Answers for the review sheet
advertisement

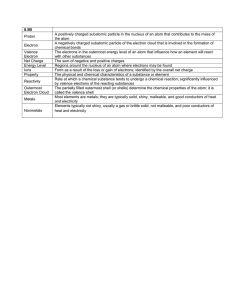
Name: ____________________________________ Date ______________________ Period _____ ATOM Review Sheet Complete this review sheet on your iPad. You may print it out if you are not able to take your iPad home. Try to fill it out without any resources except an unlabeled periodic table. That way you can figure out what you need to study. 1. Fill in the Following Table Subatomic Particle Proton Neutrons Electron Location Nucleus Nucleus Orbitals outside the nucleus Charge Positive neutral negative Mass (amu) 1 amu 1 amu 1/2000 amu 2. Write the main contribution to the atomic model of each of the people below Democritus John Dalton JJ Thomson Ernest Rutherford Niels Bohr Erwin Schrodinger First came up with the idea of an atom and named it “atomos” Greek for indivisible Imagined the atom like a billiard ball: a solid discreet neutral particle of matter Discovered the electron and came up with the plum pudding model. Negative particles in positive substance Discovered the nucleus as a positive dense part of the atom Electron Shells outside the nucleus that contained certain numbers of electrons at different distances from the nucleus Came up with the electron cloud model of the atom where one cant determine the location of an electron, but can know a general space where they are likely to be found 3. Record the missing information below: Assume neutral atoms Name of Element Chlorine Potassium Helium Oxygen Carbon Tin Aluminum Symbol Cl K He O C Sn Al Protons 17 19 2 8 6 50 13 Neutrons 18 20 2 8 6 69 14 Electrons 17 19 2 8 6 50 13 4. Name of Group Halogens Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth metals Noble Gases Location on the periodic table Second to last column on the right Column all the way to the left Second column in on the left Column farthest to the right 5. Type of Bond Main Properties of the family Reactive, have 7 valence electrons, can form covalent and ionic bonds, non-metals. All three phases Metals very reactive good conductors of electricity and heat, silver Metals a little less reactive than Alkali Metals, 2 valence electrons, form ionic bonds Un-reactive, non metals, gases, complete outer shell of electrons What happens to electrons in this type of bond? Ionic A non metal and a metal Transferred, gaines/lost Covalent 2 non metals Shared 6. Write your own definition for the following words: Valence Electron Ion Isotope Period (per table) Family (per Table) Atom Nucleus Atomic Number Atomic Mass Subatomic particle Forms between? Electrons in the outer most energy level, responsible for bonding, reactivity A charged atom that has gained or lost electrons A version of an element that has a different number of neutrons Horizontal Rows, have same number of energy levels as the period/row number Vertical Columns: elements in families have the same number of valence electrons The smallest piece of an element that still has all the properties of that element The center of an atom that contains the protons and neutrons. Where all the mass of the atom is found The smaller number for an element on the periodic table that represents the number of protons as well as the number of electrons in a neutral atom The mass of one atom of an element: made up of the neutrons and protons The parts that make up atoms: Protons neutrons and electrons 7. All elements in a period have the same number of energy levels 8. All elements in a family have the same number of valence electrons 9. In a Bohr Diagram the first energy level can hold 2 electrons, the second can hold 8 electrons and the third can hold 18 electrons 10. Bohr’s model is useful for calculating the number of valence electrons. 11. Lewis Dot structures consist of the Symbol of an element surrounded by dots representing the valence electrons (2 words). 12. An atom that loses an electron will become more positive 13. An atom that gains an electron becomes more negative Chemical Bonds: Ionic bonds form between a metal and a non-metal. In an ionic bond electrons are transferred from one atom to another. Both atoms become oppositely charged ions that are attracted to each other. Covalent Bonds form between two non-metals. In a covalent bond electrons are shared so that each atom has a complete outer energy level usually consisting of 8 electrons like the nearest noble gas.