Ch.11.4Angisperms0
advertisement

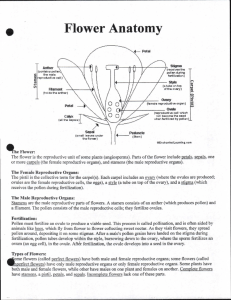
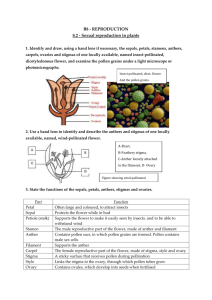
11.4 Angiosperms Many Plants are Flowering & Fruiting Plants 11.4 Angiosperms have flowers & fruit An angiosperms: Plants w/flowers & fruits. Examples: Peanuts, grapes, squash, roses, spider plants, grasses Most plant species alive now are angiosperms. Sperm of flowering plant = pollen grain Do not need an outside source of water to reach the eggs. 11.4 Angiosperms Difference between Angiosperms & Gymnosperms: Sperm and egg cells are contained in the flower in an angiosperm Flower is the reproductive structure of an angiosperm Eggs cells develop in an ovary After fertilization of egg, ovary wall thickens, & ovary becomes the fruit 11.4 Angiosperms Embryos are enclosed within seeds. Both Gen1 Gen2 occur within a single plant. Both Angiosperms and Gymnosperms have separate male & female reproductive structures. Some species have separate male and female plants 11.4 Angiosperm Life Cycle Flower is reproductive structure Stage 1 Meiosis in Anther (male part) produces sperm cell inside the pollen grains Meiosis in ovary of the Pistil (female part) produces the egg Stage 2 Pollen released; catches on pistil which has a mature egg cell in the ovary 11.4 Life Cycle cont. Stage 3 Fertilization occurs when the pollen tube reaches the ovary & sperm fertilizes the egg Fertilized egg grows into an embryo and develops a seed coat. Ovary develops into a fruit Stage 4 Fruit falls to ground; germinates into new plant 11-4 Flowers Vary in size, shape, color, fragrance Some have reproductive structures (both) in 1 flower. Some have male reproductive structures in 1 flower; female in another Sepals = leafy structures that enclose the flower. They open, fall off after blooming. 11.4 Flowers Petals are leafy structures arranged in a circle around the pistil. Petals open as reproductive structures mature. Petals=most colorful part of flower & may attract animal pollinators (butterlies;bees) Stamen = male reproductive structure of a flower. It includes: filament stalk & anther. Anther produces pollen 11.4 Flowers Pistil = female reproductive structure Ovary - Located at the base of the pistil Contains egg cells that mature into eggs Stigma = top of pistil where pollen grains attach. 11.4 Fruit Fruit = ripened plant ovary. Some ovaries contain 1 seed (Avacado) Some contain many (apple) “Fleshy” fruits because they have juicy flesh = cherry, apple, corn Dry fruits (peanuts, walnuts, sunflowers) Some seed coats have “wings” to help them spread. How seeds spread Interactions between plants and animals Food source Animals spread seeds (eat; carried on fur) Animals spread pollen Example: Bees & spread pollen & make honey; 11.4 Humans need plants For food (fruit/veggies) and O2 For Energy Resources (natural gas or coal) and Soil for growing crops Other Products Building homes Making paper Cotton for jeans/clothes Dyes for fabric Medicines like Aspirin