Name and identify the charge of the two particles in
advertisement

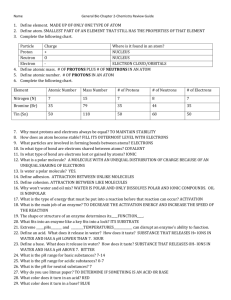
Notebook #3 Review 1.Name and identify the charge of the two particles in the nucleus of an atom. -protons-positive charge -neutrons- neutral charge 2.Name and identify the charge of the particles circling the nucleus. -electrons-negative charge 3.Using the periodic table, identify the number of protons, number of electrons (in a neutral noncharged atom), atomic mass and how many neutrons for Barium and Iodine. (Next slide) Barium=56 protons, 56 electrons, atomic mass of 137, and 81 neutrons • Iodine=53 protons, 53 electrons, atomic mass of 127, and 74 neutrons 4. Put the electrons in the energy levels for the following Neon, Aluminum, and Boron (a neutral atom). 5.Which one of the atoms above is most stable and why? • Neon because the outer energy level is full 6. Define the following • • • Atom- smallest unit of matter Element- •pure substance made of one type of atom Compound- combination of 2 or more elements 7.How do atoms combine and why? • They combine by chemical bonding to become stable 8.Which bond shares to become stable? • Covalent 9.Which bond takes or gives electrons? • Ionic 10.Define Hydrogen bond. • H-atom attaches weakly to a different compound 11.What is called when there is a slight attraction between molecules that are close? • Van der Waals Forces 12.For the six main elements of life, identify the acronym and what does each letter stand? • • • • • • S- Sulfur P-Phosphorus O-Oxygen N-Nitrogen C-Carbon H-Hydrogen 13.What element do ALL living things contain? • Carbon 14.Identify the names from the smallest singular building block to a large molecule, put them in order. • monomer • polymer • macromolecule 15.In condensation we makes _________________covalent bonds and water release______ ________. Break 16.hydrolysis we _______covalent bonds water_____ . and add______ 17.What are the 4 big macromolecules and briefly describe what their atom combinations are. –carbohydrates-C+H+O –Protein-C+H+O+N –Nucleic Acid-C+H+O+N+P –Lipid-C+H+O (long chain) 18.Using pages 45-47 draw a diagram for EACH of the four macromolecules. Carbohydrate Nucleic Acid Lipid 19.What is the main function of each of the macromolecules in living organisms? –Carbohydrates=energy –Proteins=regulate cells and bone and muscle formation –Nucleic Acid=heredity information -Lipids=store energy 20.What is the monomer for EACH of the macromolecules? Carbohydrates=monosaccharide –Protein=amino acids –Nucleic Acid=nucleotide –Lipid=glycerol and fatty acid 21. What protein can be used to catalyze many reactions, but does not change itself? • enzyme • • • • 22. What affects enzyme reactions? Temperature pH Ionic conditions Amt. of substrate 23.Hydrophobic means_____ fears ______________, while hydrophilic water Loves_________. water means_________ 24.In a lipid they have 2 different ends, identify what type they are and how they react to water. • –polar-loves water/hydrophilic • –nonpolar-doesn’t like water/hydrophobic 25.What are the ingredients in a solution and identify their roles? -solute=substance that disolves –solvent=liquid that it solute dissolves in 26.What is the “Universal Solvent” that is in an aqueous solution? • water 27.A polar molecule has uneven/partial charges, what causes this and what does it create? uneven distribution of electrons –magnetic/electrical attraction 28.What are the 2 attractive forces and what types of substances do they affect? cohesion=similar particles –adhesion=different substances up 29.Capillarity moves water____ against gravity. H+ 30.Acids form ___ions in a solution. OH31.Bases form ________ions in a solution. 32.Draw the pH scale and label 0-14. Identify strong acids, weak acids, neutral, weak bases, and strong bases.