Bone Markings and Joints

+
Bone Markings and Joints
+
Do Now
Quiz Corrections
Questions pg. 173
+
Objective
Explore the joints of the body
Arthro-
Of a joint; relating to the joint
EXAMPLE: Arthritis?
Inflammation of the joint
+
Functions
Joints have 2 functions
Hold bones together
Allow for flexibility
Structural classification
Fibrous
Cartilaginous
Synovial
+
Functional Classification
Synarthorotic Joints
Amphirarthrotic Joints
Diarthrotic Joints
+
Synarthrotic Joints
Immovable Joints
Joints of the skull
Sutures of the flat bones that make up the skull
+
Amphirarthrotic Joints
Slightly Movable Joints
Vertebrae
Don’t have full motion but provide enough motion with in the back
+
Diarthrotic Joints
Freely moveable
Shoulders
Hips
Knees
Elbows
Lubricated for joint movement
Synovial fluid
+
Diarthrotic Joints
Ball and Socket Joints
Hip and shoulder
Shoulder is relatively unstable
Golf ball on a golf tee
Hinge Joint
What do you think of with a hinge?
1 plane of movement
Elbow joint
+
Diarthrotic Joints
Pivot
What does it mean to pivot?
Allows for rotational movement
Atlas and axis vertebrae
Saddle
Concave/convex articulation
Cowboy sitting on a saddle
Biaxial
Movement in 2 planes, no rotation
Thumb joint
Caropometacarpal joint
+
Fibrous Joints
Bones joined by fibrous tissue
Some are slightly moveable, most are synarthrotic (no movement)
Sutures – bones interlock and are connected by short tissue fibers
EX: Skull joints
+
Cartilaginous Joints
Articulating ends connected by cartilage
For the most part, these joints are slightly moveable
EX: Intervertebral joints
+
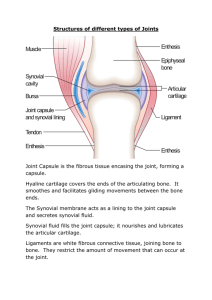
Synovial Joints
Articulating bones are separated by joint cavity containing synovial fluid
Movements vary from 1 axis to multiaxial
All synovial joints contain:
Joint surface enclosed by 2 layer articular capsule
Outer part of the capsule is a dense fibrous connective tissue.
Lines inside by synovial membrane
Articulating surfaces lined with articular cartilage
Articular capsule reinforced with ligaments, bursae or tendon sheaths
+
Homework
Read pg. 114 from the packet about “Movements Allowed by
Synovial Joints”
Understand diagrams on pg. 115
Complete pg. 117 from packet