Organic chemistry hook
advertisement
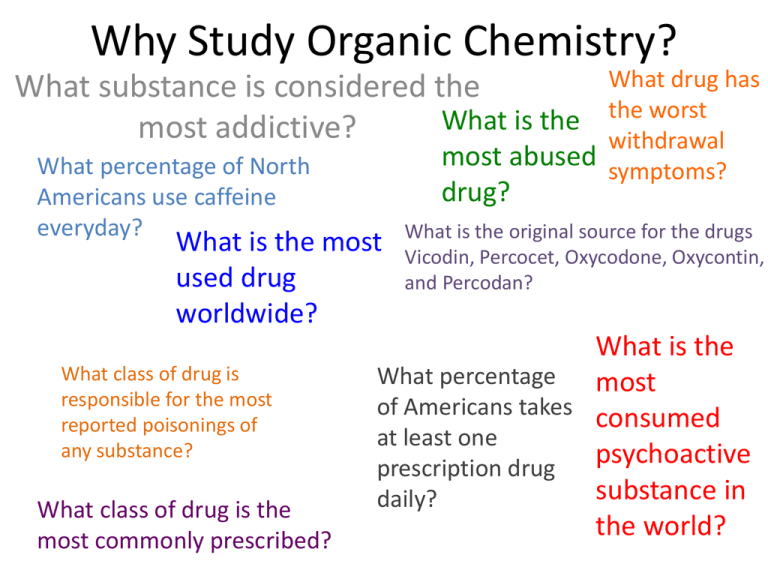
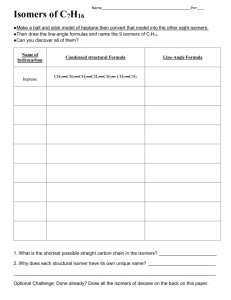
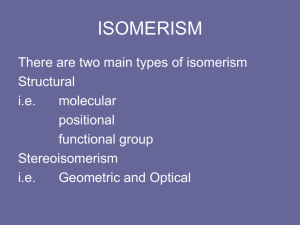
Why Study Organic Chemistry? What drug has the worst withdrawal most abused symptoms? What substance is considered the What is the most addictive? What percentage of North Americans use caffeine everyday? drug? What is the most used drug worldwide? What class of drug is responsible for the most reported poisonings of any substance? What class of drug is the most commonly prescribed? What is the original source for the drugs Vicodin, Percocet, Oxycodone, Oxycontin, and Percodan? What is the What percentage most of Americans takes consumed at least one psychoactive prescription drug substance in daily? the world? Why Study Organic Chemistry? Nicotine Caffiene 90% Opium poppy Alcohol, followed by benzodiazapines and then opiates Marijuana Opioid analgesics such Nearly 70% as morphine, hydrocodone, Lipid regulators, oxycodone, followed by methadone antidepressants and then narcotic analgesics Caffiene How Important is Organic Chemistry in Daily Life? What is the What is the starting material used to produce most pharmaceuticals? What is the most recycled material in the United States? What class of drug is responsible for the most poisoning deaths of any substance? What is the most explosive non-nuclear substance? What is the strongest substance known? most toxic substance known? Where does asphalt come from (and basketballs, lipstick, contact lenses, nylon)? What is the world’s most abundant organic compound? How Important is Organic Chemistry Botulinum toxin is a in Daily Life? protein and neurotoxin produced Of accidental deaths in the US, by the bacterium poisoning is the #1 cause; 89% Clostridium botulinum Petroleum http://www.petroleum.co.uk/ other-uses-of-petroleum Asphalt, steel, and automotive lead batteries, depending on how it’s measured of poisoning deaths were due to drugs, and 77% of these deaths were unintentional; opioid analgesics account for 40% of these deaths OCTANITOCUBANE http://news.softpedia.com/news/The-MostPowerful-Non-nuclear-Explosives-in-the-World58104.shtml Carbyne http://cleantechnica.com/2013 /10/10/carbyne-strongestmaterial-yet-known-possessesnumber-useful-propertiesresearch-finds/ http://io9.com/5861680/10of-the-most-dangerouschemicals-in-the-world http://someinterestingfacts.n et/top-10-most-deadliestsubstance-known-to-man/ Petroleum http://whgbetc.com/petroproducts.pdf Cellulose Types of Organic Compounds • Vast majority of over 20 million known compounds are based on C: organic compounds. • Generally contain C and H + other elements • Great variety of compounds Hydrocarbons • Compounds of C and H • Subgroups: –Alkanes: C-C single bonds –Alkenes: C=C double bonds –Alkynes: carbon-carbon triple bonds –Aromatic: based on benzene Hydrocarbons • • • • • • Alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2 CH4 = methane C2H6 = ethane C3H8 = propane C4H10 = butane C5H12 = pentane Hydrocarbons: Alkanes Alkanes are colorless gases, liquids, and solids Generally unreactive (but undergo combustion) Not polar (or low polarity) and so are not soluble in water. • HOW TO NAME THEM (refer to equations book)…. CH3CH2 CH2CH2 CH3 Pentane Hydrocarbons & Structural Isomerism CH3 CH3CHCH2CH3 2-Methylbutane CH3 H3CCCH3 CH3 2,2-Dimethylpropane Note names of isomers Isomers of C5H12? C4H10 has 2 strucural isomers C5H12 has 3 C6H14 has 5 C7H14 has 9 C8H18 has 18 Isomerism • Isomers have identical composition but different structures • Two forms of isomerism – Constitutional or structural – Stereoisomerism or geometric • Structural – Same empirical formula but different atom-toatom connections • Geometric – Same atom-to-atom connections but different arrangement in space. Structural Isomers Stereoisomers: Geometric Geometric isomers can occur when there is a C=C double bond. Cis-2-butene Trans-2-butene Alkenes: Compounds with C=C Double Bonds • How many isomers are possible for a compound with the formula C4H8? 3 4 CH2CH3 H 1 C H 1 C 2 C H H 1-butene 3 CH3 H 1 H 3C 2 C 4 CH3 2 C CH3 2-methylpropene (isobutene) H 4 CH3 H 3 C 2 C H cis-2-butene 1 H3 C 3 C H trans-2-butene Alkenes— Many Occur Naturally Reactions of Alkenes: ADDITION REACTIONS • Alkenes are unsaturated — more bonds can form to the C atoms • Molecules such as Br2, H2, HCl, HBr, and H2O add to the double bond H C C + Br2 H H H Br Br H C C H H H 1,2-dibromoethane An Addition Reaction Fat placed in Br2 vapor • The fat in bacon is partially unsaturated. The fat adds Br2 to the C=C bonds. • Fats can be “hydrogenated” with H2. An Addition Reaction • Fats can be “hydrogenated” with H2. Peanut butter has partially hydrogenated vegetable oil. CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7CO2H Trans Fatty Acids tend to raise total blood cholesterol Alkynes • Alkynes have carbon-carbon triple bonds. • C2H2: common name = acetylene systematic name = ethyne Preparation: CaC2(s) + H2O(liq) --> C2H2 (g) + Ca(OH)2(s) ∆Hfo(C2H2, g) = +226.7 kJ/mol ∆Hrxn for C2H2 + O2 = –1300 kJ/mol Aromatic Compounds • Benzene, C6H6, in the top 25 chemicals produced in the U.S. • Starting point for hundreds of other compounds. Resonance in Benzene • C6H6 has two resonance structures with alternating double bonds. • The π electrons are delocalized over the ring. Resonance in Benzene • C–C single bond = 154 pm C=C bond = 134 pm • CC bonds in benzene = 139 pm π electrons delocalized Functional Groups Alcohols • Characterized by –OH group • Name: add –ol to name of hydrocarbon Methanol Butanol Structures of Alcohols C3H5OH: how many structural isomers? H H H H C C C H H H 1-propanol OH H H OH H C C C H H H H 2-propanol Naming: Add -ol to name of 3-C hydrocarbon. Indicate position of OH with number. Alcohol Properties • Alcohols are a derivative of water • Many alcohols dissolve in water Methanol dissolves in water. Butanol is NOT soluble in water. GLYCOLS Alcohols with Two OH Groups Ethylene glycol Propylene glycol Amines Alcohols are derivatives of H2O (R–OH) and amines are derivatives of NH3. Methylamine Dimethylamine Trimethylamine Amines Amines generally have terrible odors! Cadaverine Pyridine Amines Amines, like NH3, are bases Amines Many natural products and drugs (such as nicotine and cocaine) are bases. H+ Nicotine O C Aldehyde Compounds with Carbonyl Group Carboxylic acid Ketone Structures of Aldehydes Cinnamaldehyde Odors from aldehydes and ketones Carboxylic Acids Acetic acid Acids are found in many natural substances: bread, fruits, milk, wine Benzoic acid Carboxylic acid group with acidic H+ All are WEAK acids Carboxylic Acids H O O C O Formic acid, HCO2H, gives the sting to ants. C CH3 O Aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid Acids + Alcohols --> ESTERS Esters have generally pleasant odors Acids + Alcohols --> ESTERS 3-methylbutanol Acetic acid O H3C C CH3 O CH2 CH2CHCH3 3-methylbutylacetate Many fruits such as bananas and strawberries contain esters. H2C HC H2C O O CR O O CR O O CR Fats and Oils Fats with C=C bonds are usually LIQUiDS Oleic acid: a monounsaturated fatty acid C=C bond H2C HC H2C O O CR O O CR O O CR Fats and Oils Fats with saturated acids (no C=C bonds) are SOLIDS. Saturated fats are more common in animals. Fats and Oils: Saponification Glyceryl stearate, a fat + NaOH O CH2 O CR O + 3 NaOH O CR CH O CH2 O CR R = —(CH2 )16CH3 CH2 O—H CH O—H CH2 O—H Glycerol O + 3 RC—O- Na+ Sodium stearate, a soap Acids + Amines --> AMIDES N-methylacetamide Acids + Amines --> AMIDES Acetoaminophen Tylenol, Datril, Momentum, ...