Electron Configuration

Electron Configuration
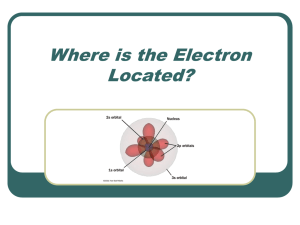
Mapping the electrons
Electron Configuration
The way electrons are arranged around the nucleus.
Quantum Mechanical Model
1920’s
Werner Heisenberg (Uncertainty Principle)
Louis de Broglie (electron has wave properties)
Erwin Schrodinger (mathematical equations using probability, quantum numbers)
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle with any great degree of accuracy or certainty.
Erwin Schrodinger
Formulated equation that describes behavior and energies of subatomic particles.
Incorporates both particle and wave behavior in terms of wave function: is proportional to the probability of finding an electron.
Leads to Quantum Mechanics: we cannot pinpoint an electron in an atom but we can define the region where electrons can be in a particular time……… called a Probability map….a 3-dimensional area in space called an ORBITAL
Principal Quantum Number, n
Indicates main energy levels n = 1, 2, 3, 4…
Each main energy level has sub-levels
Energy Sublevels s p d f g
The principle quantum number, n, determines the number of sublevels within the principle energy level.
Orbital Quantum Number, ℓ
(Angular Momentum Quantum Number)
Indicates shape of orbital sublevels ℓ = n-1 ℓ sublevel
0
1
2
3
4 f d s p g
Orbital
The space where there is a high probability that it is occupied by a pair of electrons.
Orbitals are solutions of Schrodinger’s equations.
Orbitals
Visualizing the orbitals
Orbitals in Sublevels
Sublevel # Orbitals # electrons f d s p g
1
3
5
7
9
2
6
10
14
18
Three rules are used to build the electron configuration:
Aufbau principle
Pauli Exclusion Principle
Hund’s Rule
Aufbau Principle
Electrons occupy orbitals of lower energy first.
Orbital
Diagram
Filling Order diagram
-Pauli Exclusion Principle
(Wolfgang Pauli, Austria, 1900-1958)
-Electron Spin Quantum Number
An orbital can hold only two electrons and they must have opposite spin.
Electron Spin Quantum Number (m s
):
+1/2, -1/2
Hund’s Rule
In a set of orbitals, the electrons will fill the orbitals in a way that would give the maximum number of parallel spins
(maximum number of unpaired electrons).
Analogy: Students could fill each seat of a school bus, one person at a time, before doubling up.
Orbital
Diagram for
Hydrogen
Orbital
Diagram for Helium
Orbital
Diagram for Lithium
Orbital
Diagram for
Beryllium
Orbital
Diagram for Boron
Orbital
Diagram for Carbon
Orbital
Diagram for
Nitrogen
Orbital
Diagram
Notations of Electron
Configurations
Standard
Shorthand
Orbital
Diagram for Fluorine
Standard Notation of Fluorine
Number of electrons in the sub level 2,2,5
1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 5
Sublevels
Shorthand Notation
Use the last noble gas that is located in the periodic table right before the element.
Write the symbol of the noble gas in brackets.
Write the remaining configuration after the brackets.
Ex: Fluorine: [He] 2 s 2 2 p 5
Blocks in the Periodic Table






![6) cobalt [Ar] 4s 2 3d 7](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009918562_1-1950b3428f2f6bf78209e86f923b4abf-300x300.png)
