Flower Structure and Function
advertisement

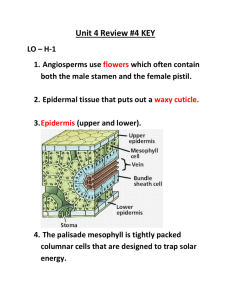
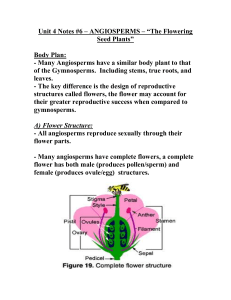
Flower Structure and Function Flowering plants are called ANGIOSPERMS. They are the greatest number of plants on Earth. What helps them survive? Diversity ! What is diversity? Diversity is variation within a community. Main Plant Parts Angiosperms are made up of 6 parts: 1. Roots-- Stabilizes the plant below ground, absorbs water and nutrients from the soil. Fibrous root system-- Trees Tap root system-- Cactus, Carrots 2. Stems-- Stabilizes the plant above ground and allows plant to grow higher and wider. Woody stems-- Trees, Roses Herbaceous stems-- Grass, Flowers 3. Leaves-- Act as food factories of the plant. Take in CO2, make glucose, release O2. Waxy coat to prevent water loss-- Cuticle 4. Flowers-Contain angiosperms reproductive parts. 5. Seeds-- Part of flowering plant that contains an embryo (young plant) and the food (cotyledon) it will need to grow into a new plant. 6. Fruit-Ripened ovary of a flowering plant that contains the seeds. Can be dry or fleshy Reproduction in Angiosperms Flowers are the reproductive structures of angiosperms. Some have male reproductive parts Others have female reproductive parts Some have both-male & female parts MALE FLOWER PARTS Anther STAMEN Filament POLLEN-- Powder containing male sperm FEMALE FLOWER PARTS P I S T I L Stigma Sticky, pollen lands here Style Ovary Hollow structure at bottom of pistil, contains female egg cell. Flower Parts Pollination Process of getting pollen (sperm) of a plant to the egg— may be the same plant/may be another plant. Things that attract pollinators: Color Aroma (Smell) Shape Size Pollinators: Organisms that carry pollen from stamens to pistils. Examples: insects, like honeybees, butterflies, moths, birds, and mammals, like bats. How Does Pollination Occur? Flowers provide food NECTAR Pollen then "sticks" pollinator Pollinator moves to feed on another flower, pollen grains fall off animal's body onto pistil of visited flower. Flowers have different colors, shapes, sizes, and fragrances to attract different pollinators. Examples: Butterflies--long, slender tongues to pollinate long, narrow flowers. Bees--open, shallow flowers Fertilization Pollen travels down—thru the style into the ovary to fertilize female egg. fertilized egg--EMBRYO embryo--SEED Ripened Ovary develops into a FRUIT Fruit protects newly fertilized egg. Inside the fruit--the seeds that can develop into new plants. Some fruits—1 seed--peaches Others—Many seeds--apples Are those fruits or veggies? Foods we call vegetables are actually fruits: tomatoes, cucumbers, squash, zucchini, and peppers. Why??? Seed Dispersal How are seeds sent out or dispersed into the environment? Animals, water, wind, hooks on certain seeds (cuckleburr) How do angiosperms and animals help one another? Seed lands—conditions right-- GERMINATION Sprouting Quiz Time !!!!!!!! How well did you listen and take notes? Number 1-4 somewhere on your notes!! 1. Some leaves and fruit possess a waxy coat. What is most likely the purpose of this coating? A. It traps insects B. It traps sunlight C. It prevents water loss D. It looks shiny 2. Roots that grow underground are important for a plant's survival. Which statement best describes their job? A. They absorb water and nutrients. B. They produce food. C. They contain the seeds for reproduction. D. They work to scare off underground predators. 3. Milkweed is a plant that secretes a milky substance poisonous to insects. What is the most likely advantage of this characteristic? 1. Reproduction 2. Respiration 3. Defense 4. Photosynthesis 4. Pollinators, such as birds and insects, are very important to flowering plants. What is the most important job that they perform? 1. They bring food to the plant. 2. They scare off predators. 3. They bring water to the plant. 4. They help plants reproduce.