Causes of Industrialization
advertisement
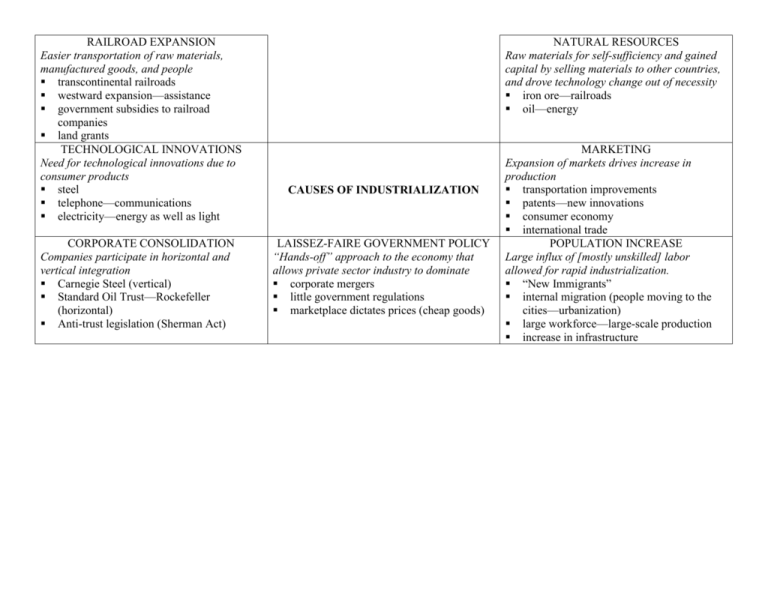
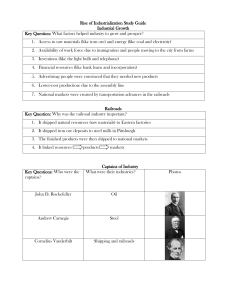
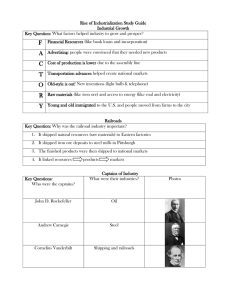
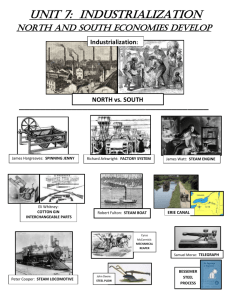
RAILROAD EXPANSION Easier transportation of raw materials, manufactured goods, and people transcontinental railroads westward expansion—assistance government subsidies to railroad companies land grants TECHNOLOGICAL INNOVATIONS Need for technological innovations due to consumer products steel telephone—communications electricity—energy as well as light CORPORATE CONSOLIDATION Companies participate in horizontal and vertical integration Carnegie Steel (vertical) Standard Oil Trust—Rockefeller (horizontal) Anti-trust legislation (Sherman Act) NATURAL RESOURCES Raw materials for self-sufficiency and gained capital by selling materials to other countries, and drove technology change out of necessity iron ore—railroads oil—energy CAUSES OF INDUSTRIALIZATION LAISSEZ-FAIRE GOVERNMENT POLICY “Hands-off” approach to the economy that allows private sector industry to dominate corporate mergers little government regulations marketplace dictates prices (cheap goods) MARKETING Expansion of markets drives increase in production transportation improvements patents—new innovations consumer economy international trade POPULATION INCREASE Large influx of [mostly unskilled] labor allowed for rapid industrialization. “New Immigrants” internal migration (people moving to the cities—urbanization) large workforce—large-scale production increase in infrastructure