CHAPTER 2
advertisement

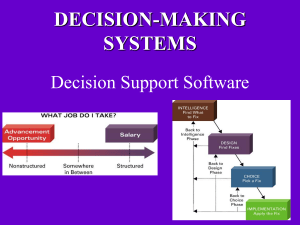
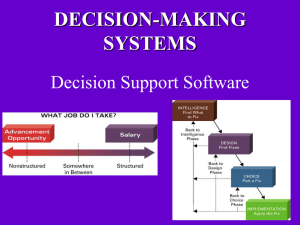
DECISION-MAKING SYSTEMS Decision Support Software Reasons for the growth of decisionmaking information systems • People need to analyze large amounts of information • People must make decisions quickly • People must apply sophisticated analysis techniques, such as modeling and forecasting, to make good decisions • People must protect the corporate asset of organizational information Transaction Processing Systems • Capture data regarding business transactions/activities. – That data is stored in a database and then mined/analyzed using one or more decision making techniques • Transactional Data being captured – – – – Debits and credits Inventory going into and out of the system Items being bought and sold. Payments being made and received • Uses source data automation: captures data at the point of origin The Organizational Pyramid and Information Needs • As you move from lower to upper levels in an organization, information needs move from transactional in nature to analytical. Analytical information supports strategic decision making. Info also becomes less detailed and more concise. Different Decision Types • Programmed Decisions (structured decision) – Structured situations with well defined relationships – Quantifiable. There is an understood and accepted method for making the decision. – Very easy to automate (program) these types of decisions. • Nonprogrammed Decisions (nonstructured decision) – Ill-structured situations with vague or changing relationships between variables – Not easily quantifiable in advance. No agreed-on decision making method. – There may be several “right” answers (although some answers could be better than other answers). Different Decision Types Structured decisions • Routine and repetitive problems with standard procedures and solutions Unstructured decisions • Fuzzy, complex problems with no cutand-dried procedures and solutions • Most decisions that you make fall somewhere in between structured and nonstructured (containing elements of both). • Various forms of decision support tend to be used when dealing with nonstructured aspects of a decision. (DSS helps you analyze information) • With artificial intelligence, the decision making expertise is built into the system so that the AI system makes the decision for you Problem Solving Approaches Used by Computer-Aided Decision Making Systems • Optimization: find the very best solution given the constraints provided (aka the optimal answer) • Satisficing: find a good solution, one that satisfies all of your decision criteria, without necessarily being the best solution. DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM (DSS) Highly flexible and interactive IT system that is designed to support decision making when the problem is not structured ( i.e. Nonprogrammed decision). Spreadsheets are a common form of decision support system (DSS) Alliance between You and a DSS • Decision support systems help you analyze, but you must know how to solve the problem, and how to use the results of the analysis – A DSS assists you in making a decision, as opposed to making the decision for you. – Power of a DSS is its ability to analyze information and its ease of use. QUANTITATIVE MODELS OFTEN USED BY A DSS • Three quantitative (mathematical) models often used by DSSs include: 1. Sensitivity analysis – the study of the impact that changes in one (or more) parts of the model have on other parts of the model 2. What-if analysis – checks the impact of a change in an assumption on the proposed solution 3. Goal-seeking analysis – finds the inputs necessary to achieve a goal such as a desired level of output DSS Quantitative Model: What-if analysis: change one assumption and see what impact it has on the model DSSQuantitative Model:Goal-seeking analysis what inputs must occur in order to achieve the desired result? A DSS Can Help With Analysis Tasks Like • • • • • • Deciding where to spend advertising dollars Analyzing sales trend information Analyzing drug interactions Developing airline schedules Pricing products Allocating limited investment dollars among several potential projects. • Budget setting. Inventory control. • Cash flow forecasting. Processing rules are imprecise. Human judgment required. Applied Uses of a DSS YIELD MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS are a form of DSS used by airlines to alter the price of seats on available flights on a minute by minute basis, comparing the number of seats sold to an estimate of what was expected. If fewer seats have sold, more low-cost seats are made available. If more seats have sold, less low-cost seats are made available. Objective: have the plane take off full at the highest possible average cost per seat • Airlines are using optimization software to save money on the costs associated with each flight by reducing the number of miles traveled, fuel used and/or overflight fees paid, with the system also taking weather and wind speed & direction into account. GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS (GIS) Geographic Information Systems • A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a specialized decision support system designed specifically to analyze spatial information. – Spatial information is any information that can be shown in map form, such as roads, population distribution characteristics, sewer systems and other utilities, income levels, health conditions, areas of high or low crime, etc. – The strength of a GIS is the ability to layer information with a mouse click. • ArcExplorer 2: showing features in San Diego (can find out more info about an attraction by placing your mouse over it) • Haag text examples – GIS used in the space shuttle Challenger investigation – GIS used in tree maintenance in Chattanooga – GIS used in the 2001 Virginia highway sniper investigation. – Analyzing hurricane destruction in Florida. • Businesses use GIS software to analyze information, generate business intelligence, and make decisions. • Can layer in info with a mouse click • Marketing applications • Westar Outage Map • Airline Flights • US Army Command Post of the Future (CPOF) EXECUTIVE INFORMATION SYSTEMS • Executive information system (EIS) – specialized DSSs designed for use by senior-level executives in order to make upper level decisions. • Most EISs offering the following capabilities: – Consolidation – involves the aggregation of information and features simple roll-ups to complex groupings of interrelated information – Drill-down – enables users to get details, and details of details, of information – Slice-and-dice – looks at information from different perspectives Table 5.1 The Capabilities of Dashboards Figure 5.3 Sample Performance Dashboard © NAN104/iStockphoto Figure 5.5 A Human Resource Dashboard/Scorecard Courtesy of iDashboards Figure 5.6 Management Cockpit The Management Cockpit is a registered trademark of SAP, created by Professor M. Georges. Data Visualization Technologies • Data visualization • The process of presenting data to users in visual formats, thereby making IT applications more attractive and understandable to users • The Value of Visualization • Geographic Information Systems (GIS) • A computer-based system for capturing, integrating, manipulating, and displaying data using digitized maps • Geocoding • the process of assigning geographical location to every object • Enables users to generate information for planning, problem solving, and decision making • Examples: ESRI, Intergraph, Pitney Bowes Mapinfo • Reality mining • Using GISs and Global Positioning Systems (GPSs) together • Allowing analysts to extract information from the usage patterns of mobile phones and other wireless devices Digital Dashboards • Digital dashboard – integrates information from multiple components and presents it in a unified display The End Click Here for Artificial Intelligence • As you move from lower to upper levels in an organization, information needs move from ___________ in nature to __________. – Transactional in nature to analytical Decision support systems Transactional decisions Ad-hoc decisions Nonprogrammed decisions Programmed decisions Analytical decisions (these are the answers) • ____________ have well-defined relationships and are easily quantifiable while _________________ may have several answers that will work, and they are not easily quantifiable. • If you are trying to find the very best solution given the constraints provided, you are using a technique called ___________ – optimization • If you want to find a good solution, one that satisfies all your decision criteria, without necessarily being the best solution., you are using a technique called _____________. – satisficing Components of a DSS • Model management component – consists of both the DSS models and the model management system • Data management component – stores and maintains the information that you want your DSS to use • User interface management component – allows you to communicate with the DSS