles. Gross impression: translation of GRPs into people; number of audience exposures x number of times they will see or hear vehicles. Cost per rating point (CPP): cost of buying one rating point in a given media vehicle or type. Audience: number or % of homes or persons using a media vehicle. Coverage: Same as reach – the % of homes or persons receiving broadcast signal within specified area, or receiving specific magazine or newspaper. Evaluating the Media: Key Terms, Continued Circulation: Total number of copies of a publication sold through various forms of distribution. Readers per copy: average number of people who read each issue of publication. Types of Media Plans Geographic Local, spot, key market Regional National International Selective Combination Sample Flowchart of a Media Plan Evaluating the Media Plan Follow up—getting make-goods, tearsheets. Measuring the impact: Test consumer awareness of campaign before, during, and after. Sales data. Compare actual reach/frequency figures to proposed estimates. Syndicated Media Research Services Nielson, Arbitron, Simmons, Audit Bureau of Circulation