Human Physiology Unit 5C:
Reproductive
Supplemental Instruction
Iowa State University
Leader:
Course:
Instructor:
Date:
Paige Stieneke
BIOL 256
Dr. Karri Haen
May 1, 2013
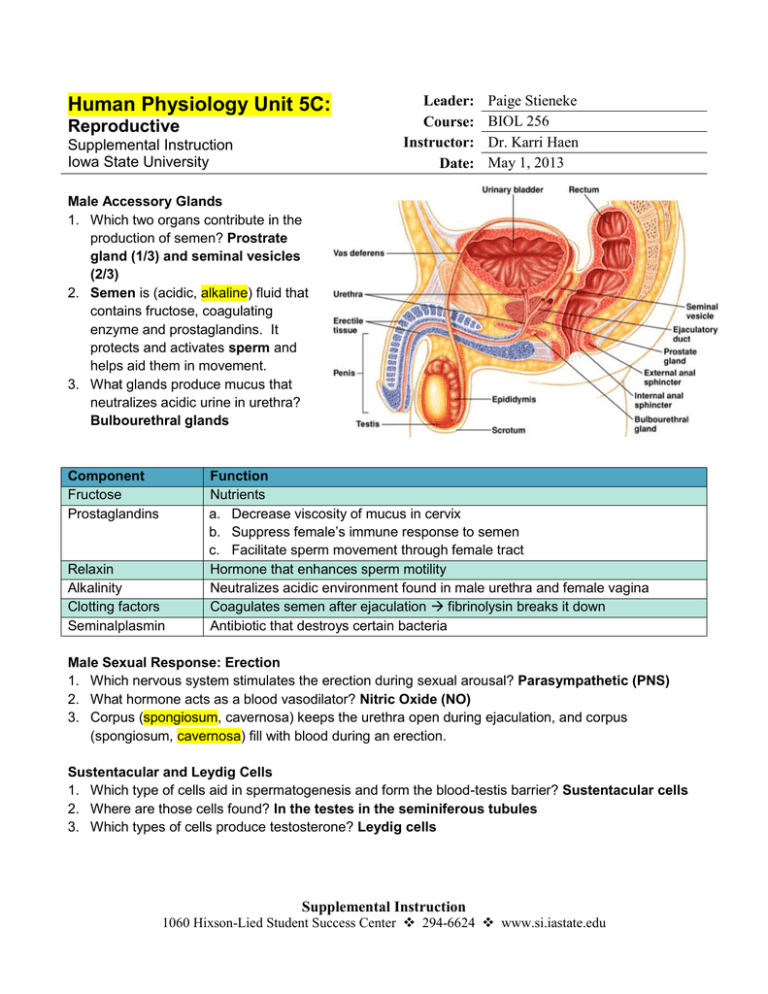
Male Accessory Glands
1. Which two organs contribute in the
production of semen? Prostrate
gland (1/3) and seminal vesicles
(2/3)
2. Semen is (acidic, alkaline) fluid that
contains fructose, coagulating
enzyme and prostaglandins. It
protects and activates sperm and
helps aid them in movement.
3. What glands produce mucus that
neutralizes acidic urine in urethra?
Bulbourethral glands
Component
Fructose
Prostaglandins
Relaxin
Alkalinity
Clotting factors
Seminalplasmin
Function
Nutrients
a. Decrease viscosity of mucus in cervix
b. Suppress female’s immune response to semen
c. Facilitate sperm movement through female tract
Hormone that enhances sperm motility
Neutralizes acidic environment found in male urethra and female vagina
Coagulates semen after ejaculation fibrinolysin breaks it down
Antibiotic that destroys certain bacteria
Male Sexual Response: Erection
1. Which nervous system stimulates the erection during sexual arousal? Parasympathetic (PNS)
2. What hormone acts as a blood vasodilator? Nitric Oxide (NO)
3. Corpus (spongiosum, cavernosa) keeps the urethra open during ejaculation, and corpus
(spongiosum, cavernosa) fill with blood during an erection.
Sustentacular and Leydig Cells
1. Which type of cells aid in spermatogenesis and form the blood-testis barrier? Sustentacular cells
2. Where are those cells found? In the testes in the seminiferous tubules
3. Which types of cells produce testosterone? Leydig cells
Supplemental Instruction
1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu
Brain-Testicular Axis
Location
Hormone
Hypothalamus
GnRH
Anterior Pituitary
Lutetinizing Hormone
Follicle Stimulating
Hormone
Leydig Cells
Testosterone
Sertoli Cells
Inhibin
Function
Stimulates anterior pituitary to produce FSH and LH
Stimulates leydig cells to secrete testosterone
Stimulates sertoli cells to release Androgen Binding
Protein (ABP) to enhance spermatogenesis
Sperm development
Negative feedback mechanism for FSH
Female Reproductive System
1. Follicular Phase: Period of follicle growth;
occurs at days 1-14.
a. Primordial follicle Primary
Secondary Mature Graafian follicle
2. What process occurs midcycle? Ovulation
a. What two hormones “spike” and signify
ovulation? LH and FSH (LH triggers
ovulation)
b. What happens to an egg during ovulation?
It is released from a follicle into oviduct
and will be available for fertilization by
sperm during the luteal phase
3. Luteal Phase: Period of corpus luteum activity;
occurs at days 14-28.
a. What is the primary hormone that stops
LH and FSH release? Estrogen
b. Which cells enlarge to form the corpus
luteum? Granulosa cells
c. Which two hormones are secreted by the
corpus luteum? Progesterone and
estrogen
d. What is the function of these two
hormones? Maintain uterine
endometrium
e. If a pregnancy occurs, which two
hormones are secreted to maintain the
endometrium? Estradiol and
progesterone
f. If there is no pregnancy, what process
occurs? Menstruation
Supplemental Instruction
1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu