Many Plants Reproduce With Flowers and Fruit
advertisement

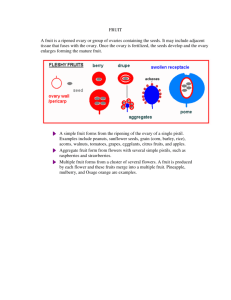
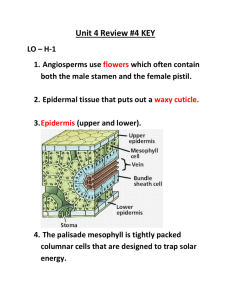
Many Plants Reproduce With Flowers and Fruit • ANGIOSPERMS HAVE FLOWERS AND FRUIT • ANIMALS SPREAD BOTH POLLEN AND SEEDS • HUMANS DEPEND ON PLANTS FOR THEIR SURVIVAL – Land animals rely on plants for food & oxygen (and materials). Angiosperms: Flower & Fruit • Angiosperms are seed plants that make flowers and fruit (peanuts, grapes, strawberries, roses, grass etc,); most plants are angiosperms • Sperm of a flowering plant are protected in a pollen grain & don’t need water to get to egg. • Eggs develop into embryos that are enclosed within seeds. • Both angiosperm & gymnosperm have male & female reproductive structures; sometimes on same plant or sometimes male & female plants. • Angiosperms have sperm & egg in flowers • Flower = reproductive part of angiosperm; egg forms in ovary & if fertilized forms seed(s) with ovary becoming fruit around the seed(s). • • • • • • ANGIOSPERM FLOWER Anther= male part (meiosis forms sperm within pollen grains) Pistil= female part (meiosis forms egg cells within ovary) Pollen grains released & if caught on pistil grows a pollen tube into ovary Sperm travels via p. tube to ovary to fertilize the egg (grows into embryo & forms seed coat) Ovary forms into fruit around seed(s); may fall to ground or be eaten by animal. If lands in place where it can germinate & survive, will grow into a new plant. Asexual reproduction may also occur in angiosperms by root shoots or “runners” forming new plants. Angiosperms: Flowers • Flowers vary in color, shape, size & scent. • In some species, male & female parts are on different flowers, & sometimes separate male & female trees/plants. • Sepals: leafy structure enclosing flower before it opens. • Petals: leafy structures around the pistil, usually colorful (attract pollinators) • Stamen: male part including stalk (filament) and anther tip (makes sperm inside of pollen grains) • Pistil: female part- ovary is at the base with egg cells. Top of pistil= stigma (pollen grain attaches) Angiosperms: Fruit • Fruit: a ripened plant ovary, may have more than 1 seed (apple) • Fleshy fruit has juicy flesh (cherry,corn) • Dry fruit (nuts, wing fruit of maple tree, feathery dandelion & sunflowers). May have shells to protect them or structures to transport them. Animals spread Pollen & Seeds • As animals eat, they move pollen from flower to flower & seeds are transported. • Animals that pollinate flowers are pollinators. Bees are very important ones. • Relationship between angiosperms & pollinators can be very specific (hummingbirds with long beaks for some) • Animal pollinators bring it to where it is needed most (bee to another flower) while wind pollination scatters it everywhere. • Many seeds go through animals digestive tract (after fruit is eaten) & deposited in its waste (to help scatter seeds widely) • Dry fruit seeds (burrs) catch on fur & are spread. Humans Need Plants to Survive • Land animals rely on plants for food & oxygen (and materials). • All organisms need energy to live; animals get it via food. Plants & algae capture energy from Sun to make sugars and oxygen (photosynthesis). Angiosperms are main food supplier & algae main oxygen supplier. Animals need oxygen to release energy stored in food. • Plants are an important source of natural resources (natural gas/coal from plant remains under ground; soil made from rocks broken down partially by plant roots & decayed plants) • Plants provide wood (lumber & paper) cotton (clothes) aspirin & other drugs made based on chemicals originally found in plants.