The Menstrual Cycle - Haiku for Ignatius
advertisement

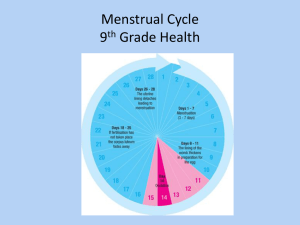
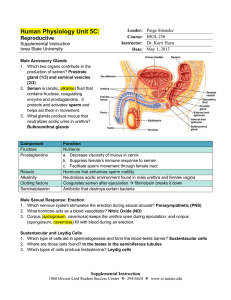
200,000 to 300,000 immature ova are present in the ovaries at birth. Each cycle allows for one egg to develop. First Cycle – Menarche, on average, occurs around the age of 12 years old. Heredity, diet, overall health influence time. Last Cycle – Menopause, on average, occurs around the age of 52. Cycle Length – 28 days is the average but cycles may last between 21 – 36 days. Each woman is different. Menstrual Phase – days 1 – 7, when the menstrual flow will occur. Proliferative Phase – days 7 -21, when the egg is present and fertilization and implantation may occur. Secretory Phase – days 21 – 28, when the wall breaks down. Secretory Phase Day 21 - 28 Menstrual Phase Day 1-7 Proliferative Phase Day 8- 20 Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Source: Pituitary Gland Causes the egg to begin to mature within the egg follicle. Estrogen Source: Egg Follicle Causes the endometrium to begin to thicken. Inhibits FSH. Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Source: Pituitary Gland Causes final egg development Causes ovulation Converts egg follicle into Corpus Luteum/Corpus Albicans Progesterone Source: Corpus Luteum Maintains thickness of the endometrium Inhibits FSH Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (HcG) Source: Zygote Stimulates the corpus to grow maintaining progesterone levels. Amenorrhea Lack of menstruation or the stopping of menstrual cycles. Physical defects in female sex organs Diseases such as diabetes, tumors, infections. More common – physical activity, emotional distress, eating disorders Dysmenorrhea Painful contractions in the uterus during menstruation. Lasting several hours to a day or two. Not uncommon. Severe or persistent cramping – seek medical attention. Premenstrual Syndrome Symptoms occur before menstrual periods a few days to two weeks. Many females never experience symptoms. Tension, anxiety, irritability, bloating, weight gain, depression, mood swings, fatigue. Treatment includes change in diet, exercise, and, in more serious cases, medication. Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS) – rare disease Caused by a bacteria that produces toxins (poisons) that affect the immune system and the liver. Symptoms: high fever, vomiting, diarrhea, low blood pressure, dizziness, fainting, and a rash. Treatable in most cases with antibiotics.