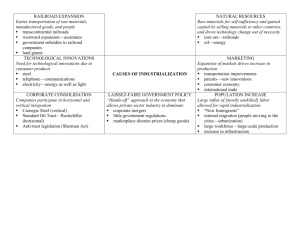
Causes of Industrialization
advertisement

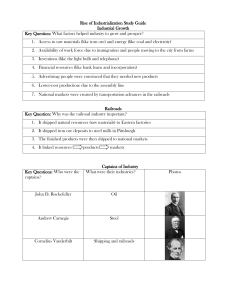
The Industrial Age 1877-1920 1 I. Causes of Industrialization A. The 2nd Industrial Revolution in the 60 years following the Civil War was a period of tremendous change in society, technology, and the economy. 2 B. Transforms the US into a booming industrialized nation. 1. Steam and electricity replace human muscle 2. Iron replaced wood, and steel replaced iron 3. oil will light homes, streets, factories, and lubricate machines 4. People and goods move quickly on Railroads 5. Manufactured ice now meant transport of food over large areas. 6. Before the Civil War, it took 61 hours of labor to produce an acre of wheat. By 1900, because of mechanized farming, it took 3 hours and 19 minutes. 3 C. What allows for this transformation of technology, society, and economy? 1. Extensive natural resources. 2. Government support of business 3. Growing urban population. (lots of cheap labor and people to buy the things produced. 4 D. Extensive Natural Resources 1. Timber, coal, iron, and copper were important resources that fueled industrialization. 5 2. The fact that they are located in the US meant that they could be obtained cheaply. 3. Railroads brought natural resources from the west to the east. 6 4. Even before cars, petroleum was in high demand because it was used for kerosene, a fuel used in lanterns and stoves. 7 E. Large Workforce 1. Between 1860 and 1910, the population of the United States nearly tripled. a. Means a large workforce and people to buy goods. 8 2. People were having larger families, and more children were growing to adulthood. 3. Large numbers of immigrants from southern and eastern Europe were coming to the US. a.17 million immigrants arrived between 1870 and 1910. 9 F. New Inventions 1. Technology and inventions made transportation and communication easier. It encouraged new industries, produced more wealth, and created new jobs. 10 a. Telephone b. Phonograph c. Incandescent light bulb d. Washing machine e. Skyscrapers f. Automobile g. Air plane h. Ice machine 11 2. New technologies allowed farmers to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency in planting and harvesting crops. a. Seed Drill – helped planting seed In tough western soil d. The Harvester (1870s) – used for binding wheat b. John Deere Plow – easily turned over prairie grasses and highly compacted soil e. Automatic Knotter (1880s) – tied them together f. Mechanized corn planters, mowing and raking machines. c. Cyrus McCormack’s Reaper – used for cutting grain 12 3. Before the introduction of the wire binder in 1875, a farmer could plant and harvest 8 acres of wheat with no help. AFTER 1890, a farmer could handle 135 acres with no help. 13 4. Assembly Line a. Used by Henry Ford to revolutionize the car making industry in Detroit. b. Cut the amount of time to assemble a Model T from 12.5 hours to 93 minutes. 14 c. Goods could now be produced quicker, more efficiently, and cheaper. 1. Cut the price down from $850 in 1908 to $295 in 1924 d. Quicker production and less skilled laborers. e. Other industries adopted it. Everything from caskets to cereals made on assembly lines. 15 G. Free Enterprise 1. Laissez-Faire Economics a. belief that government should not interfere in the economy with regulations. b. belief that supply and demand will regulate wages and prices. 16 c. Government built the transportation networks that support business. 1.Subsidies that built roads, canals, railroads d. Tariffs on foreign goods to protect American businesses. 17