Potential Energy Diagrams: Enthalpy & Reaction Energy
advertisement

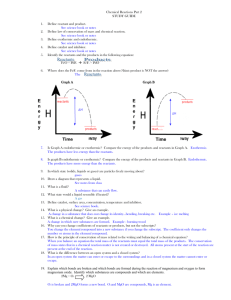
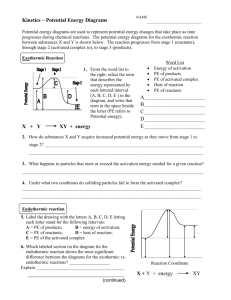
ENTERING PROCEDURE Make sure that all your pages have been locked in and locked down into your Interactive Notebooks for today’s lesson. Pages have been convenience. numbered for your BELL RINGER Take a few minutes and jot down some information related to Potential Energy. 5-6 sentences and at least 1 drawing. Questions to Consider • What do you remember about potential Energy from our previous classes? • Are there pictures that you associate with this term? If so draw them. • How does this term relate to chemical reactions YOU DO NOT HAVE TO WRITE THE QUESTIONS POTENTIAL ENERGY DIAGRAMS TODAY’S OBJECTIVES • Students will be able to (SWBAT) calculate enthalpy of a reaction using potential energy diagrams. • SWBAT Create and interpret Potential Energy diagrams for exothermic and endothermic reactions • SWBAT identify energy of activation, effects of a catalyst and PE of Reactants and Products using potential energy diagrams. ENERGY IN ALL OF ITS FORMS. WHAT CAUSES MOVEMENT? Rollercoaster Video DEFINITIONS AND SYMBOLS 1. Potential energy (PE): the energy stored in a substance (measured in kJ) 2. PE reactants: Potential energy of the reactants 3. PE products: Potential energy of the products 4. Activation Energy (Ea): Energy needed to make the reaction go 5. Heat of reaction (∆H): PE products - PE reactants POTENTIAL ENERGY (PE)- THE ENERGY STORED IN A SUBSTANCE ∆H = heat of reaction Activation Energy (Energy needed to make the rxn go) PE reactants PE products ∆ H = PE products – PE reactants *If the reaction was reversed* ∆H = heat of reaction PE products Activation Energy (Energy needed to make the rxn go) PE reactants ∆ H = PE products – PE reactants You might want to copy this down A B 1. PE reactants? 40 kJ 2. PE Products? 20 kJ 3. Ea forward (find this by subtracting the number at the top of the hill minus the value for the PE reactants) 100 kJ – 40 kJ = 60 kJ 4. Find ∆Hrxn? 20 kJ – 40 kJ = -20 kJ +∆H = Endothermic What is the heat of reaction? ∆ H = PE products – PE reactants ∆ H =350 – 200 = 150 kJ -∆H = EXOTHERMIC What is the heat of reaction? Which type of reaction is more likely to happen, fwd or backward? 40 10 ∆ H = PE products – PE reactants = -30 ∆ H = 10 – 40 kJ What does adding a catalyst do in a reaction? EA without a catalyst EA with a catalyst •Adding a catalyst lowers the activation energy. •This speeds up the reaction, but ∆H remains unchanged. Answer: Lowers the activation energy! Post-lab questions: 1.Was this experiment exothermic or endothermic? Explain how you know. 2.What was the role of the yeast in this experiment? Do you think the experiment could have happened without yeast? 3.What would have happened if a stronger concentration of hydrogen peroxide had been used? 4.Given your answer to question #1, make a SKETCH of a potential energy diagram. Make sure your diagram either matches an exothermic graph or an endothermic graph. Be sure to label parts of your graph INDEPENDENT WORK TIME Now work on the Potential Energy Diagram Worksheets EXIT SLIP ANSWERS A. Labeled Potential energy Ea PE products B. 412kJ – 2631kJ = -2219 kJ C. Exothermic PE reactants Reaction coordinate Grading Scale 6 = 100 5 = 83 4 = 66 3 = 50 2 = 33 1 = 16 0=0