Cell Cycle - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

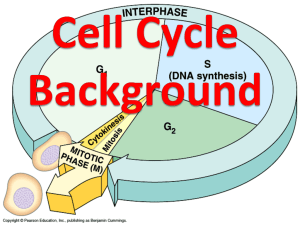
CELL CYCLE Look both ways before you cross the street H2 O (Water) See eye to eye CELL CYCLE Target: I will be able to identify and describe the main stages of the cell cycle. Cell Division: the process when a cell divides into two daughter cells. Why do cells divide? 1. To get materials, such as food, water, oxygen, and waste in and out of the cell efficiently. 2. So DNA can make enough proteins to run the cell. Pg. 97 Cell Cycle: Process of one cell dividing to become two cells. Occurs in Somatic Cells – body cells. Each cell will have the same genetic information. Main Stages: Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis. 1. Interphase: a period of cell growth and DNA replication for all cells. G1: The cell grows in size so it can divide into two. The chromosomes are single stranded. Chromosomes condense in the nucleus. S: Synthesis of DNA. The cell stops growing. Chromosomes replicate, become double stranded. G2: The cell grows new organelles. The cell prepares to divide. 2. Mitosis: Division of the Nucleus. 3. Cytokinesis: Division of the cytoplasm. Plant Cytokinesis: The cell builds a cell plate between the two nuclei that will become the new cell wall for each cell. Animal Cytokinesis: The cell cleaves (pinches) in the middle and becomes two distinct cells. Cyclins: Proteins that regulate the timing of the cell cycle. Cyclins make sure that there is not uncontrolled cell growth. Without cyclins, the uncontrolled growth leads to cancer or a tumor. Summary: MAIN STAGES OF THE CELL CYCLE G1(Interphase) S(Interphase) G2(Interphase) Draw pictures to represent what is happening in each stage of interphase (G1, S, and G2), Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Then draw a picture to represent the role of cyclins in the cell cycle. *Use a minimum of 4 colors Mitosis Cytokinesis Cyclins Pg. 96