File
advertisement

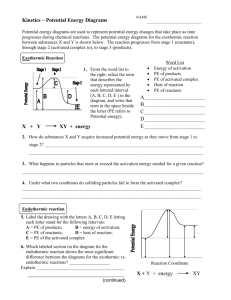
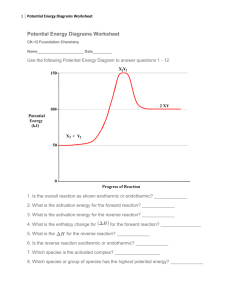
DO NOW When the bell rings In your seat: With pen/pencil With Notebook With Handout Silent and ready for Do Now After the bell (2 min) Read and answer the following riddle: I’m tall when I’m young and I’m short when I’m old. What am I? AGENDA Do Now (5 min) Warm Up: (15 min) Notes: Potential Energy Diagrams(20 min) Group Practice (15 min) Independent Practice(15 min) Closeout (2 min) WARM UP (2 MIN) • Redraw this heating curve and label • Solid • Liquid • Gas • Melting • Freezing • Boiling • Condensati on • Sublimation • Deposition WARM UP • Where on the heating curve does potential energy increase? • What happens to the temperature of a substance when it is boiling? UNIT: THERMODYNAMICS TOPIC: POTENTIAL ENERGY DIAGRAMS Objective: Construct and interpret potential energy diagrams for chemical reactions How can you show what happens to energy during a chemical reaction? GUIDING QUESTION Potential Energy (PE): the energy stored in a substance (measured in KJ) Activation Energy (Ea): The amount of energy needed to make a reaction occur. Heat of Reaction (∆H): The difference in potential energy of reactants and products (PE Products – PE Reactants) Catalyst: A substance that lowers the activation energy of a reaction VOCABULARY AND DEFINITIONS KP #1: POTENTIAL ENERGY • Potential Energy (PE): The energy stored in a substance • Turn & Discuss: • What real-life examples can you think of that demonstrate potential energy? KP #2: P.E. DIAGRAMS 1. KP #2: P.E. DIAGRAMS Check for Understanding: 1. What is the value of the PE Reactants? 2. What is the value of the PE Products? 3. What is the activation energy? KP #2: P.E. DIAGRAMS 1. Sometimes reactions go in reverse. KP #2: P.E. DIAGRAMS Check for Understanding: Draw the reverse and 4. What is the value of the PE Reactants? 5. What is the value of the PE Products? 6. What is the activation energy? KP #3: ∆H The difference between the PE of the Products and the Reactants. Also called enthalpy change KP #3: ∆H Check for Understanding: 7. What is the ∆H of the reaction to the right. KP #4: CATALYST What effect does adding a catalyst have on a chemical reaction? • Lowers the activation energy GROUP PRACTICE How C: 1 – 2, only on task conversation H: Raise hand, move on to next question until I am available A: Completing questions M: In clusters. 3 Hall passes. P: Answering questions on worksheet, using notes, head up, discussing What 15 minutes All heads together One sheet Answers on worksheet INDEPENDENT PRACTICE What How C: 0 – 1, only on task conversation H: Raise hand, move on to next question until I am available A: Completing questions M: In clusters. 3 Hall passes. P: Answering questions on notebook paper, using notes, head up, discussing in groups, using boxes 15 minutes Complete practice on reverse side of notes EXIT SLIP What? (5 min) How? C – No talking H – Raise hand A – Taking exit slip M P – In seat – Completing exit slip without notes and turning in Write answers on the paper you were given If you finish early, summarize what you learned at the bottom of your notes OR answer today’s guiding question Exit Slip Identify each of the following: 1. PE reactants 2. PE Products 3. Activation energy 4. ∆H 5. Ea of reverse reaction