US Imperialism
advertisement

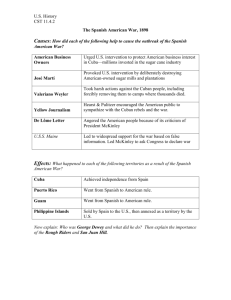
Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker nations Major Factors • Economic: increase need for natural resources • Nationalist: competition for large empire • Military: superior to those in Africa and Asia • Humanitarian: duty to spread the blessing of western civilization Annexation of Alaska • William Seward • 1867: Russian $7.2 million • 1959: becomes a state Annexation of Hawaii • American sugar planters gain control of Hawaii’s govt and economy • McKinley Tariff • Queen Liliuokalani • Sanford B. Dole Spanish American Cuban War • Cuban Rebellion – General Valeriano Wyler – Jose Marti • Yellow Journalism • http://images.google.com/images?sourceid=navclient&rls=GGLG,GGLG:200821,GGLG:en&q=yellow+journalism+spanish+american+war&um=1&ie=UTF-8&ei=ln5SvXUFsmrngfG9aiCDQ&sa=X&oi=image_result_group&ct=title&resnum=1&ved=0CBAQsAQwAA • De Lome Letter • Enrique De Lome (Spanish Minister to US) • Criticized McKinley Spanish American Cuban War • USS Maine – Sent to Cuba to protect Amer – Remember the Maine – War with Spain • Philippines – George Dewey’s victory • Cuba – Rough Riders – Lead to invasion of Puerto Rico Spanish American Cuban War • Treaty of Paris – 1. 2. 3. Ended Splendid Little War Cuba gain independence Sp give Puerto Rico and Guam to US US pay Sp $20 million for annexation of Philippine Islands - Residents would not become US Citizens US and Puerto Rico • Not smart enough to govern themselves • Needed for maintaining presence in Caribbean and protecting future canal across Isthmus of Panama • Foraker Act Cuba and US • Platt Amendment 1. Cuba could not make treaties that allowed foreign country control 2. US reserved right to intervene to preserve independence 3. Cuba was not to go into debt 4. US could buy/lease land for naval or coaling stations * Became a US Protectorate Philippine-American War • Emilio Aguinaldo • Rebelled against US • US forced Filipinos to live in designated areas • US set up govt; 2 houses • Finally gained independence Open Door Policy • US needed to maintain trade with China • Sec of State John Hay • US called for open access to China’s coastal ports, elimination of special privileges for any trading nations and the maintenance of China’s independence Boxer Rebellion • Chinese opposed to Western influence in their country • Boxers: drive out evils • Rebellion stopped by outside forces • US scared about fate of China and issued 2nd open door notes – US safeguard trade with China Impact of gains • Not necessary to own people to trade with them • Expense of maintaining Amer empire would out weight benefits • McKinley assassinated and Teddy Roosevelt steps in Russo-Jap War • Russia controlled Manchuria, wanted Korea which Japan set up as an independent nation • War broke out b/w Russia and Japan • Japan wanted Roosevelt to intervene-> Nobel Peace Prize Panama Canal • Roosevelt wanted canal, shortcut b/w Atlantic and Pacific Ocean • Hay-Pauncefote Treaty • Panama claimed independence from Columbia with help of US • Panama gave US control of strip in exchange for help Roosevelt Corollary • US did not want Europe to intervene in Latin America due to monies owed • Speak softly and carry and big stick and you will go far • Dollar Diplomacy: US policy of using the nation’s economic power to exert influence over other countries Wilson and Missionary Diplomacy • Monroe Doctrine • Wilson’s Missionary Diplomacy Mexican Revolution • Porfirio Diaz-> Frances Madero -> General Victoriana Huerta • Wilson refused to recognize Huerta • War broke out • Huerta regime collapsed -> Venustiano Carranza • Emiliano Zapata and Franscisco Pancho Villa – Led revolts against Carranza & US US Goals Achieved 1. Expanded its access to foreign markets in order to ensure the continued growth of the domestic economy 2. Built a modern Navy to protect its interest abroad 3. Exercised its power to ensure American dominance in Latin America