Cell Theory
advertisement

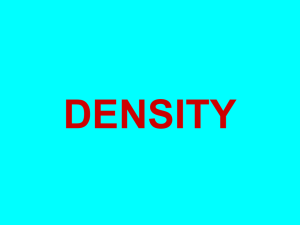
TOPIC: Cells AIM: Describe the cell theory. Do Now: Measurement Review (Take out yesterday’s notes) HW: 4 ?’s on bottom of microscopic measurement sheet 1. The amount of matter an object has is called (1)mass (2) volume (3) milliliters (4) density 2. The SI unit of mass is the ______. (1)cubic meter (2) kilogram (3) liter (4) meter 3. In the metric system, the height of a building would be given in (1)centimeters (2) milliliters (3) meters (4) millimeters 4. Which instrument would be used to obtain the volume of a glass of water? (1) triple beam balance (2) graduated cylinder (3) beaker (4) metric ruler 5. An object has a length of 2 cm, a width of 3 cm, and a height of 4 cm. What is it’s volume? (1)11 cm3 (2) 26 cm3 (3) 9 cm3 (4) 24 cm3 6. Which measurement of an average classroom door is closest to 1 meter? 1. its thickness 2. its width 3. its height The basic unit of length in the metric system is the 1. kilogram 2. gallon 3. liter 4. meter Carrie is working with a graduated cylinder as shown in the diagram. What should Carrie do to get a volume of 12.5 milliliters (mL) of liquid in the graduated cylinder? 1. Add 0.5 mL of liquid 2. Add 1.5 mL of liquid 3. Remove 0.5 mL of liquid 4. Remove 1.5 mL of liquid Which pieces of laboratory equipment could be used in the laboratory to measure density? 1. A and B 3. B and C 2. B and D 4. B and D The diagram represents a thermometer. The temperature reading on the thermometer would most likely indicate the temperature 1. of a human body on a very hot summer day 2. at which water freezes 3. at which water boils 4. of a human with a very high fever The diagram shows equal masses of four different earth materials at different temperatures. 2.7g/cm3 7.7 g/cm3 1.0 g/cm3 .00012 g/cm3 Which material has the greatest density? 1. water 2. iron 3. granite 4. dry air Excretion • Removal of cellular (metabolic) waste Locomotion • Ability of an organism to move Factors that influence metabolism • Gender • Age • Exercise • Diet • Drugs and alcohol Cells • Carry out life processes • Make up living things (ORGANISMS) Just like bricks make up a brick house, cells make up an organism The Robert Cell Theory timeline Hooke–( a1665) 1. Cells are the basic unit of Cell structure in all living Theory things. (Living things are made of cells) 2. Cells are the basic unit of function of all living things (They carry out life processes) 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. Exceptions to the Cell Theory • Viruses: - not composed of cells - contain genetic information - reproduce inside host cell Virus do not reproduce by division because they are not cells. Did you know… • The first virus was found in both plants and animals 100 years ago. • The common cold is a type of virus. • Viruses can be treated with antiviral drugs. Let’s summarize… 1. What do all organisms consist of? 2. Explain the three parts of the cell theory. 3. Explain why viruses are exceptions to the cell theory. Review: Which statement is not a part of the cell theory? 1. Cells are the basic unit of structure of living things. 2. Cells are the basic unit of function of living things. 3. Cell parts such as chloroplasts are selfreplicating. 4. Cells come from preexisting cells. 2. The cell theory states that all living things are made up of 1. organisms 2. cells 3. tissues 4. proteins 3. Which choice is NOT part of cell theory? 1. Cells are the basic units of life. 2. All living things are made of one or more cells. 3. All cells come from other living cells. 4. New cells have the same nuclei as those of pre-existing cells.