Decision Making Systems
advertisement

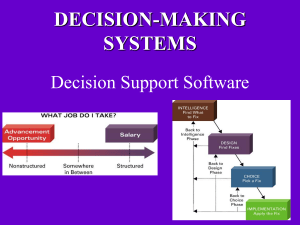
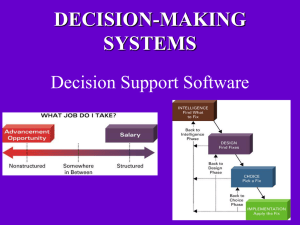
DECISION-MAKING SYSTEMS Decision Support Software Reasons for the growth of decisionmaking information systems • People need to • People must make • People must techniques, such as modeling and forecasting, to make good decisions • People must the corporate asset of organizational information Transaction Processing Systems • C transactions/activities. regarding business – That data is stored in a database and then mined/analyzed using one or more decision making techniques • Transactional Data being captured – – – – D Inventory Items being Payments and • Uses at the point of origin and of the system . : captures data The Organizational Pyramid and Information Needs • As you move from lower to upper levels in an organization, information needs move from in nature to . Analytical information supports . Info also becomes and more Different Decision Types • Programmed Decisions (structured decision) –S – Quantifiable. relationships – Very easy to automate (program) these types of decisions. • Nonprogrammed Decisions (nonstructured decision) – Ill-structured situations with between variables – Not easily quantifiable in advance. No agreed-on decision making method. – There may be (although some answers could be better than other answers). • Most decisions that you make structured and nonstructured (containing elements of both). • Various forms of decision support tend to be used when dealing with nonstructured aspects of a decision. (DSS helps you ) • With artificial intelligence, the decision making expertise is so that the AI system Problem Solving Approaches Used by Computer-Aided Decision Making Systems • O : find the very best solution given the constraints provided (aka the • S ) : find a , one that of your decision , without necessarily being the best solution. DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM (DSS) Highly flexible and interactive IT system that is designed to support decision making when the problem is ( i.e. Nonprogrammed decision). are a common form of decision support system (DSS) Alliance between You and a DSS • Decision support systems help you , but you must know how to , and how to use the results of the analysis – A DSS in making a decision, as opposed to making the decision for you. – Power of a DSS is its ability to analyze information and its ease of use. QUANTITATIVE MODELS OFTEN USED BY A DSS • Three quantitative ( include: ) models often used by DSSs 1. S – the study of the impact that changes in one (or more) parts of the model have on other parts of the model 2. W analysis – checks the impact of a change in an assumption on the proposed solution 3. G analysis – finds the inputs necessary to achieve a goal such as a desired level of output DSS Quantitative Model: What-if analysis: change and see what on the model DSSQuantitative Model:Goal-seeking analysis what must occur in order to achieve the ? A DSS Can Help With Analysis Tasks Like • • • • • • Deciding where to spend advertising dollars Analyzing sales trend information Analyzing drug interactions Developing airline schedules Pricing products Allocating limited investment dollars among several potential projects. • Budget setting. Inventory control. • Cash flow forecasting. Processing rules are . Human required. Applied Uses of a DSS Y SYSTEMS are a form of DSS used by airlines to alter the price of seats on available flights on a minute by minute basis, comparing the number of seats sold to an estimate of what was expected. If fewer seats have sold, more low-cost seats are made available. If more seats have sold, less low-cost seats are made available. Objective: have the • Airlines are using optimization software to save money on the costs associated with each flight by reducing the number of miles traveled, fuel used and/or overflight fees paid, with the system also taking weather and wind speed & direction into account. GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS (GIS) • A Geospatial Information System (GIS) is a specialized decision support system designed specifically to – Spatial information is that can be shown in , such as roads, population distribution characteristics, sewer systems and other utilities, income levels, health conditions, areas of high or low crime, etc. – The strength of a GIS is the ability to with a mouse click. • ArcExplorer 2: showing features in San Diego (can find out more info about an attraction by placing your mouse over it) • Pg. 213: Haag – GIS used in the space shuttle Challenger investigation – GIS used in tree maintenance in Chattanooga – GIS used in the 2001 Virginia highway sniper investigation. • Pg. 188: Analyzing hurricane destruction in Florida. • Businesses use GIS software to information, , and make decisions. • Can layer in info with a mouse click • Marketing applications • Westar Outage Map EXECUTIVE INFORMATION SYSTEMS • Executive information system (EIS) – specialized DSSs designed for use by in order to make • Most EISs offering the following capabilities: – Consolidation – involves the and features simple roll-ups to complex groupings of interrelated information – Drill-down – enables users to get information – , and Slice-and-dice – looks at information from , of Digital Dashboards • Digital dashboard – from multiple components and presents it in a unified display