teacher: lindsey
advertisement

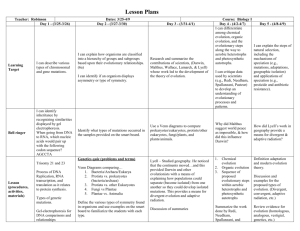
TEACHER: Bush CLASS Biology OBJECTIVE/OUTCOME MONDAY 04/16/2012 6. Demonstrate an understanding of principles that explain the diversity of life and biological evolution. a. Draw conclusions about how organisms are classified into a hierarchy of groups and subgroups based on similarities that reflect their evolutionary relationships. (DOK 2) Characteristics of the six kingdoms Major levels in the hierarchy of taxa (e.g., kingdom, phylum/division, class, order, family, genus, and species) Body plans (symmetry) Methods of sexual reproduction (e.g., conjugation, fertilization, pollination) Methods of asexual reproduction (e.g., budding, binary fission, regeneration, spore formation) b. Critique data (e.g., comparative anatomy, Biogeography, molecular biology, fossil record, etc.) used by scientists (e.g., Redi, Needham, Spallanzani, Pasteur) to develop an understanding of evolutionary processes and patterns. (DOK 3) c. Research and summarize the contributions of scientists, WEEK: _15__________________ TEACHING STRATEGIES/ ACTIVITIES ASSESSMENT Bell Ringer – SATP Questions Student Participation Anticipatory: Diagram of a food wed Power Point Lecture on Ecology with emphasis on Food Chains, Food Webs, and Biomass Chapter 2.1 Preview Closure: Oral Cell SATP Review Questions SATP Review Packets Chapter 2.1 Preview HOMEWORK Homework:usatestprep. com TUESDAY 04/17/2012 (including Darwin, Malthus, Wallace, Lamarck, and Lyell) whose work led to the development of the theory of evolution. (DOK 2) d. Analyze and explain the roles of natural selection, including the mechanisms of speciation (e.g., mutations, adaptations, geographic isolation) and applications of speciation (e.g., pesticide and antibiotic resistance). (DOK 3) e. Differentiate among chemical evolution, organic evolution, and the evolutionary steps along the way to aerobic heterotrophs and photosynthetic autotrophs. (DOK 2) 6. Demonstrate an understanding of principles that explain the diversity of life and biological evolution. a. Draw conclusions about how organisms are classified into a hierarchy of groups and subgroups based on similarities that reflect their evolutionary relationships. (DOK 2) Characteristics of the six kingdoms Major levels in the hierarchy of taxa (e.g., kingdom, phylum/division, class, order, family, genus, and species) Body plans (symmetry) Methods of sexual reproduction (e.g., conjugation, fertilization, Bell Ringer – SATP Questions Anticipatory: Introduction to the ecology video Student Participation Biomes Video Group Participation Focusing on Ecology and Taxonomy (Groups will be assigned a topic to present to the class – “Peer Teaching”) Class work 2.2 Preview Class work / Homework – Chapter 2.2 Preview Closure: “Quiz Bowl” Homework:usatestprep. com pollination) Methods of asexual reproduction (e.g., budding, binary fission, regeneration, spore formation) b. Critique data (e.g., comparative anatomy, Biogeography, molecular biology, fossil record, etc.) used by scientists (e.g., Redi, Needham, Spallanzani, Pasteur) to develop an understanding of evolutionary processes and patterns. (DOK 3) c. Research and summarize the contributions of scientists, (including Darwin, Malthus, Wallace, Lamarck, and Lyell) whose work led to the development of the theory of evolution. (DOK 2) d. Analyze and explain the roles of natural selection, including the mechanisms of speciation (e.g., mutations, adaptations, geographic isolation) and applications of speciation (e.g., pesticide and antibiotic resistance). (DOK 3) e. Differentiate among chemical evolution, organic evolution, and the evolutionary steps along the way to aerobic heterotrophs and photosynthetic autotrophs. (DOK 2) WEDNESDAY 04/18/2012 6. Demonstrate an understanding of principles that explain the diversity of life and biological evolution. a. Draw conclusions about how organisms are classified into a hierarchy of groups and subgroups based on similarities that reflect their evolutionary relationships. (DOK 2) Characteristics of the six kingdoms Major levels in the hierarchy of taxa (e.g., kingdom, phylum/division, class, order, family, genus, and species) Body plans (symmetry) Methods of sexual reproduction (e.g., conjugation, fertilization, pollination) Methods of asexual reproduction (e.g., budding, binary fission, regeneration, spore formation) b. Critique data (e.g., comparative anatomy, Biogeography, molecular biology, fossil record, etc.) used by scientists (e.g., Redi, Needham, Spallanzani, Pasteur) to develop an understanding of evolutionary processes and patterns. (DOK 3) c. Research and summarize the contributions of scientists, (including Darwin, Malthus, Wallace, Lamarck, and Lyell) whose work led to the development of the theory of Bell Work – SATP Questions Anticipatory: Example of the group presentations Students’ Group Presentations – “Peer Teaching” SATP Review Packets Closure: “Benefits of Predators Gizmo” Student Participation Homework:usatestprep. com Group Participation Quiz, tomorrow on chemistry Quiz – Scientific Methods and Lab Safety THURSDAY 04/18/2012 evolution. (DOK 2) d. Analyze and explain the roles of natural selection, including the mechanisms of speciation (e.g., mutations, adaptations, geographic isolation) and applications of speciation (e.g., pesticide and antibiotic resistance). (DOK 3) e. Differentiate among chemical evolution, organic evolution, and the evolutionary steps along the way to aerobic heterotrophs and photosynthetic autotrophs. (DOK 2) 6. Demonstrate an understanding of principles that explain the diversity of life and biological evolution. a. Draw conclusions about how organisms are classified into a hierarchy of groups and subgroups based on similarities that reflect their evolutionary relationships. (DOK 2) Characteristics of the six kingdoms Major levels in the hierarchy of taxa (e.g., kingdom, phylum/division, class, order, family, genus, and species) Body plans (symmetry) Methods of sexual reproduction (e.g., conjugation, fertilization, pollination) Methods of asexual reproduction (e.g., budding, binary fission, regeneration, spore formation) b. Critique data (e.g., Bell ringer – SATP Question Anticipatory: Power Point on Charles Darwin Lecture – Evolution Theories! We will be identifying Redi, Needham,Spallanzani, Pastuer, Darwin, Malthus, Wallace, Lamarck and Lyell) and Reviewing Ecology and Taxonomy SATP Review Packets Closure: Review for MPQ Student Participation Homework:usatestprep. com Mix Practice Quiz Tomorrow FRIDAY 04/20/2012 comparative anatomy, Biogeography, molecular biology, fossil record, etc.) used by scientists (e.g., Redi, Needham, Spallanzani, Pasteur) to develop an understanding of evolutionary processes and patterns. (DOK 3) c. Research and summarize the contributions of scientists, (including Darwin, Malthus, Wallace, Lamarck, and Lyell) whose work led to the development of the theory of evolution. (DOK 2) d. Analyze and explain the roles of natural selection, including the mechanisms of speciation (e.g., mutations, adaptations, geographic isolation) and applications of speciation (e.g., pesticide and antibiotic resistance). (DOK 3) e. Differentiate among chemical evolution, organic evolution, and the evolutionary steps along the way to aerobic heterotrophs and photosynthetic autotrophs. (DOK 2) 6. Demonstrate an understanding of principles that explain the diversity of life and biological evolution. a. Draw conclusions about how organisms are classified into a hierarchy of groups and subgroups Bell Ringer – SATP Questions Mix Practice Quiz SATP REVIEW PACKETS- Both Class and Home Work Student Participation Homework:usatestprep. com Mix Practice Quiz SATP REVIEW PACKET! SATP Review Packet (class and home work) based on similarities that reflect their evolutionary relationships. (DOK 2) Characteristics of the six kingdoms Major levels in the hierarchy of taxa (e.g., kingdom, phylum/division, class, order, family, genus, and species) Body plans (symmetry) Methods of sexual reproduction (e.g., conjugation, fertilization, pollination) Methods of asexual reproduction (e.g., budding, binary fission, regeneration, spore formation) b. Critique data (e.g., comparative anatomy, Biogeography, molecular biology, fossil record, etc.) used by scientists (e.g., Redi, Needham, Spallanzani, Pasteur) to develop an understanding of evolutionary processes and patterns. (DOK 3) c. Research and summarize the contributions of scientists, (including Darwin, Malthus, Wallace, Lamarck, and Lyell) whose work led to the development of the theory of evolution. (DOK 2) d. Analyze and explain the roles of natural selection, including the mechanisms of speciation (e.g., mutations, adaptations, geographic isolation) and applications of speciation (e.g., pesticide and antibiotic resistance). (DOK 3) e. Differentiate among chemical evolution, organic evolution, and the evolutionary steps along the way to aerobic heterotrophs and photosynthetic autotrophs. (DOK 2)