ART: The New, The Old and The
Ugly
Our Current ARVS
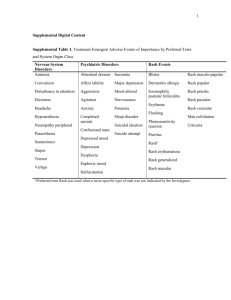
The
Nucleoside/
Nucleotide
Reverse
Transcriptase
Inhibitors
(NRTIs/ NtRTIs)
Abacavir
Emtricitabine
Lamivudine
Stavudine
Tenofovir
Zidovudine
Fixed-drug
combinations
Combivir, Kivexa,
Truvada
The Non-Nucleoside
Reverse Transcriptase
Inhibitors (NNRTIs
)
The
Protease
Inhibitors
(PIs)
Efavirenz
Nevirapine
Triomune, Atripla,
Triplavar
Atazanavir
Darunavir
Lopinavir
Ritonavir
ARVS REGISTSERED IN SOUTH AFRICA
The
Nucleoside/
Nucleotide
Reverse
Transcriptase
Inhibitors
(NRTIs/ NtRTIs)
Abacavir
Didanosine
Emtricitabine
Lamivudine
Stavudine
Tenofovir
Zidovudine
Fixed-drug
combinations
Combivir, Kivexa,
Truvada
The Non-Nucleoside
Reverse Transcriptase
Inhibitors (NNRTIs)
Efavirenz
Nevirapine
Etravirine
Rilpivirine
Triomune, Atripla,
Tripalvar, Complera
The Integrase
Inhibitors (ISTIs)
Raltegravir
The
Protease
Inhibitors
(PIs)
Amprenavir
Atazanavir
Darunavir
Indinavir
Lopinavir
Ritonavir
Saquinavir
THE ANTIRETROVIRAL DRUGS
The
Nucleoside/
Nucleotide
Reverse
Transcriptase
Inhibitors
(NRTIs/ NtRTIs)
Abacavir
Didanosine
Emtricitabine
Lamivudine
Stavudine
Tenofovir
Zidovudine
Fixed-drug
combinations
Combivir, Kivexa,
Truvada
The Non-Nucleoside
Reverse Transcriptase
Inhibitors (NNRTIs
)
The
Protease
Inhibitors
(PIs)
Etravirine
Rilpivirine
Amprenavir
Atazanavir
Darunavir
Indinavir
Lopinavir
Ritonavir
Saquinavir
Tipranavir
Efavirenz
Nevirapine
Triomune, Atripla,
Complera
The Integrase
Inhibitors (ISTIs)
Raltegravir
Elvitegravir
Dolutegravir
The QUAD
Drugs to be covered
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Etravirine
Rilpivirine
Raltegravir
Elvitegravir
Dolutegravir
Darunavir/r
Maraviroc
Etravirine
• Etravirine (ETV) is a second generation NNRTI that
• ETV works like other NNRTIs by binding to the
catalytic site of the RT enzyme
• Active against HIV with K103N and Y181C
• This potency appears to be related to etravirine's
flexibility as a molecule
• Dosage 200mg bd
Etravirine (2)
• Pivotal study DUET 1 and 2
• OBR +darunavir/r +etravirine/placebo
• After 24 weeks, pooled analysis - etravirine study
arm achieved an undetectable viral load (58.9% vs
41.1%; p<0.0001).
• There was also a significantly greater increase in CD4
cell count from baseline in the etravirine arm (86 vs
67 cells/mm3; p<0.006).
Summary of Study Design
DUET 1 and 2
Week 24
HIV-infected patients with
virologic failure on current
HAART regimen,
history of ≥ 1 NNRTI RAM,
≥ 3 primary PI mutations, and
HIV-1 RNA > 5000 copies/mL
(DUET-1: N = 612;
DUET-2: N = 591)
Week 48
Etravirine 200 mg BID +
Darunavir/Ritonavir-containing OBR*
(DUET-1: n = 304;
DUET-2: n = 295)
Placebo +
Darunavir/Ritonavir-containing OBR*
(DUET-1: n = 308;
DUET-2: n = 296)
*Investigator-selected OBR included darunavir/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily + ≥ 2 NRTIs ± enfuvirtide.
1. Madruga JV, et al. Lancet. 2007;370:29-38.
2. Lazzarin A, et al. Lancet. 2007;370:39-48.
Main Findings
• Significantly more patients achieved HIV-1 RNA < 50
copies/mL with etravirine vs placebo
• HIV-1 RNA reduction from baseline greater in
etravirine arms than placebo arms
• Etravirine treatment resulted in greater CD4+ cell
count increases from baseline compared with
placebo (statistical significance reached in DUET-1
only)
Madruga JV, et al. Lancet. 2007;370:29-38.
Lazzarin A, et al. Lancet. 2007;370:39-48.
• 13 RT mutations at eight positions were found
to reduce ETV activity
– V90I, A98G, L100I, K101E/P, V106I, V179D/F,
Y181C/I/V and G190A/S
Etravirine
Etravirine
FDC
Single day dosage
Low side effect
profile
High barrier to
resistance
TB friendly
Pregnancy friendly
NO
NO
YES
?
NO
UNK
Rilpivirine
Rilpivirine
• Novel NNRTI
• Single day dosage
• Co-formulated with TDF and FTC as Complera
ECHO, THRIVE: Rilpivirine vs EFV in
Treatment-Naive Patients
•
Randomized, double-blind phase III trials
Stratification by BL
HIV-1 RNA < 100,000
vs ≥ 100,000 copies/mL,
NRTI use*
ECHO
(N = 690)
Treatment-naive,
HIV-1 RNA ≥ 5000 copies/mL
no NNRTI RAMs,
susceptible to NRTIs
THRIVE
(N = 678)
Wk 48
primary analysis
Rilpivirine 25 mg QD
+ TDF/FTC 300/200 mg QD
(n = 346)
EFV 600 mg QD
+ TDF/FTC 300/200 mg QD
(n = 344)
Rilpivirine 25 mg QD
+ 2 NRTIs†
(n = 340)
EFV 600 mg QD
+ 2 NRTIs†
(n = 338)
*THRIVE only. †Selected by investigator from ABC/3TC, TDF/FTC, ZDV/3TC.
Cohen C, et al. AIDS 2010. Abstract THLBB206.
Wk 96
final analysis
ECHO, THRIVE: Rilpivirine vs EFV in
Treatment-Naive Patients
Rilpivirine
EFV
100
84.3
82.3
Patients (%)
80
85.6
82.9
82.8
81.7
Patients (%)
HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL (ITT-TLOVR) at Wk 48
HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL at Wk 48 by BL VL
6.6 (1.6-11.5)
100
91
90
90
84
83
84
80
60
60
40
20
0
40
100
0
n = 686
682
Pooled
346
344
ECHO
340
338
THRIVE
Patients (%)
20
*P < .0001 for noninferiority at -12% margin.
80
162/ 136/
181 163
170/ 140/
187 167
Pooled
ECHO
THRIVE
≤100,000 copies/mL
-3.6 (-9.8 to +2.5)
77
81
76
82
79
80
60
40
20
0
Cohen C, et al. AIDS 2010. Abstract THLBB206. Graphics used
with permission.
332/ 276/
368 330
246/ 285/
318 352
Pooled
125/ 149/
165 181
121/ 136/
153 171
THRIVE
ECHO
> 100,000 copies/mL
ECHO, THRIVE: Treatment Failure,
Resistance, and Adverse Events
Patients (%)
Treatment Failure in ECHO and THRIVE
15
Rilpivirine
12
9
EFV
9.0
6.7
3
0
Wk 48 Outcome,
%
4.8
6
686 682
n = 346
AE
Rilpivirine
(n = 686)
Efavirenz
(n = 682)
VF with resistance data, n
62
28
No NNRTI or NRTI RAMs,%
29
43
1 Emergent NNRTI RAM,%
63
54
E138K
K103N
68
32
M184I
M184V
Most frequent NNRTI RAM
1 Emergent NRTI RAMs, %
Most frequent NRTI RAM
Efavirenz
(n = 682)
P Value
3
8
.0005
Most Common AEs of Interest, %
Resistance at Virologic Failure
Wk 48 Outcome
Rilpivirine
(n = 686)
DC for AE
2.0
686 682
VF
Adverse Events and Discontinuation
Any neurologic AE
17
38
< .0001
Any psychiatric AE
15
23
.0002
Any rash
3
14
< .0001
Cohen C, et al. AIDS 2010. Abstract THLBB206. Table used with permission.
Rilpivirine
FDC
Single day dosage
Low side effect
profile
High barrier to
resistance
TB friendly
Pregnancy friendly
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
UNK
Raltegravir
• Novel mode of action
• Acts on intergrase as an inhibitor
• 400mg bd
HIV Replication Cycle
and Drug Targets
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
Entry inhibitors
Reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Protease inhibitors
3′-processing inhibitors
Strand transfer inhibitors
Pommier Y, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:236-248.
BENCHMRK-1 & -2: Patients With
HIV-1 RNA < 50 c/mL at Week 48
RAL + OBR
BENCHMRK-1[1]
Placebo + OBR
100
62%*
80
65%*
60
40
20
33%
31%
0
Patients (%)
100
Patients (%)
BENCHMRK-2[2]
80
62%*
60%*
36%
34%
60
40
20
0
0 24
8 12 16
n = 232 231 231 230 229
n = 118 118 118 118 117
24
Weeks
32
40
48
0 24
8
12 16
232
118
229
118
230
118
231
118
230 228 227 230 229
119 119 118 119 119
24
Weeks
32
40
48
229
119
224
119
228
119
228
119
*P < .001 for RAL vs placebo, derived from a logistic regression model adjusted for baseline HIV-1
RNA level (log10), first ENF use in OBR, first DRV use in OBR, active PI in OBR.
1. Cooper DA, et al. CROI 2008. Abstract 788. 2. Steigbigel R, et al. CROI 2008.
Abstract 789. Adapted with permission of Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, New
Jersey, USA, Copyright © 2008 Merck & Co., Inc. All Rights Reserved.
•
•
STARTMRK: Efavirenz vs Raltegravir at
156 Wks in Antiretroviral-Naive
Patients
Phase III trial of EFV vs RAL, both with
TDF/FTC in tx-naive patients
At Wk 156, RAL noninferior to EFV (ITT, NC
= F analysis)
HIV-1 RNA < 50 c/mL by
Prespecified BL Characteristic*
Subgroup, n/N (%)
RAL
EFV
172/194 (89)
40/43 (93)
159/188 (85)
33/39 (85)
18/23 (78)
83/94 (88)
50/54 (93)
17/22 (77)
82/90 (91)
42/55 (76)
VL ≤ 100K
VL > 100K
99/105 (94)
113/132 (86)
93/111 (84)
99/116 (85)
CD4 ≤ 50
CD4 > 50 - ≤ 200
CD4 > 200
16/23 (70)
80/89 (90)
116/125 (93)
24/28 (86)
68/84 (81)
100/115 (87)
281
282
HBV ± HCV
No coinfection
11/12 (92)
201/225 (89)
11/13 (85)
181/214 (85)
CD4+ count : +332 (RAL) vs +295 (EFV)
Age ≤ median
Age > median
109/124 (88)
103/113 (91)
108/131 (82)
84/96 (88)
HIV-1 RNA < 50 c/mL (%)
Male
Female
100
75
80
82
RAL
EFV
79
60
68
40
20
∆ (95% CI) = +7.3 (-0.2 to +14.7)
Noninferiority P < .001
0
0 16 32 48 60 72 84 96 108 120 132 144 156
Patients at Risk, n
RAL
281
278
EFV
282
280
81
86
Wks
281
282
280
281
281
279
279
281
Lazzarin A, et al. ICAAC 2011. Abstract H2-790.
Black
White
Latino
*Study not powered for statistical significance for these
comparisons.
REALMRK: 48-Wk Efficacy of
Raltegravir BID in Women, Blacks
•
•
•
•
Multicenter, multinational, open-label, single-arm study to determine efficacy of RAL 400 mg BID
(+ investigator-selected ARVs) in women, blacks—populations underrepresented in clinical trials
Enrollment goals: 25% women (actual 47%), 50% black (actual 74%)
No difference in PK parameters by race or sex; no new RAL safety signals noted
Retention 84% throughout study; bolstered by strict selection criteria and retention initiatives
Male
Female
Nonblack
Black
HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL at Wk
48 (%)
Naive
100
80
Previously Treated
Failure
85.7
Intolerant
100
80.5
78.6
71.4
71.4
66.0 61.4
63.8 64.0
33/50 27/44
44/69 16/25
71.8
69.4
60
40
20
10/14
6/7
11/14
5/7
0
Squires K, et al. ICAAC 2011. Abstract H2-789.
33/41 28/39
43/62 18/18
ANRS REFLATE: EFV- vs RAL-Based ART
in HIV/TB-Coinfected Pts
• Multicenter, randomized, open-label phase II trial
– Primary endpoint: HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL at Wk 24
Wk 24
Primary endpoint
Wk 48
Raltegravir 400 mg BID +
Tenofovir + Lamivudine
(n = 51)
Antiretroviral-naive pts
initiating rifampincontaining therapy* for
TB coinfection
(N = 154)
Raltegravir 800 mg BID +
Tenofovir + Lamivudine
(n = 51)
Raltegravir 400 mg BID +
Tenofovir + Lamivudine
Efavirenz +
Tenofovir + Lamivudine
(n = 52)
*Rifampin-containing therapy initiated before ART and consisted of rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and
ethambutol for 2 mos, followed by rifampin and isoniazid for 4 mos.
Grinsztejn B, et al. AIDS 2012. Abstract THLBB01.
REFLATE: Virologic Suppression at Wk
24 by ART Regimen
Pts with VL < 50 c/mL (%)
100
RAL 400 mg
RAL 800 mg
EFV
80
78
76
67
60
ITT; M = F, D/C = F
40
20
0
0
2
4
8
Virologic Failure at
Wk 24
RAL 400
(n = 51)
RAL 800
(n = 51)
EFV
(n = 51)
VL > 50 c/mL, n (%)
12 (24)
4 (8)
15 (29)
12
16
20
24
Wks
Grinsztejn B, et al. AIDS 2012. Abstract THLBB01. Graphic reproduced with permission.
Raltegravir
FDC
Single day dosage
Low side effect
profile
High barrier to
resistance
TB friendly
Pregnancy friendly
NO
NO
YES
NO
MAYBE
UNK
Elvitegravir
• Intergrase inhibitors.
• Requires boosting
– ritonavir
– Cobicistat
• Co-formulated with a booster, TDF and FTC
• QUAD-Stribild
Cobicistat: A New Boosting Agent
• Small molecule with no HIV activity
– No concern of drug resistance in pts with suboptimal virologic response
• Similar from BL in fasting TC and TGs compared with RTV when boosting
same agent[1]
• Inhibitor of CYP3A4; many drug–drug interactions[2,3]
• Modest, rapid increase in serum Cr due to inhibition of tubular secretion[3]
– Not associated with any change in actual GFR
– Other drugs (including ARVs) have similar effect[4,5]
• Availability of cobicistat has allowed for development of new
coformulated agents and regimens
1. Gallant JE, et al. J Infect Dis. 2013;208:32-39. 2. DHHS Guidelines February 2013.
3. TDF/FTC/EVG/COBI [package insert]. 4. RPV [package insert]. 5. DTG [package insert].
Renal Monitoring With Cobicistat
Change From BL in
Serum Cr
(mg/dL; IQR)
At BL,*
Estimated CrCl
Urine glucose
Urine protein
0.20
0.15
0.10
0.05
0
-0.05
-0.10
Wk 4—new baseline against which further changes should be measured
BL 2 4
8
12
16
24
Wks
32
40
*Serum phosphorus should be measured in patients at risk for renal impairment
9. TDF/FTC/EVG/COBI [package insert]. 10. DHHS Guidelines February 2013.
48
Renal Monitoring With Cobicistat
Serum Cr*
Change From BL in
Serum Cr
(mg/dL; IQR)
At BL,*
Estimated CrCl
Urine glucose
Urine protein
0.20
0.15
0.10
0.05
0
-0.05
-0.10
Serum Cr*
Serum Cr*
Serum Cr*
UA
UA
Wk 4—new baseline against which further changes should be measured
BL 2 4
8
12
16
24
Wks
32
40
48
*Serum phosphorus should be measured in patients at risk for renal impairment
•
•
•
Coformulated drugs containing COBI should not be initiated in pts with estimated CrCl < 70 mL/min
– Studies ongoing in pts with CrCl < 70
Interpretation of changes in renal function may be problematic when using coformulations of COBI and TDF
TDF/FTC/EVG/COBI should not be used with other nephrotoxic drugs
12. TDF/FTC/EVG/COBI [package insert]. 13. DHHS Guidelines February 2013.
Key Drug–Drug Interactions With COBI
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Antacids
Benzodiazepines
Beta-blockers
Calcium channel blockers
Erectile dysfunction drugs
Inhaled/injectable corticosteroids
MVC
OCPs (norgestimate)
Rifampin
Statins
14. DHHS Adult Guidelines. February 2013
Cobicistat—Status in EU and US
• In July 2013, EMEA approved cobicistat as a PK
enhancer of atazanavir 300 mg once daily or
darunavir 800 mg once daily as part of a
complete ART regimen in adults
• In US, currently approved only as part of
coformulated single-tablet regimen
TDF/FTC/EVG/COBI
– Approval as single agent pending
15. EMA.europa.eu. Assessment report on cobicistat. 16. FDA.gov. Approval of TDF/FTC/EVG/COBI.
Elvitegravir/Cobicistat vs EFV or
ATV/RTV + TDF/FTC in Treatment-Naive
Patients
•
•
Randomized, double-blind, active-controlled phase III studies
Primary endpoint: HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL at Wk 48
EVG/COBI/TDF/FTC QD
(n = 348)
Study 102[17]
(N = 700)
Treatment naive
HIV-1 RNA ≥ 5000 copies/mL
Any CD4+ cell count
Susceptible to TDF, FTC, and EFV, or ATV
eGFR ≥ 70 mL/min
EFV/FTC/TDF QD
(n = 352)
EVG/COBI/TDF/FTC QD
(n = 353)
Study 103[18]
(N = 708)
ATV/RTV + TDF/FTC QD
(n = 355)
17. Sax P, et al. Lancet. 2012;379:2439-2448. 18. DeJesus E, et al. Lancet. 2012;379:2429-2438.
EVG/COBI/TDF/FTC Noninferior to
EFV/TDF/FTC Through Wk 144
100
Subjects (%)
80
EVG/COBI/TDF/FTC
(n = 348)
88
84 84 82
80
EFV/TDF/FTC
(n = 352)
95% CI for Difference
Favors
EFV
75
Favors
EVG/COBI
Wk 48[1]
60
Wk 96[2]
40
3.6%
-1.6%
2.7%
8.8%
-2.9%
20
7 7
0
6
8
7 10
Wk 144[3]
4 5
5
7
6 7
Wk Wk
Wk
Wk Wk
Wk Wk Wk
Wk
48
96
144
48
96
144
48
96
144
Virologic Success*
Virologic Failure
D/c due to AEs
4.9%
-1.3%
-12%
0
*HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL as defined by FDA Snapshot algorithm.
19. Sax PE, et al. Lancet. 2012;379:2439-2448. 20. Zolopa A, et al. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr.
2013;63:96-100. 21. Wohl D, et al. ICAAC 2013. Abstract H-672a.
11.1%
12%
EVG/COBI/TDF/FTC Noninferior to
ATV/RTV + TDF/FTC Through Wk 144
100
Subjects (%)
80
90 87
EVG/COBI/TDF/FTC
(n = 353)
83 82
ATV/RTV + TDF/FTC
(n = 355)
95% CI for Difference
Favors
ATV/RTV
78 75
Favors
EVG/COBI
Wk 48[22]
60
2.7%
-2.1%
40
Wk
96[23]
Wk
144[24]
7.5%
1.1%
6.7%
-4.5%
20
5 5
0
7 7
8 7
4 5
4 6
6 8
Wk Wk
Wk
Wk Wk
Wk Wk Wk
Wk
48
96
144
48
96
144
48
96
144
Virologic Success*
Virologic Failure
D/c due to AEs
3.1%
9.4%
-3.2%
-12%
0
*HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL as defined by FDA Snapshot algorithm.
22. De Jesus E, et al. Lancet. 2012;379:2429-2438. 23. Rockstroh J, et al. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr.
2013;62:483-486. 24. Clumeck N, et al. EACS 2013. Abstract LBPS7/2.
12%
QUAD
FDC
Single day dosage
Low side effect
profile
High barrier to
resistance
TB friendly
Pregnancy friendly
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
UNK
Dolutegravir
• Dolutegravir (DTG) is a newer, potent INSI with
low nanomolar activity that is suitable for
once-daily, unboosted dosing
• Furthermore, in vitro, DTG retains activity
against most isolates carrying major integrase
resistance mutations to RAL and/or EVG
VL < 50:
DTG/ABC/3TC
•
•
VL < 50
at Wk 48
Dolutegravir Phase III Trials in
Treatment-Naive Patients
DTG 50 mg QD + 2 NRTIs*
(n = 411)
88
86
RAL 400 mg BID + 2 NRTIs*
(n = 411)
85
DTG 50 mg QD + ABC/3TC QD
(n = 414)
88
EFV/TDF/FTC QD
(n = 419)
81
DTG 50 mg QD + 2 NRTIs*
(n = 242)
90
DRV/RTV 800/100 mg QD + 2 NRTIs*
(n = 242)
83
Randomized, noninferiority phase III studies
Primary endpoint: HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL at Wk 48
SPRING-2[30]
(active
controlled,
double blind)
ART-naive pts
VL ≥ 1000 c/mL
(N = 822)
SINGLE[31]
(active
controlled,
double blind)
ART-naive pts
VL ≥ 1000 c/mL
HLA-B*5701 neg
CrCl > 50 mL/min
(N = 833)
FLAMINGO[32]
(open label)
ART-naive pts
VL ≥ 1000 c/mL
(N = 484)
*Investigator-selected NRTI backbone: either TDF/FTC or ABC/3TC.
30. Raffi F, et al. Lancet. 2013;381:735-743. 31. Walmsley S, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1807-1818.
32. Feinberg J, et al. ICAAC 2013. Abstract H1464a. .
88
90
Resistance on SPRING 1
• Samples from participants meeting Protocol
defined Virological failure criteria were sent
for resistance testing.
• No participants on DTG have had emergence
of a virus with an INI resistance mutation.
• One participant receiving DTG 10mg
developed virus with the mutation M184M/V
in reverse transcriptase.
SINGLE
• No treatment-emergent genotypic resistance
that resulted in reduced susceptibility to
either DLG or the background regimen was
seen in the DLG arm in SINGLE.
OF course the ever present TB and
pregnancy question
• Increase the dose of DLG- poor evidence
• Category B drug.
DLV/ABC and TDF
• In treatment-naive HIV-infected patients starting initial ART,
dolutegravir (DTG) plus abacavir (ABV)/lamivudine (3TC)
maintained superiority over efavirenz (EFV)/tenofovir DF
(TDF)/emtricitabine (FTC) at Week 96
– DTG arm associated with higher virologic response rate,
primarily due to lower rate of discontinuations related to
tolerability
– DTG arm associated with more favorable safety profile vs control
arm, with lower rates of central nervous system (CNS) events,
rash, and liver function test elevations
• No major treatment-emergent mutations conferring INSTI
or NRTI resistance detected through 96 weeks in DTGtreated patients
Dolutegravir
FDC
Single day dosage
Low side effect
profile
High barrier to
resistance
TB friendly
Pregnancy friendly
YES
YES
YES
YEs
NO
UNK
Darunavir dosing summary
Darunavir/r dosing is determined by treatment
experience and presence or absence of
darunavir mutations on genotypic lab analysis.
Treatment-experienced patients
• POWER 1 compared the efficacy and safety of four
doses of DRV (TMC114) plus 100 mg RTV with
investigator-selected control protease inhibitors (CPIs)
• 63% of the patients were resistant to all commercially
available PI.
• Virologic and immunologic outcomes were significantly
better in the DRV/r arms compared to the CPI arm. In
the 600 mg DRV twice daily arm, mean CD4 gains were
as high as 124 cells at 24 weeks and 53 percent
attained an HIV RNA level <50 copies/mL;
Treatment-experienced patients
• POWER 3 DRV/r plus optimized background
therapy. No comparator arm was used.
• Of 324 patients who were treated for 48
weeks, 45 percent achieved HIV RNA
reductions to <50 copies/ml.
Treatment-experienced patients
• Treatment-experienced patients with recent
genotypic testing demonstrating the absence
of darunavir-associated mutations: darunavir
(800 mg) once daily plus ritonavir (100 mg)
once daily. The relevant darunavir mutations
include: V11I, V32I, L33F, I47V, I50V, I54L,
I54M, T74P, L76V, I84V and L89V.
Treatment-experienced patients
• POWER 1 and POWER 2 were randomized,
multinational, phase IIB trials, which
compared DRV co-administered with low-dose
RTV to other PIs in a population of highly
treatment-experienced patients
Treatment-experienced patients
• Darunavir-associated mutations on genotype:
darunavir (600 mg; given as one tablet) twice
daily plus ritonavir (100 mg) twice daily.
• The relevant darunavir mutations include:
V11I, V32I, L33F, I47V, I50V, I54L, I54M, T74P,
L76V, I84V and L89V.
Treatment-naïve patients
• Darunavir (800 mg) once daily plus ritonavir
(100 mg) once daily
• ARTEMIS: randomized, open-label, phase 3
non-inferiority trial compared the safety and
efficacy of DRV/r (800/100 mg once daily) with
LPV/r in 689 treatment-naive patients
Treatment-naïve patients
• At week 48, DRV/r was found to be noninferior to LPV/r; viral suppression was
achieved in 84 versus 78 percent, respectively.
• At 96 weeks, significantly more patients in the
DRV/r arm achieved viral suppression than in
the LPV/r arm (79 versus 71 percent)
• Both treatments were well tolerated.
Darunavir
FDC
Single day dosage
Low side effect
profile
High barrier to
resistance
TB friendly
Pregnancy friendly
NO
MAYBE
YES
YES
NO
UNK
Third line Peer Revivew committee
• Third line drugs now on tender
• Centrally procured
– Receive motivation
– Screen
– Add to database
– Send to Virtual Committee
– Committee recommendation to motivator and
CPU
– Update database
Third line committee
•
•
•
•
•
130 patients on the database.
115 have already been reviewed.
(5 motivations no GT results)
Number of motivations declined 12
Number of patients on third line treatment 98