(+) and # of Electrons
advertisement

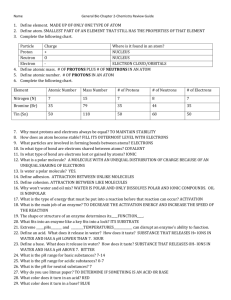
Biology Chemistry Unit Test Review Images in this power point w obtained from Google Image What is Matter? Anything that has mass and volume. What is the smallest unit of matter? Hint: not a Chihuahua! An Atom! What are atoms made up of? Think: 3 Things What 2 larger particles are in the nucleus of the atom and make up the MASS of the atom? What are their charges? What small particles are in the space outside of the nucleus and make up the VOLUME of the atom? What is its charge? Protons (+) and Neutrons (0) Electrons (-) This is the element Boron and how it appears on the periodic table. What is this number called? What does this number represent? What is this number called? What does this number represent? Represents the # of Protons (+) and # of Electrons (-) Represents the Protons + Neutrons (0) Element Symbol Protons Chlorine Cl 17 Nitrogen N 7 Neutrons Electrons Atomic # Mass # 35 7 Fill in the missing items from this chart. Element Symbol Protons Neutrons Electrons Atomic # Mass # Chlorine Cl 17 18 17 17 35 Nitrogen N 7 7 7 7 14 How did I get those #’s? Proton # = Atomic # Electron # = Atomic # Mass # = Proton # + Neutron # Neutron # = Mass # - Proton # Electron Shell Level First Level Second Level Third Level Maximum Number of Electrons in the Shell ? ? ? Electron Energy Levels Maximum Number of Electrons in that energy level. First Level 2 Second Level 8 Third Level 8 Sodium loses an electron Becomes (+) Chloride gains an electron Becomes (-) OK, now you know what an ion is, so what is an ionic bond? When one atom loses or gains an electron and a compound is formed. (NO SHARING) NaCl What is a covalent bond? Think: Covalent bond is when two atoms are sharing electrons in a compound. What are….. Neutron # has changed in the element. Mass # Changes What is an ? Hint: It’s not the skateboarding company! An element is “pure stuff”. It is only one kind of atom in matter such as pure gold (Au) from the periodic table. Other Examples: Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Sodium Phosphorous Define: •Molecule •Compound •Molecule •Compound Same Definition: 2 or more atoms chemically combined What elements make up the molecule water? How many of each? 2 atoms of Hydrogen and 1 atom of Oxygen H H (+) (+) O (-) See a resemblance? The Chemical and Physical Properties of Matter What is the difference?? Physical changes keep the matter in the same chemical formula just change shape or state Chemical changes are the formation of an entirely new compound with a different chemical formula than the original compound. What does a pH scale indicate (do not say the pH number). It is the concentration of ___?___ in a solution. What does a pH scale indicate (do not say the pH number). It is the concentration of Hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. Strong Acid pH= 1,2,3 Weak Acid pH=4,5,6 Weak Base pH= 8,9,10 Neutral pH = 7 Strong Base pH=11, 12, 13, 14 What is a buffer? Don’t have a clue? We have been dealing with pH, so it probably has something to do with pH & HOMEOSTASIS A weak acid or base that can react with strong acids or bases to help maintain pH. HOMEOSTASIS Define & Give and Example: •Solute •Solvent •Solution Solvent : What does the dissolving WATER Solute: What is dissolved by the solvent SALT Solution: When a solute is dissolved into a solvent Salt + Water What is the name for a type of mixture that there is NO DISSOLVING taking place? Suspension Examples: Sand + Water Oil + Vinegar What is COHESION? COHESION? Same molecules sticking together What is Adhesion? What is ADHESION? 2 different molecules that stick together Water on glass What is the weak bond called that forms between the polar molecules of water? MACROMOLECULES •What are the 4 types of macromolecules? They are all organic compounds •What is the function of each? Carbohydrates – Energy & Structure Lipids – Energy Storage, membranes, chemical messengers Proteins –movement, enzymes, immune system, carrying oxygen Nucleic Acids – Heredity, DNA, RNA, ATP Way to remember: Can Linda Play Nintendo? Monosaccharides linked together make Polysaccharides What elements make up all carbohydrates? Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen What type of carbohydrates do animals and plants store? Glycogen (Sugar) Starch What is cellulose? Hint: We can’t digest it. What is chitin? Hint: On outside of insect What is cellulose? Carbohydrate of plant cell walls. What is chitin? Carbohydrate of insect exoskeletons A polymer that consists of a __?__ and a _?__ is a A polymer that consists of a Glycerol + 3 Fatty Acids is a lipid. Lipids make up cell membranes AMINO ACIDS There are 20 different amino acids Know the 3 PARTS of an AMINO ACID Amino Group R Group Acid Group 3 PARTS of an AMINO ACID What are the 4 elements that are found in proteins? What are Enzymes? Proteins that speed up chemical reactions in our bodies. Which macromolecule creates pigments for our skin, hair, eyes? Which macromolecule creates pigments for our skin, hair, eyes? Nucleic Acids What are the monomers of nucleic acids? NUCLEOTIDES Phosphate group Nitrogen Base 5 Carbon Sugar Nucleic Acids: What are 3 types of nucleic acids? DNA, RNA, ATP What are 5 the elements? C, H, O, N, P Chemical Reactions A + B → AB What are the reactants? What are the products? What are the reactants? 2H₂ and O₂ What are the products? 2H₂O Activation Energy (energy needed to get a reaction started) of Exogonic and Endogonic Reactions Energy Released Energy Absorbed Energy released during a chemical reaction is in the form of……… Heat, Light, and or Sound Enzymes are catalysts in the body that help speed up chemical reactions. Must know the 3 parts What is the difference between reaction A & B? A B You need to find the answer in your notes. You have completed the Biology Chemistry Unit Review! How did you do? Are you ready for the test, or need to study some more?