31.-3.3 Sex Cell Development, Birth review .ppt
advertisement
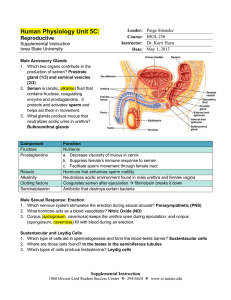
Sex Cell Development & Human Conception Male Sex Cell Development • Head • Body The capsule is filled with chemicals that allow the head to enter the egg; contains nucleus Energy-producing organelle (mitochondria) • Flagellum A whip-like tail propels the sperm cell Spermatogenesis • Sperm produced in seminiferous tubules (testes) Egg Production • The eggs form and mature in two ovaries, which contain • • follicles Each follicle contains an egg When the egg is ready, the ovary wall ruptures and the egg is released into the oviduct – This is called ovulation • After ovulation, the ruptured follicle forms into the corpus luteum Note: • The ovary does not produce new egg cells throughout adult life • The ovary contains approximately 40 000 immature follicles at puberty, and that number continually decreases • Only one follicle matures every month; the others break down and are absorbed by the ovary Oogenesis ♀ Hormones • FSH: Follicle stimulating hormone – Signals the ovaries to produce mature eggs • LH: Luteinising hormone – Released by the pituitary gland (base of brain) • Progesterone – Released by corpus luteum • Estrogen – Reproductive hormone – Causes appearance of ♀ secondary sexual characteristics Hormones & Menstruation • • • • • • • • • • • Pituitary gland releases FSH FSH stimulates follicle development Developing follicle secretes estrogen ↑ estrogen levels stimulates thickening of endometrium Estrogen travels to pituitary, stimulating release of LH LH causes developing follicle to release a mature egg LH stimulates empty follicle to develop in corpus luteum Corpus luteum produces progesterone and estrogen ↓ progesterone increases thickening of endometrium Progesterone causes pituitary to decrease FSH production ↓ FSH and LH prevent more eggs from being released until progesterone decreases again Hormone Levels Fertilization • The head of the sperm breaks • • • • through the cell membrane of the egg Only one sperm enters the egg The egg (n) and sperm (n) nuclei combine together (2n) This is called a zygote The flagellum of the sperm is pinched off Ovulation to Implantation • The zygote undergoes many cell divisions • When it reaches the uterus, it has become a blastocyst (hollow ball of cells) – Outer cells of the blastocyst will become the placenta – Inner cells will form the embryo • Implantation occurs when the blastocyst attaches to the endometrium – This produces a hormonal signal that prevents the corpus luteum from disintegrating – If the corpus luteum breaks down, menstruation occurs Ovulation to Implantation Gastrulation • Ectoderm – skin, nervous system • Mesoderm – kidneys, skeleton, muscles, blood vessels, gonads • Endoderm – lungs, lining of digestive tract Conception and Fertilization • • • • • Yolk sac: supplies nutrients Amniom: fluid-filled sac protects the embryo from Allantois: waste removal Placenta: exchange of food and Umbilical cord: connects the embryo to the mother Pregnancy - Trimester 1 • Week 1 – 12 • 4 Weeks – Basic heart, large brain, limb buds, eyes, spine – Embryos have a tail • 8 Weeks – – – – – Cartilage replaced by bone The embryo is now a fetus Facial features, limbs, hands, feet, fingers, and toes are visible The nervous system responds to stimulus The internal organs begin to function • High Risks – Spontaneous abortions or miscarriages, birth defects • Signs of Pregnancy – Nausea/vomitting, frequent urination, no menstruation Pregnancy - Trimester 2 • Week 12 – 24 • Development – – – – – – External sex organs Hair grows on head and body Blink, grasp, swallow, suck, hear, and cry Functioning nervous system Skeleton development 300 mm long • Risks – If born at this time, the fetus has a 50% chance of survival • Signs of Pregnancy – The mother appears pregnant – The mother will feel fetal movement (quickening) Pregnancy - Trimester 3 • Week 24 – 38 • Development – Open eyes in 8th month – The fetus is very active (kicking, stretching) – The body hair begins to disappear – Bones begin to harden • Head bones remain soft to help the head fit through the birth canal – 500 mm long • Signs of Pregnancy – Heartburn, constipation, hemorrhoids, abdominal pain – Mother’s health and nutrition is very important Risks during Pregnancy Birth • Dilation – Contractions and oxytocin cause the cervix to dilate; the amnion breaks and releases the amniotic fluid (2 – 20 hr) • Expulsion – Baby is pushed through the cervix out the birth canal (0.5 – 2 hr) • Placental – Placenta and umbilical cord are expelled from the uterus (10 – 15 min after birth)