Media Strategy & Planning
advertisement

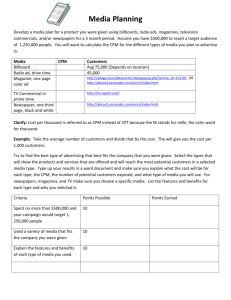
Media Strategy & Planning with Duane Weaver MEDIA PLANNING - Changes • Agency Compensation (15% stat…now negotiated individually) • More Media (e.g. internet) • Media outlets are large and powerful now • Thinner margins for Media Agencies • ROI more important • Globalization • Consumers get Free Content • E-Commerce • Hyper-Clutter • Ethnic Media (on the increase) Media Planning Process Media Plan – specifies the media for messages to target audience Media Class – broad category of media (tv, radio, etc.) Media Vehicle – that particular class’s option (e.g. Nanaimo Daily News for newspaper) Media Mix – the effective blend of media used to obtain best GRP (reach and frequency). Reach and Frequency • Reach – number of people or households in a target audience that are exposed to the vehicle. • Frequency – average number of times an individual or household within the target audience is exposed to the vehicle within a given time period. • GRP = Gross Rating Point = reach X frequency • Effective Frequency – number of times a target audience needs to be exposed before the advertiser’s objectives are reached. Reach and Frequency • Continuity – pattern of placement of advertisements in the media schedule: – Continuous – Flighting – Pulsing MEASURING MEDIA EFFICIENCY • CPM (Cost Per Thousand) – dollar cost of reaching 1,000 • CPM-TM (CPM per Target Market) • CPRP (Cost per Rating Point) • Share of Voice = one brand’s ad expenditures divided by total product category expenditures in a medium MEDIA TYPES - Newspapers • Advantages – Geographic Selectivity – Timeliness – Creative Opp’s (lots of info at low cost) – Credibility – Audience Interest – Cost (low cost) • Disadvantages – Limited Segmentation – Creative constraints (low quality print medium) – Cluttered – Short Life Media Types - Magazines • Advantages – Audience Selectivity – Audience Interest – Creative Opportunities (better quality printing) – Long Life (saved issue by issue by subscribers) • Disadvantages – – – – Limited reach and frequency Clutter Long lead times Cost (more expensive than newspaper) Media Types – TV • TV advantages – – Creative opp’s – Coverage, Reach, Repetition – Cost per contact (for broad masses) – Audience Selectivity • TV disadvantages – – – – – Fleeting Message High Absolute cost Poor Geographic selectivity Poor Audience attitude and attentiveness – Clutter Types of Advertising - Radio • Advantages – Cost (tends to be most cost effective per target audience) – Reach and Frequency – widest exposure (portable medium) – Target Audience Selectivity – geographic, demographic and psychographic • Disadvantages – – – – Poor audience attentiveness Creative limitations Fragmented audiences Chaotic buying procedures DISCUSSION