ppt
advertisement

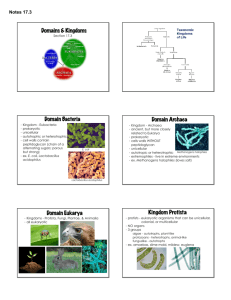
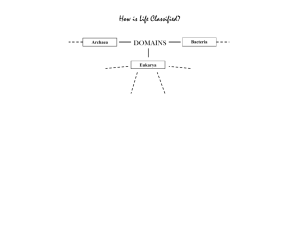
TAXONOMY: CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS Miss Napolitano & Mrs. Haas CP Biology CLASSIFICATION You use classification techniques all the time! Miss Napolitano’s classification: Employee State employee Robbinsville High School employee Teacher Science teacher Biology teacher TAXONOMY Taxonomy: the science of classifying organisms Carolus Linnaeus – father of modern taxonomy Grouped organisms into taxa based on similarities Developed scientific names - common names became too confusing! Binomial nomenclature: each species is assigned a twopart scientific name WHAT IS THIS? WHAT IS THIS? You may have said: • • • • • Mountain lion Puma Cougar Panther Or something else! Scientific names (binomial nomenclature) eliminates this problem! Simply, Felis concolor. DO YOU KNOW THE FOLLOWING SCIENTIFIC NAMES? DO YOU KNOW THE FOLLOWING SCIENTIFIC NAMES? Felis catus Homo sapien Helianthus annuus Canis familiaris Spongiforma squarepantsii THE SEVEN LEVELS OF BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION Domain is the most diverse, species is the most specific Species: organisms that can interbreed with each other and produce fertile offspring Binomial nomenclature = genus & species of an individual BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION HUMAN CLASSIFICATION Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primates Family: Hominidae Genus: Homo Species: sapiens Shorthand: Homo sapiens (H. sapiens) Genus & species italicized or underlined ONLY genus capitalized If abbreviated, shorten genus to 1 st letter VOCAB BEFORE WE PROCEED... Unicellular: made of 1 cell Multicellular: made of more than 1 cell Prokaryotic: cell does not have a nucleus Eukaryotic: cells have nuclei Autotrophic: makes own food (photosynthesis, etc.) Heterotrophic: consumes food Cell wall: rigid structure surrounding the cell membrane THE 3 DOMAINS OF LIFE Bacteria: true bacteria Archaea: extreme bacteria Eukarya: eukaryotes DOMAIN BACTERIA Unicellular Prokaryotic Cell walls Corresponds to kingdom Eubacteria Diverse! DOMAIN ARCHAEA Unicellular Prokaryotic Live in extreme environments with no oxygen Volcanic hot springs, brine pools, black organic mud Cell walls Corresponds to kingdom Archaebacteria DOMAIN EUKARYA All eukaryotes Organized into 4 kingdoms Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia DOMAIN EUKARYA: KINGDOM PROTISTA The super random group Can be unicellular or multicellular Plant-like: Euglena Some autotrophic, some heterotrophic Categorized by plant-like, animal-like, or fungus-like Fungus-like: Slime mold Animal-like: Amoeba DOMAIN EUKARYA: KINGDOM FUNGI Heterotrophic Many feed on dead or decaying matter Most multicellular but some unicellular DOMAIN EUKARYA: KINGDOM PLANTAE Multicellular Autotrophic – photosynthesis Nonmotile – do not move from place to place Cell walls Include cone-bearing plants, flowering plants, mosses, & ferns **Algae are NOT plants – they’re protists! DOMAIN EUKARYA: KINGDOM ANIMALIA Multicellular Heterotrophic No cell walls Most can move Very diverse & complex! COMPARING DOMAINS & KINGDOMS Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea COMPARING DOMAINS & KINGDOMS Domain Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Cell Structures Cell walls Cell walls Some have cell walls, some have chloroplasts Cell walls Cell walls, chloroplasts No cell walls or chloroplasts Number of Cells Unicellular Unicellular Some unicellular, some multicellular Most multicellular, some unicellular Multicellular Multicellular Autotrophic or Heterotrophic Both Both Both Heterotrophic Autotrophic Heterotrophic Examples E. coli Halophiles Amoeba Mushrooms, yeasts Mosses, ferns, flowering plants Sponges, worms, insects, fishes, mammals Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia DICHOTOMOUS KEY Used to help identify an unknown specimen Works by asking yes or no questions about certain traits Eventually leads the reader to the correct taxa for the organism DICHOTOMOUS KEY EXAMPLE Traits Direction 1a. Organism has 4 legs Go to #2 1b. Organism has more than 4 legs Go to #20 2a. Organism has a tail Go to #3 2b. Organism has no tail Go to #35 3a. Organism has stripes Bengal Tiger 3b. Organism has no stripes African Lion TRY THIS! Trait Direction 1a. Organism walks on 4 legs Go to #2 1b. Organism walks on 2 legs Go to #8 2a. Organism has visible fur Go to #3 2b. Organism has no visible fur Go to #20 3a. Organism lives in warm climates Go to #7 3b. Organism lives in cold climates Go to #4 4a. Organism has black or brown fur Ursus americanus 4b. Organism has white fur Ursus maritimus