Science & Technology: Chapter 2 Section 1
advertisement

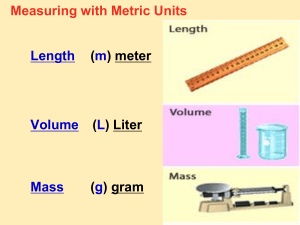
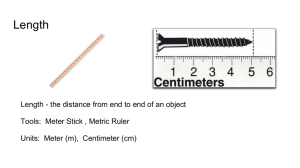
The Metric System Objectives: 1. Explain why scientists use a standard measurement system. 2. Identify SI units of measure for length, mass, volume, and density 3. Calculate volume and density The metric system is a system of measurement based on the number ten. Modern scientist use a version of the metric system called the international system of units abbreviated as SI. Scientists all over the world use SI units to measure length, volume, mass, density, temperature and time Using SI as the standard system of measurement allows scientists to compare data and communicate with each other about their results. The basic unit of length in the SI system is the meter. One meter is about the distance from the floor to a doorknob. To measure objects smaller than a meter, scientists use the centimeter or millimeter. One meter is equal to 100 centimeters or 1000 millimeters. Mass is the measure of the amount of matter an object contains. The basic unit of mass in the SI system is the kilogram. The mass of a wooden baseball bat is about 1 kilogram. To measure the mass of smaller objects, you can use the gram or milligram. One kilogram is equal to 1000 grams. A very common tool to measure mass is the triplebeam balance. Volume is the amount of space an object takes up. The basic unit of volume in SI is known as the liter (L) One liter is equal to 1000 mL Scientists commonly use a graduated cylinder to measure liquid volumes. The liquid at the top of a graduated cylinder will be curved. This curve is called a meniscus. One cubic centimeter is exactly equal to one millilter. The volume of a regular shaped solid can be found using this formula: Length x Width x Height. To measure the volume of an irregular solid, you record the volume of water in a graduated cylinder. Then, carefully place the irregular solid into the water. Record the volume of the water with the object in the water. Subtract the volume of water alone from the volume of the water and the object. Density is the measure of how much mass is contained in a given volume. The formula to solve for density is: Density = Mass/Volume Because density is actually made up of two measurements; mass and volume an object’s density is expressed as a combination of two units. Two common density units are grams per cubic centimeter and grams per milliliter. The density of a substance is the same for all samples of that substance. For example, all samples of pure gold no matter how large or small have a density of 19.3 g/cm3 An object will float if it is less dense than the surrounding liquid. For example, the density of water is 1 g/cm3. A piece of wood with a density of 0.8 g/cm3 will float in water. Substance Density (g/cm3) Air 0.001 Ice 0.9 Water 1.0 Aluminum 2.7