Whitworth_Amenorrhea_3.1.10
advertisement

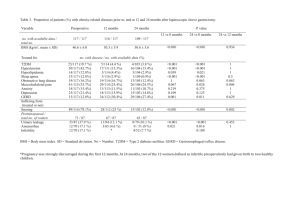
Dr. Whitworth – Amenorrhea – 3.1.10 Definitions Amenorrhea Primary amenorrhea Secondary amenorrhea: Oligomenorrhea 1 absence of menstruation – Sx not Dx no spontaneous uterine bleeding by age 14 in the absence of secondary sexual characteristics OR by age 16 with otherwise normal development the absence of menstrual bleeding for six months in a woman with prior regular menses or for 12 months in a woman with previous oligomenorrhea Decreased frequency of menstruation more than 40 days but less than 6 months Normal Menstrual Cycle -The normal cycle is an integration of the hypothalamus, pituitary, ovary and the responsiveness of the uterus to these hormones -For the cycle to proceed normally a woman must have an intact uterus with responsive endometrium, a patent outflow tract, and a functioning endocrine system and feedback loops, (functioning ovaries and pituitary); disruption at any level can cause amenorrhea -GnRH from the hypothalamus acts on the pituitary to secrete FSH/LH -FSH acts on the ovary to stimulate follicular thecal cells -These cells produce androgens which are converted to estrogens-decreasing FSH -One follicle is maintained,up regulation of FSH receptors -LH levels inc-positive feedback of estradiol—causing ovulation in 24-48 hrs.-Granulosa cells of the follicle increase progesterone production -Estrogen on the endometrium--increased thickness and vascularity -Progesterone-increased glandular secretion and tortuosity Causes of Amenorrhea -Physiologic -Primary Amenorrhea: Pregnancy and Constitutional delay of puberty -Secondary Amenorrhea: Pregnancy, Lactation, Menopause Causes: Compartment Definition Differnetial Dx. Compartment One disorder of uterus or outflow tract -Imperforate hymen -Ashermans Syndrome--destruction of endometrium. (after D/C) -Mullerian Anomolies -Mullerian Agenesis -Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser Syndrome -Testicular Feminization (Androgen Insensitivity) Compartment Two disorders of ovary -Turners Syndrome 46XO -Mosaicism (blend of 46 XO & 46 XX) -Gonadal agenesis/dysgenesis -Resistant ovary syndrome (rare) -Premature (before age 40) ovarian failure -Radiation/chemotherapy (can have norm cycles later & be fertile) -n17 a hydroxylase defeciency Compartment Three disorder of anterior pituitary -Pituitary Adenoma (hyperprolactinemia) -Empty Sella Syndrome -Sheehans Syndrome – acute necrosis of ant pit post trauma -Hypopituitarism -Hypothyroid – high TSH acts as FSH & LH – fools the pit -Infiltrative (Sarcoidosis/hemochromostosis) -(medications) neg feedback on ant pit Compartment Four disorder of the CNS/hypothalamus -Tumors -Craniopharyngioma, harmartoma nHypothalamic amenorrhea- decrease in pulsitile GnRH secretion -Eating disorder, weight loss (or gain), excessive exercise -Kallmanns Syndrome -disease-JRA,syphillis, TB -psychosocial stress -Anovulation Evaluation of Amenorrhea Obtain a History -Menstrual history: Age of onset of menses, previous pattern -Reproductive history: Use of BCP’s, previous ob/gyn procedures, development,pregnancy -General medical history: Endocrine/metobolic disorders, medications, illnesses -Family history- sister/mother -Social history is patient a med student?,marathon runner? Nutritional or emotional stressors? -Physical Exam -In a complete physical look for normal anatomy and development 2 Dr. Whitworth – Amenorrhea – 3.1.10 -Look for signs of androgen excess, estrogen deficiency or estrogen excess -Labs: goal is to identify a problem in the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis -GET A PRGENANCY TEST! If negative use the below flow chart. Treatment: Need clear diagnosis -Hypothyroid-- thyroid replacement -Ovarian Failure-- estrogen replacement -Pituitary Tumor--medication or surgery -Hypothalamic --change lifestyle, cyclical hormones Consequences of Amenorrhea: -Psychological: Dx of genetic abnormality, - Altered self image, Impaired fertility -Stress the normalcy of it & find out if something abnorm is going on -Physiological -Decreased Estrogen -Vasomotor symptoms -Vaginal dryness -Decreased libido -Osteoporosis -? Increase cardiac risk factors Questions: 1. What is the difference between primary and secondary amenorrhea? 2. What are the causes of primary and secondary amenorrhea? 3. Identify which compartment the following disorders belong to: a. Disorder of ovary b. Disorder of CNS/hypothalamus c. Disorder of uterus out flow d. Disorder of anterior pituitary Answers: 1. Definition no spontaneous uterine bleeding by age 14 in the absence of secondary sexual characteristics OR by age 16 with otherwise normal development Secondary the absence of menstrual bleeding for six months in a amenorrhea: woman with prior regular menses or for 12 months in a woman with previous oligomenorrhea 3. A = II, B = IV, C = I, D = III Primary amenorrhea 2. Cause Pregnancy and Constitutional delay of puberty Pregnancy, Lactation, Menopause