Standard 2 Review PPT
advertisement

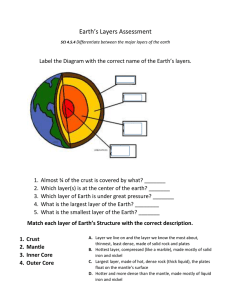
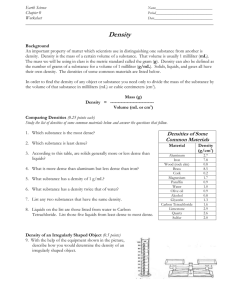
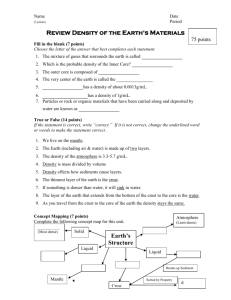
Objective 1 Sorting: The process that separates particles based on differences in density and/or particle size. Mixture: A combination or blend of two or more substances that have not chemically combined. Each substance maintains its own identity. Particle: A small piece of something. Typically used to represent a small part of matter. The formula for calculating density is Density = Mass/ Volume Water has a density of 1 g/mL= 1 g/cm3 Material that has a density greater than 1g/mL will sink. Material that has a density less than 1g/mL will float. Example rock sinks, wood floats in water Element Hydrogen (H) 1) If you have a 4 cm3 sample of rock salt with Helium (He) mass of 10 grams, what is the density? Aluminum (Al) 2) You have a 10 cm3 sample of water with a Zinc (Zn) mass of 10 grams what is the density? Tin (Sn) 3) You have an unknown metal with a volume of Iron (Fe) Nickel (Ni) 4 cm3 and a mass of 42.0 grams. Compared to the chart, what is this metal most likely to be? Copper (Cu) Silver (Ag) 4) Find the density of an unknown liquid in a beaker. The empty beaker's mass is 165 grams. Lead (Pb) With the unknown liquid inside the beaker, the Mercury (Hg) total mass is 309 grams. The volume of the Gold (Au) unknown liquid is 125mL. Is the liquid pure Platinum (Pt) water? Explain your answer. Density (g/cm3) .00009 .00018 2.7 7.13 7.31 7.87 8.9 8.96 10.5 11.35 11.55 19.32 21.45 The earth’s materials are naturally sorted according to density AND particle size. More dense items settle on the bottom. Items with larger particle size settle on the bottom, then smaller particles fill in the empty spaces between the more dense objects. Larger, more dense materials are found at the beginning of a stream bed and finer, less dense particles are found at the end of a streambed. On a beach, more dense particles stay at the bottom of ocean and sand on beach all has the same density. Sort silt, gravel, pebbles and rocks and place them in a jar with water. Shake it up and let the materials settle. How do they settle, and why do they settle that way? Objective 2 Density: comparison of the mass and volume of an object. Calculated as mass/volume. Atmosphere: various layers of air that surround the earth. The densest layers are closer to the earth, the least dense layers are further away from the earth. Crust: solid outer layer of Earth where life is found. This is the thinnest Earth layer. Inner core: centermost layer of Earth. Solid metal, is the hottest and most dense. Outer core: Liquid layer of Earth found near the center. Found between the mantle and inner core. Made of metals. Mantle: semi-solid layer of Earth that takes up the most volume. Found directly below the crust. The earth is layered because of density. The order from most dense to least: Inner Core – Outer Core – Mantle – Crust – Water – Atmosphere http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth /structure.html Most dense to least dense from the Earth’s Core to the Atmosphere. The denser the material the deeper it sinks to the center of the earth. Composition Atmosphere Approximate Density 0.0013 g/mL Water 1.00 g/mL Liquid Crust 2.7 - 3.0 g/mL Hard and rocky Mantle 3.3 - 5.7 g/mL Soft and flexible Outer Core 9.0 - 12.0 g/mL Liquid nickel and iron Inner Core 12.7 - 13.0 g/mL Solid nickel and iron Layer Gases Many models of Earth exaggerate the size of surface features such as mountains. If Earth were shrunk to globe size, it would be very smooth.