FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM HORMONAL REGULATION
advertisement

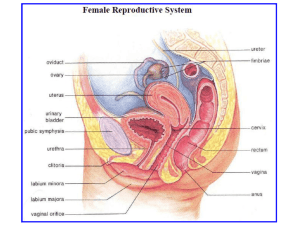
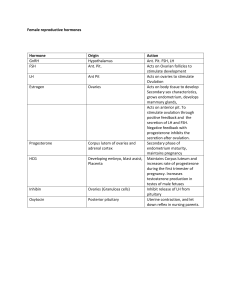
The Reproductive System of female • Oviducts and Uterus 1. Female system not completely closed 2. Egg cell released into abdominal cavity near oviduct— fallopian tube 3. Oviduct has a funnel like opening and cilia on the epithelium lining the duct helping collect the egg by drawing fluid from the body cavity into the duct. Cilia also convey egg down duct to the uterus—womb 4. Uterus—thick muscular organ that can expand during pregnancy to accommodate 4-kg fetus 5. Endometrium—inner lining of uterus; richly supplied with blood vessels. 6. Neck of uterus = cervix. Opens into the vagina female hormones FSH follicle stimulating hormone promotes maturation of follicles LH luteinizing hormone promotes development of corpus luteum estrogen progesterone rebuild endometrium 2º sex. char. prepare/maintain endometrium Figure 28.15 Oogenesis Figure 28.15 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM HORMONAL REGULATION OF OOGENSIS AND OVULATION FOLLICULAR PHASE OVULATION LUTEAL PHASE 10-20 primordial follicles begin to develop in response to FSH and LH levels theca and granulosa cells transform into the corpus luteum and secrete large amounts of progesterone FSH and LH stimulate theca and granulosa production of estrogen and progesterone if fertilization does not occur, corpus luteum degenerates ... if fertilization does occur, HCG released from the embryo maintains corpus luteum surge of LH induces ovulation Gonadotropins, Hormones, and the Ovarian and Uterine Cycles Figure 27.22c, d Gonadotropins, Hormones, and the Ovarian and Uterine Cycles Figure 27.22a, b Feedback Mechanisms in Ovarian Function Figure 27.21 FSH, LH Same a Different b